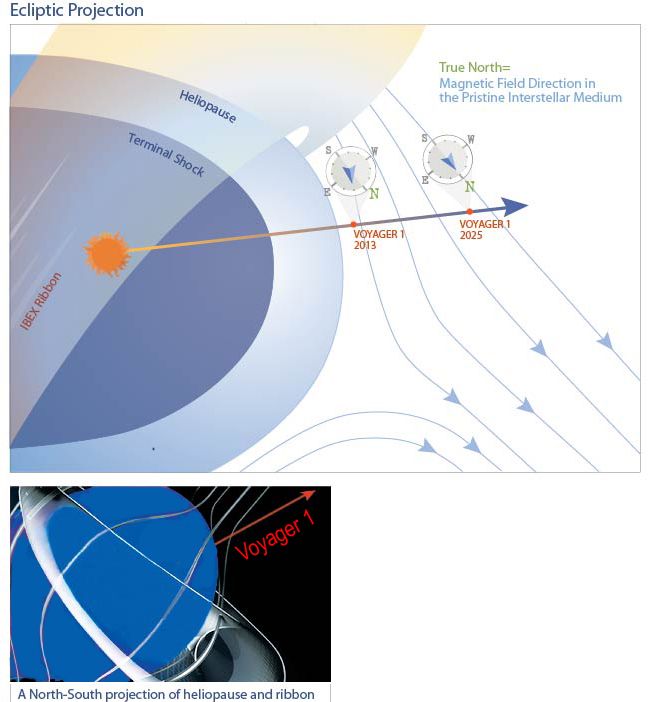
In a study published today in the Astrophysical Journal Letters, scientists from the University of New Hampshire and colleagues answer the question of why NASA’s Voyager 1, when it became the first probe to enter interstellar space in mid-2012, observed a magnetic field that was inconsistent with that derived from other spacecraft observations.
Voyager 1 sent back several different indications that it had punched through the edge of our sun’s massive protective bubble inflated by solar wind—the heliosphere—after a 35-year journey. But the magnetic field data gathered by the spacecraft was not what scientists had expected to see. The UNH-led study resolves the inconsistencies.
“There are still naysayers out there regarding Voyager 1 crossing through the heliopause—the edge of the heliosphere,” says astrophysicist Nathan Schwadron of the UNH Institute for the Study of Earth, Oceans, and Space and department of physics and lead author of the paper. “And the reason for this doubt is that when the spacecraft supposedly broke through the heliopause we should have seen some sort of distinctive shift in the magnetic field from one medium to the other,” Schwadron says.