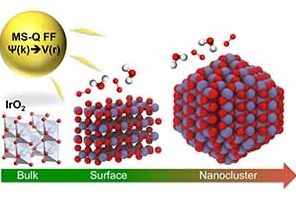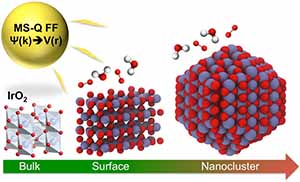
Iridium oxide (IrO2) nanoparticles are useful electrocatalysts for splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen — a clean source of hydrogen for fuel and power. However, its high cost demands that researchers find the most efficient structure for IrO2 nanoparticles for hydrogen production.
A study conducted by a team of researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Argonne National Laboratory, published in Journal of Materials Chemistry A, describes a new empirical interatomic potential that models the IrO2 properties important to catalytic activity at scales relevant to technology development. Also known as a force field, the interatomic potential is a set of values describing the relationship between structure and energy in a system based on its configuration in space. The team developed their new force field based on the MS-Q force field.
“Before, it was not possible to optimize the shape and size of a particle, but this tool enables us to do this,” says Maria Chan, assistant scientist at Argonne’s Center for Nanoscale Materials (CNM), a DOE Office of Science User Facility.