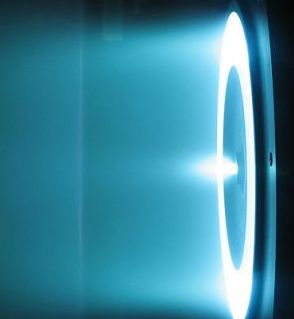
A Hall thruster is powering many of the satellites moving around Earth right now. It needs 100 million (yes, you read that right, 100 million) times less fuel than chemical thrusters. But it was never remotely sturdy enough to get anything to Mars—until now.
Typical chemical thrusters are pretty simple. Fuel combusts, gases shoot one way, and a rocket shoots the other way.
Ion thrusters are a little different. They contain charged electrodes, an anode and a cathode, and allow positively charged ions to shoot from the anode to the cathode. Thanks to momentum, the ions will “overshoot” the cathode. Under regular circumstances they’d be sucked back, but once they’ve cleared the cathode, they’re hit by a beam of electrons, neutralizing them and allowing them to go on their way without interference from the charged cathode. So the neutralized atoms shoot one way, and the rocket shoots another.