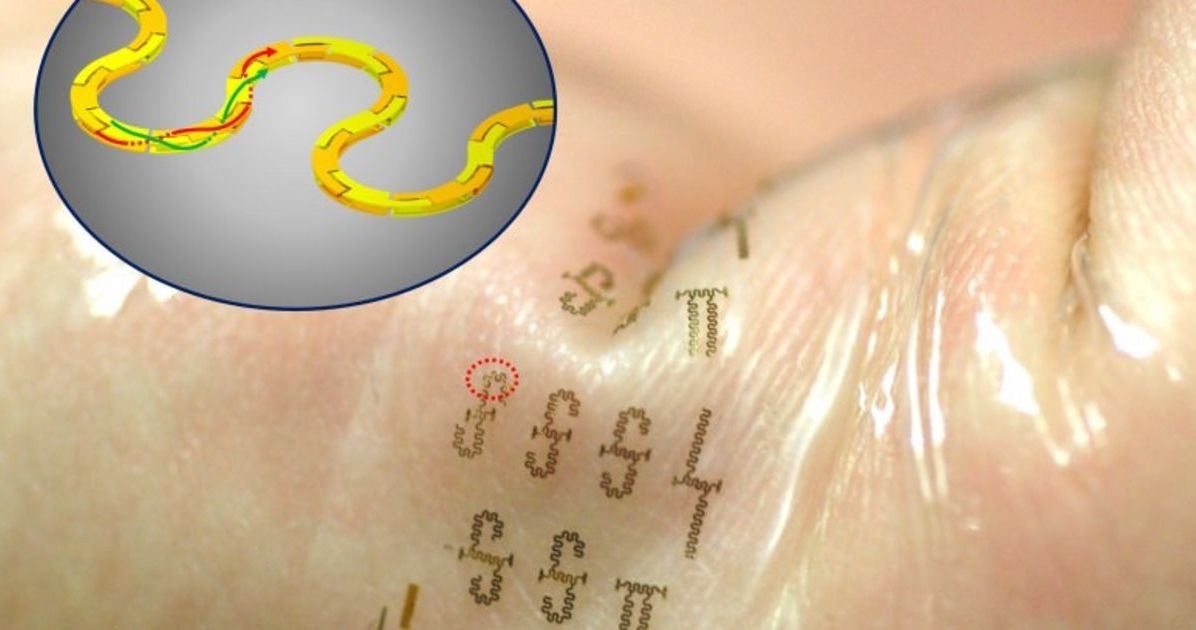
Make no mistake, today’s wearables are clever pieces of kit. But they can be bulky and restricted by the devices they must be tethered to. This has led engineers to create thinner and more powerful pieces of wearable technology that can be applied directly to the skin. Now, researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, led by Zhenqiang “Jack” Ma, have developed “the world’s fastest stretchable, wearable integrated circuits,” that could let hospitals apply a temporary tattoo and remove the need for wires and clips.
With its snake-like shape, the new platform supports frequencies in the .3 gigahertz to 300 gigahertz range. This falls in what is set to become the 5G standard. For a mobile phone, 5G enables faster speeds and greater coverage, but with epidermal electronics, engineers have discussed the possibility that wearers could transmit their vitals to a doctor without having to leave their home.
While the idea isn’t unique, the integrated circuits created by Ma and his team have a much smaller footprint than those developed by other researchers. Earlier transmission lines can measure up to 640 micrometers (or .64 millimeters), but UW–Madison’s solution is just 25 micrometers (or .025 millimeters) thick. The Air Force Office of Scientific Research also supports Ma’s research, suggesting that his wearable breakthroughs may help pilots of the future.