If you pry open one of today’s ubiquitous high-tech devices—whether a cellphone, a laptop, or an electric car—you’ll find that batteries take up most of the space inside. Indeed, the recent evolution of batteries has made it possible to pack ample power in small places.
But people still always want their devices to last even longer, or go further on a charge, so researchers work night and day to boost the power a given size battery can hold. Rare, but widely publicized, incidents of overheating or combustion in lithium-ion batteries have also highlighted the importance of safety in battery technology.
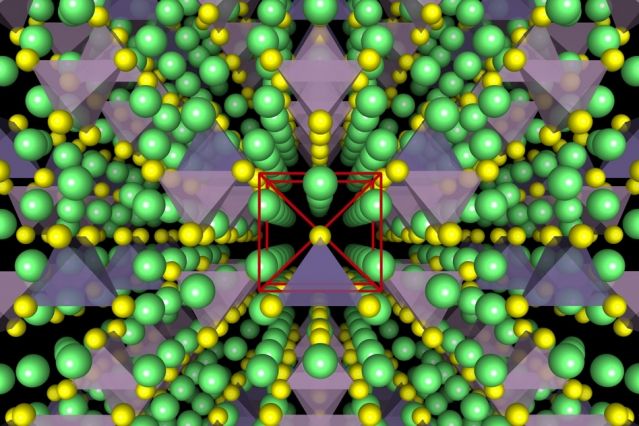
Now researchers at MIT and Samsung, and in California and Maryland, have developed a new approach to one of the three basic components of batteries, the electrolyte. The new findings are based on the idea that a solid electrolyte, rather than the liquid used in today’s most common rechargeables, could greatly improve both device lifetime and safety—while providing a significant boost in the amount of power stored in a given space.