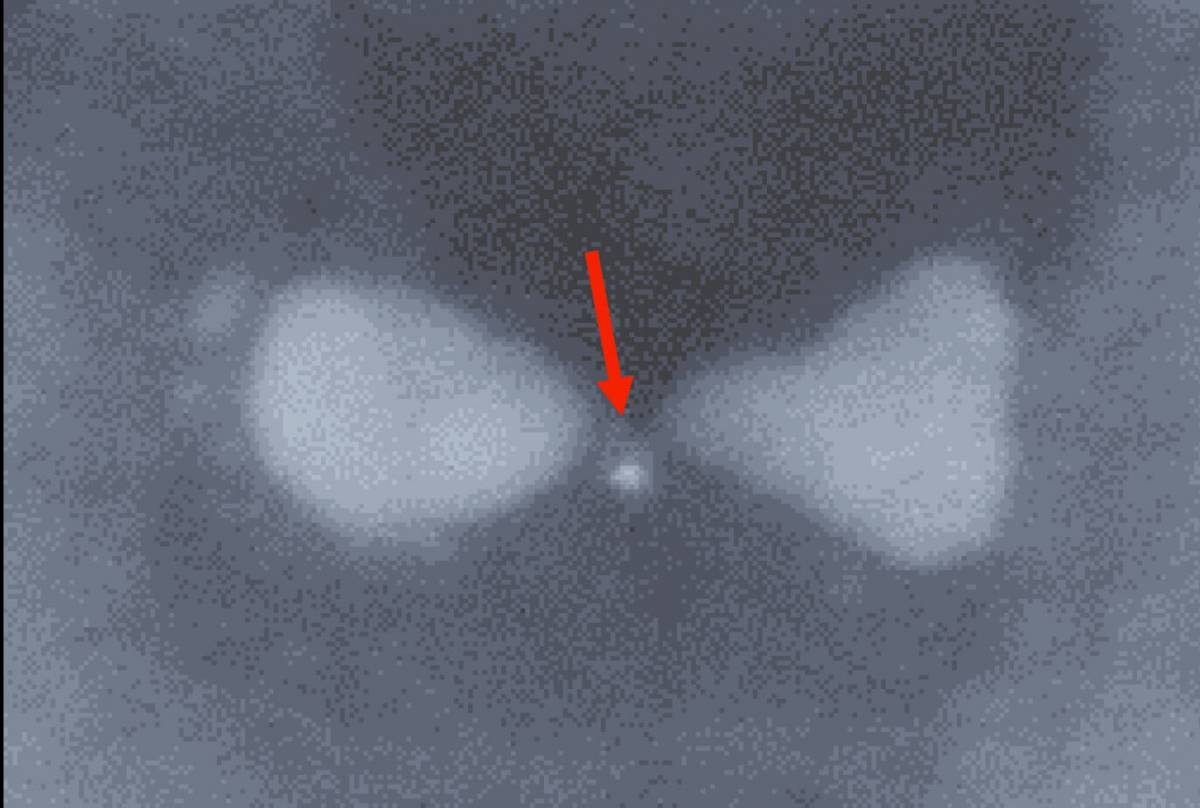
Bowtie-shaped nanoparticles made of silver may help bring the dream of quantum computing and quantum information processing closer to reality. These nanostructures, created at the Weizmann Institute of Science and described recently in Nature Communications, greatly simplify the experimental conditions for studying quantum phenomena and may one day be developed into crucial components of quantum devices.
The research team led by Prof. Gilad Haran of Weizmann’s Chemical Physics Department — postdoctoral fellow Dr. Kotni Santhosh, Dr. Ora Bitton of Chemical Research Support and Prof. Lev Chuntonov of the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology — manufactured two-dimensional bowtie-shaped silver nanoparticles with a minuscule gap of about 20 nanometers (billionths of a meter) in the center. The researchers then dipped the “bowties” in a solution containing quantum dots, tiny semiconductor particles that can absorb and emit light, each measuring six to eight nanometers across. In the course of the dipping, some of the quantum dots became trapped in the bowtie gaps.
Under exposure to light, the trapped dots became “coupled” with the bowties — a scientific term referring to the formation of a mixed state, in which a photon in the bowtie is shared, so to speak, with the quantum dot. The coupling was sufficiently strong to be observed even when the gaps contained a single quantum dot, as opposed to several. The bowtie nanoparticles could thus be prompted to switch from one state to another: from a state without coupling to quantum dots, before exposure to light, to the mixed state characterized by strong coupling, following such exposure.