CRISPR/Cas9, a powerful gene editing technique that has already been used in a human, is thought by many as a “cut and paste” for DNA in living organisms. While in a sense that is what happens, delivering the ribonucleoprotein that does the genetic editing and the RNA that hones in on the target, into the cellular nucleus without being damaged is a challenge. That is why the efficiency of successful edits remains very low. Researchers at University of Massachusetts Amherst have now come up with nanoparticles that protect the protein and RNA as they’re brought to their work site.
The nanoparticles are engineered around their cargo and have shown a 90% success rate of getting the cargo into the nucleus, and a 30% editing efficiency, which is “remarkable” according to the researchers. So far the team has tested their technique on cultured cells, but they’re already working on trying the same in laboratory animals. As part of their research, they developed a novel way of tracking the Cas9 protein inside the cells, something that will certainly help other scientists in this area.
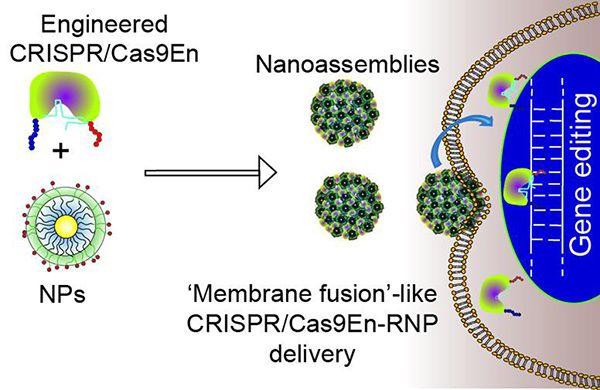
“By finely tuning the interactions between engineered Cas9En protein and nanoparticles, we were able to construct these delivery vectors. The vectors carrying the Cas9 protein and sgRNA come into contact with the cell membrane, fuse, and release the Cas9:sgRNA directly into the cell cytoplasm,” in a statement said Vincent Rotello, lead author of the study in ACS Nano. “Cas9 protein also has a nuclear guiding sequence that ushers the complex into the destination nucleus. The key is to tweak the Cas9 protein,” he adds. “We have delivered this Cas9 protein and sgRNA pair into the cell nucleus without getting it trapped on its way. We have watched the delivery process live in real time using sophisticated microscopy.”