Nice.
When we think of synthetic biology, we often think of engineering a cell to give it some useful function. But SEED 2016 had quite a few speakers working outside of a biological cell. Some broke open cells to utilize just the cellular machinery to create “cell-free” systems. Others showed what could be done inside of the computer (in silico) to improve our understanding and prediction of synthetic gene networks. Here, we’re highlighting SEED speakers who showed how both of these approaches can advance synthetic biology.
Cell-free synthetic biology
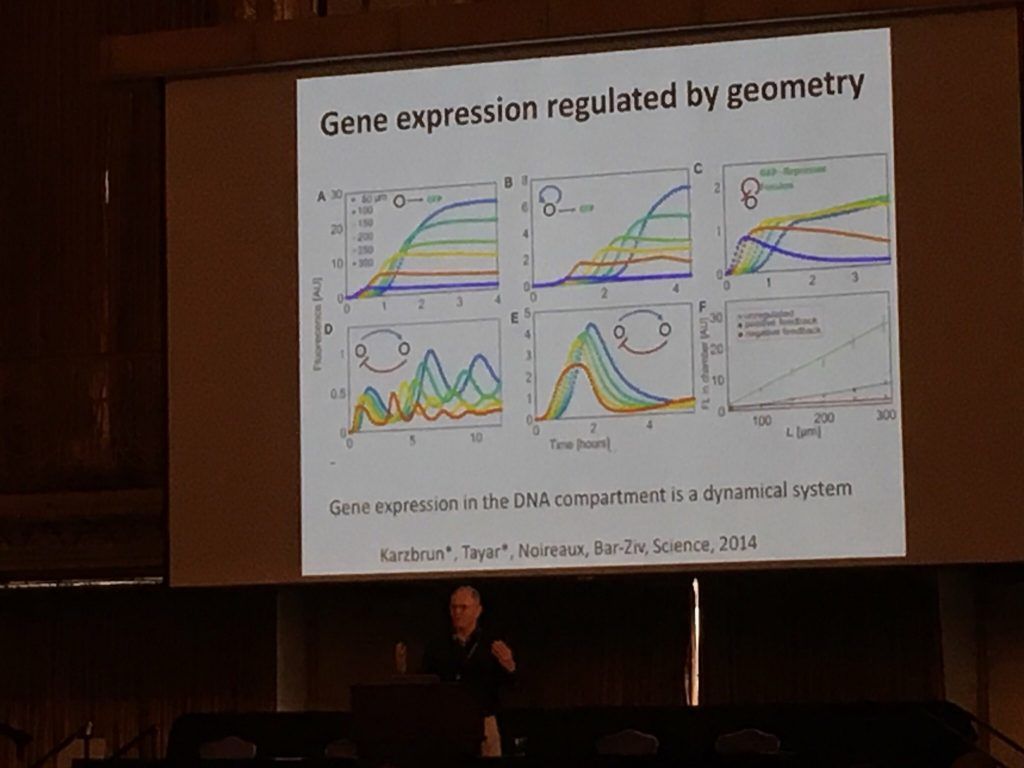
Roy Bar-Ziv gave the first keynote at SEED 2016. His group at the Weissman Institute has made tremendous progress toward using cell-free expression that can mimic the behavior of real cells. Over the last 12 years they developed their ‘artificial cells’ using microfluidics and DNA arrayed on 2D substrates as DNA brushes. Each spot of DNA can be programmed the same as DNA in cells, and unlike other cell-free expression setups the microfluidics allows for dynamics.