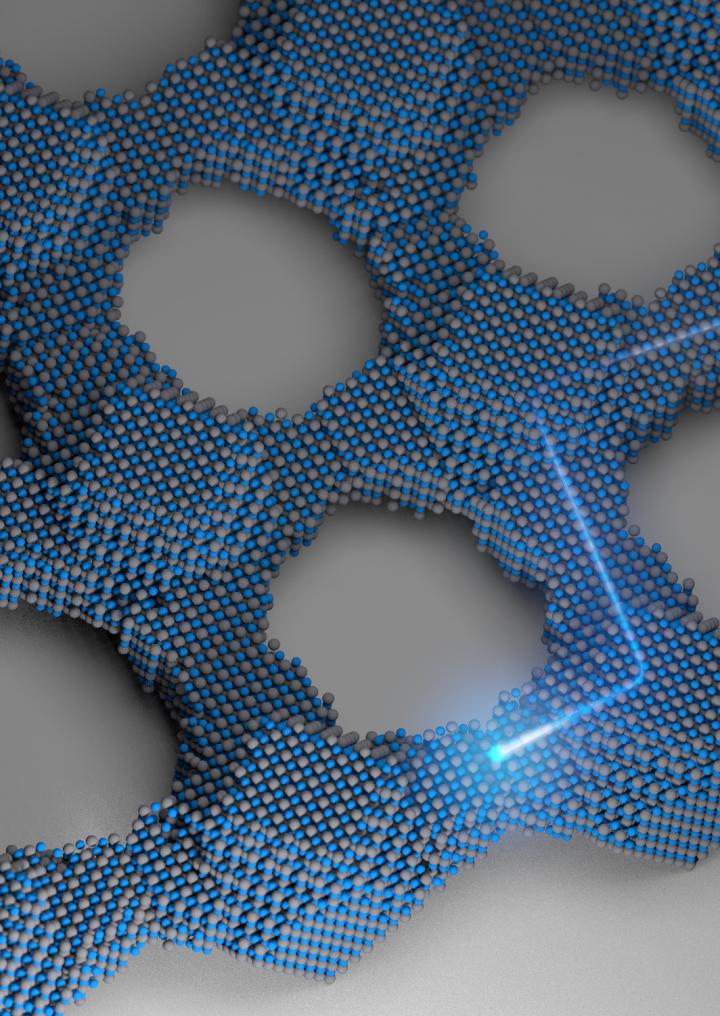
Just as the single-crystal silicon wafer forever changed the nature of communication 60 years ago, Cornell researchers hope their work with quantum dot solids — crystals made out of crystals — can help usher in a new era in electronics.
The team has fashioned two-dimensional superstructures out of single-crystal building blocks. Using a pair of chemical processes, the lead-selenium nanocrystals are synthesized into larger crystals, then fused together to form atomically coherent square superlattices.
Cornell University | Quantum dot solids
The difference between these and previous crystalline structures is the atomic coherence of each 5-nanometer crystal (a nanometer is one-billionth of a meter). They’re not connected by a substance between each crystal — they’re connected to each other directly. The electrical properties of these superstructures are potentially superior to existing semiconductor nanocrystals, with anticipated applications in energy absorption and light emission.