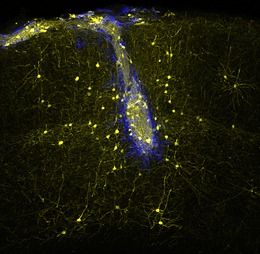
As shown in this in vivo two-photon image, neuronal transplants (blue) connect with host neurons (yellow) in the adult mouse brain in a highly specific manner, rebuilding neural networks lost upon injury. (credit: Sofia Grade/LMU/Helmholtz Zentrum München)
Embryonic neural stem cells transplanted into damaged areas of the visual cortex of adult mice were able to differentiate into pyramidal cells — forming normal synaptic connections, responding to visual stimuli, and integrating into neural networks — researchers at LMU Munich, the Max Planck Institute for Neurobiology in Martinsried and the Helmholtz Zentrum München have demonstrated.
The adult human brain has very little ability to compensate for nerve-cell loss, so biomedical researchers and clinicians are exploring the possibility of using transplanted nerve cells to replace neurons that have been irreparably damaged as a result of trauma or disease, leading to a lifelong neurological deficit.
Read more