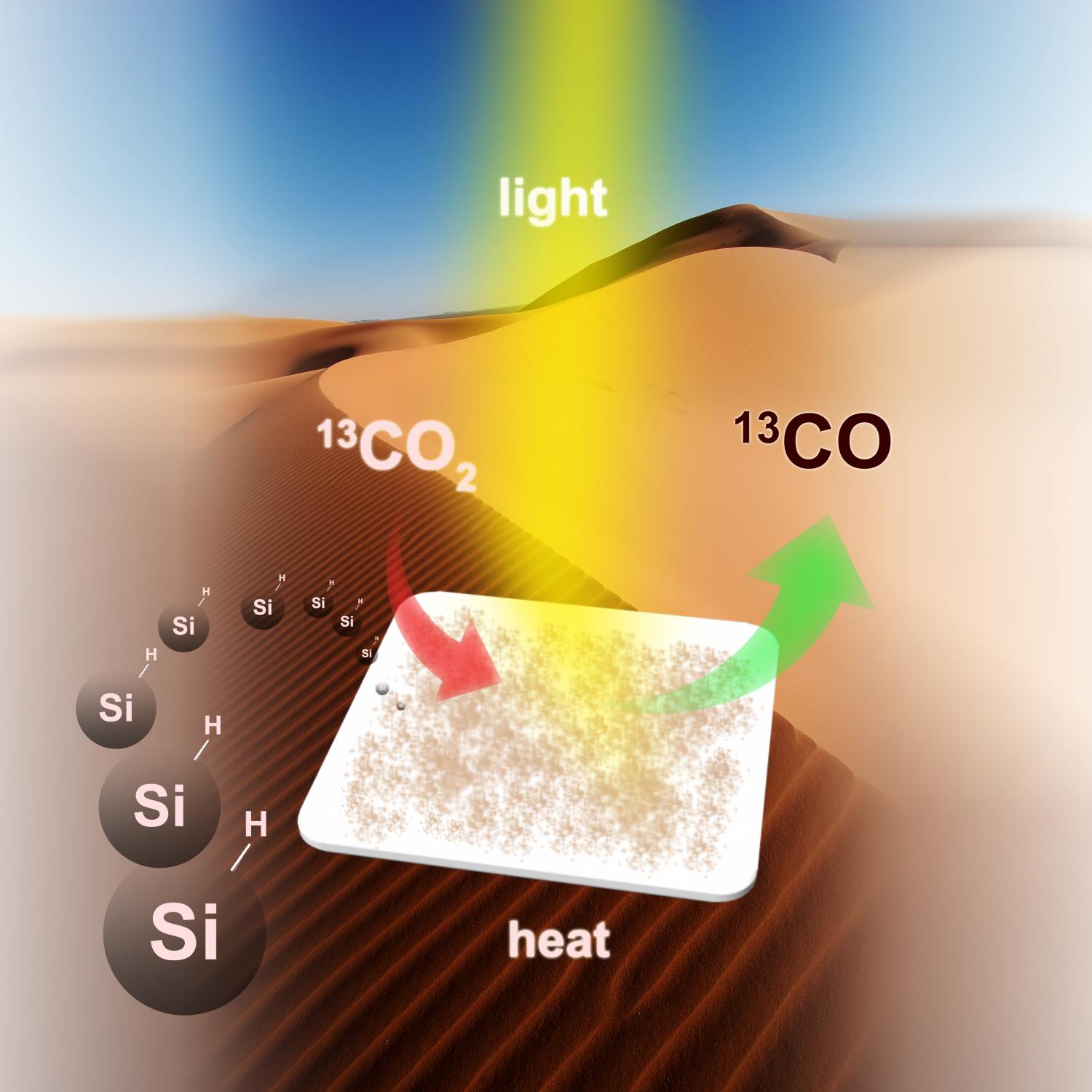
Every year, humans advance climate change and global warming — and quite likely our own eventual extinction — by injecting about 30 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
A team of scientists from the University of Toronto (U of T) believes they’ve found a way to convert all these emissions into energy-rich fuel in a carbon-neutral cycle that uses a very abundant natural resource: silicon. Silicon, readily available in sand, is the seventh most-abundant element in the universe and the second most-abundant element in the earth’s crust.
The idea of converting carbon dioxide emissions to energy isn’t new: there’s been a global race to discover a material that can efficiently convert sunlight, carbon dioxide and water or hydrogen to fuel for decades. However, the chemical stability of carbon dioxide has made it difficult to find a practical solution.