“What are the implications of a technology that wires brains together, that in theory at least permits the existence of hive minds? In fact, you know a lot more about that than you might think. You already are a hive mind. You always have been.” Read more
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Will Superintelligent AI Ignore Humans Instead of Destroying Us? — Jason Koebler | Motherboard
“It’s a nice thought that humans could one day create a superintelligent artificial intelligence, and that intelligence takes a look at us, says “thanks, creator,” and blasts off into space, never to be heard from again. Or maybe the AI moves to the deserts or the Arctic or some other uninhabited place, and we live together peacefully. But it seems like such an outcome is unlikely.” Read more
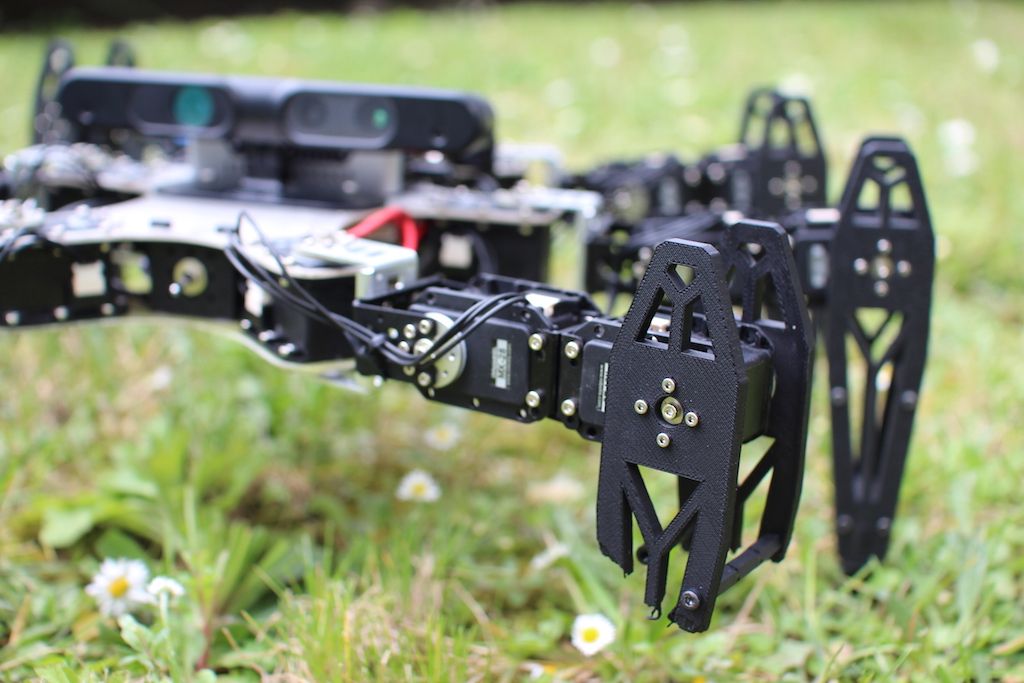

Damage Recovery Algorithm Could Make All Robots Unstoppable — Evan Ackerman | IEEE Spectrum
“But instead of having to figure out which leg is broken and how, or doing any sort of self-analysis at all, the robot simply starts trying a whole bunch of different gait behaviors through ‘intelligent trial and error,’ converging on something that works by exploring an enormous pregenerated set of potentially effective motions in about two minutes.” Read more
Quantum Computing Is About to Overturn Cybersecurity’s Balance of Power — By Vivek Wadhwa SingularityHub
“Spooky action at a distance” is how Albert Einstein described one of the key principles of quantum mechanics: entanglement. Entanglement occurs when two particles become related such that they can coordinate their properties instantly even across a galaxy. Think of wormholes in space or Star Trek transporters that beam atoms to distant locations. Quantum mechanics posits other spooky things too: particles with a mysterious property called superposition, which allows them to have a value of one and zero at the same time; and particles’ ability to tunnel through barriers as if they were walking through a wall.
All of this seems crazy, but it is how things operate at the atomic level: the laws of physics are different. Einstein was so skeptical about quantum entanglement that he wrote a paper in 1935 titled “Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be considered complete?” He argued that it was not possible. Read more

Technology Demonstrations May 2015
This video shows our key technology demonstrations and equipment developed in our lab, including: 100kW CW gyrotron assembly and operation, beaming of 100kW of…
Bionic Eyes Give Second Sight to the Blind
The blind can now see with the help of bionic eyes. In this edition of Wiring the World, Bloomberg’s Ramy Inocencio meets one man diagnosed with retinitis pigmentosa, an incurable form of eye decay, who sees his wife’s face, the ocean’s surf and fireworks for the first time. (Source: Bloomberg)

Moore’s Law Keeps Going, Defying Expectations — By Annie Sneed Scientific American
Personal computers, cellphones, self-driving cars—Gordon Moore predicted the invention of all these technologies half a century ago in a 1965 article for Electronics magazine. The enabling force behind those inventions would be computing power, and Moore laid out how he thought computing power would evolve over the coming decade. Last week the tech world celebrated his prediction here because it has held true with uncanny accuracy—for the past 50 years. Read more
Robot learns skills through trial and error, like you do — by Jon Fingas Engadget
As a rule, robots have to learn through explicit instruction, whether it’s through new programming, watching videos or holding their hands. UC Berkeley’s BRETT (Berkeley Robot for the Elimination of Tedious Tasks) isn’t nearly that dependent, however. The machine uses neural network-based deep learning algorithms to master tasks through trial and error, much like humans do. Ask it to assemble a toy and it’ll keep trying until it understands what works. In theory, you’d rarely need to give the robot new code — you’d just make requests and give the automaton enough time to figure things out.
New York State Governor Cuomo Announces Living Breakwaters Project Launch via bfi.org
https://vimeo.com/91648619
“Living Breakwaters is a comprehensive design for coastal resiliency along the Northeastern Seaboard of the United States and beyond. This approach to climate change adaptation and flood mitigation includes the deployment of innovative, layered ecologically-engineered breakwaters, the strengthening of biodiversity and coastal habitats through “reef streets”, the nurturing and resuscitation of fisheries and historic livelihoods, and deep community engagement through diverse partnerships and innovative educational programs. The transformative educational dimension amplifies impact to the next generation of shoreline stewards while leveraging the expertise of the members of the SCAPE Architecture team, who are making groundbreaking inroads into state and federal agencies, setting new precedents for multi-layered and systemic approaches to infrastructure planning.”
LINK: Governor Cuomo Announces Living Breakwaters Project Launch
MIT aims to give bitcoin research, development a stable home -
Bitcoin survived a wild youth marked by drug trafficking, money laundering, theft, bankruptcy, and political spats. Now, the digital currency is getting cleaned up and heading to grad school.
A fledgling project at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Media Lab is offering researchers and software developers a quiet home to work on bitcoin’s core technology, a computer science breakthrough that lets people trade money securely without paying a middleman. Read more