The most important set of genetic instructions we all get comes from our DNA, passed down through generations. But the environment we live in can make genetic changes, too.
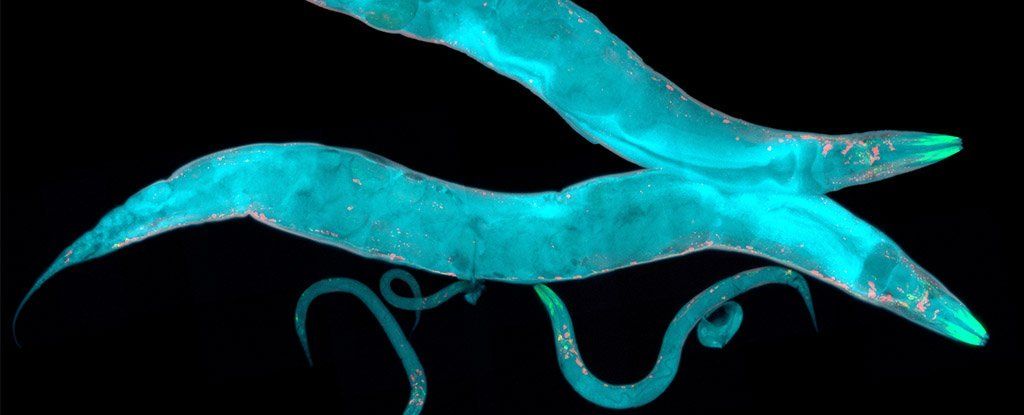
Researchers have now discovered that these kinds of environmental genetic changes can be passed down for a whopping 14 generations in an animal – the largest span ever observed in a creature, in this case being a dynasty of C. elegans nematodes (roundworms).
To study how long the environment can leave a mark on genetic expression, a team led by scientists from the European Molecular Biology Organisation (EMBO) in Spain took genetically engineered nematode worms that carry a transgene for a fluorescent protein. When activated, this gene made the worms glow under ultraviolet light.