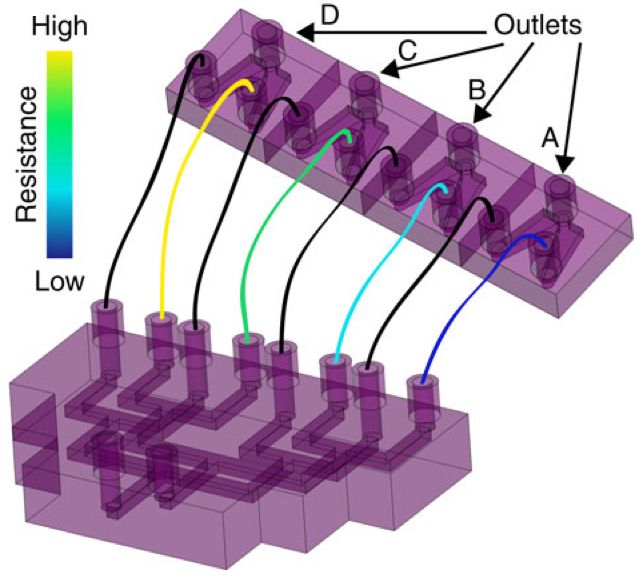
Nanoparticles form in a 3-D-printed microfluidic channel. Each droplet shown here is about 250 micrometers in diameter, and contains billions of platinum nanoparticles. (credit: Richard Brutchey and Noah Malmstadt/USC)
USC researchers have created an automated method of manufacturing nanoparticles that may transform the process from an expensive, painstaking, batch-by-batch process by a technician in a chemistry lab, mixing up a batch of chemicals by hand in traditional lab flasks and beakers.
Consider, for example, gold nanoparticles. Their ability to slip through the cell’s membrane makes them ideal delivery devices for medications to healthy cells, or fatal doses of radiation to cancer cells. But the price of gold nanoparticles at $80,000 per gram, compared to about $50 for pure raw gold goes.