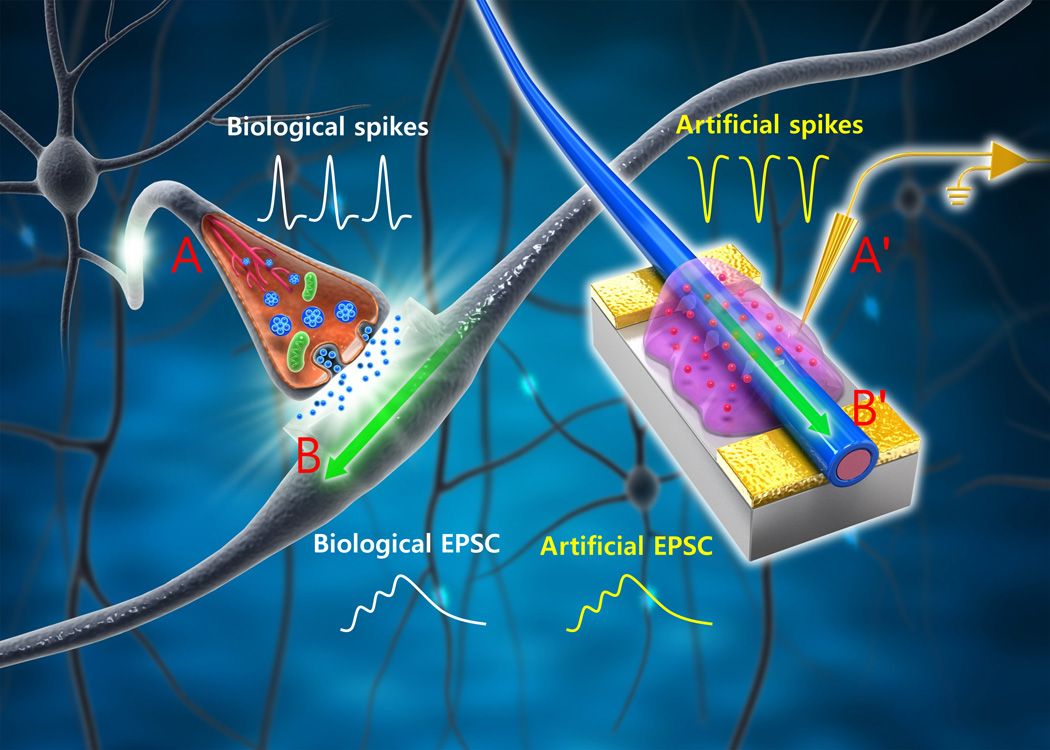
(Phys.org)—A team of researchers with the Pohang University of Science and Technology in Korea has created organic nanowire synaptic transistors that emulate the working principles of biological synapses. As they describe in their paper published in the journal Science Advances, the artificial synapses they have created use much smaller amounts of power than other devices developed thus far and rival that of their biological counterparts.
Scientists are taking multiple paths towards building next generation computers—some are fixated on finding a material to replace silicon, others are working towards building a quantum machine, while still others are busy trying to build something much more like the human mind. A hybrid system of sorts that has organic artificial parts meant to mimic those found in the brain. In this new effort, the team in Korea has reached a new milestone in creating an artificial synapse—one that has very nearly the same power requirements as those inside our skulls.
Up till now, artificial synapses have consumed far more power than human synapses, which researchers have calculated is on the order of 10 femtojoules each time a single one fires. The new synapse created by the team requires just 1.23 femtojoules per event—far lower than anything achieved thus far, and on par with their natural rival. Though it might seem the artificial creations are using less power, they do not perform the same functions just yet, so natural biology is still ahead. Plus there is the issue of transferring information from one neuron to another. The “wires” used by the human body are still much thinner than the metal kind still being used by scientists—still, researchers are gaining.