A new experiment provides the most robust proof that quantum mechanics doesn’t follow the rules we take for granted in everyday life.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


16 Things You Probably Never Knew About The Short Circuit Movies
Right now, we’re falling in love with BB-8 from Star Wars—and yet, there’s still a special place in our hearts for Johnny Five, the robot from the Short Circuit films. But how much do you actually know about these films? Check out this video, featuring 16 electrifying facts about the making of this duology.
Physics-Astronomy: NASA’s Warp-Drive Solution for Faster-Than-Light Space Travel
Agreeing to state-of-the art theory, a warp drive might cut the travel time between stars from tens of thousands of years to only weeks or months. Harold G. White, a physicist and innovative propulsion engineer at NASA and other NASA engineers are working to regulate whether faster-than-light travel — warp drive — might soon be possible. The group is trying to some extent warp the course of a photon, altering the distance it travels in a definite area, and then detecting the change with a device called an interferometer.
In 1994, a Mexican physicist, Miguel Alcubierre, speculated that faster-than-light speeds were conceivable in a technique that did not deny Einstein by binding the growth and reduction of space itself. Under Dr. Alcubierre’s theory, a ship still couldn’t surpass light speed in a native region of space. But a theoretical thrust system he sketched out operated space-time by producing a so-called “warp bubble” that would inflate space on one side of a spacecraft and contract it on another.
Image source: With thanks to Shutterstock.com.
An Alcubierre Warp Drive expanses spacetime in a wave producing the material of space ahead of a spacecraft to contract and the space behind it to enlarge. The ship can ride the wave to go faster to high speeds and time travel. The Alcubierre drive, also famous as the Alcubierre metric or Warp Drive, is a mathematical model of a spacetime showing features suggestive of the fictional “warp drive” from Star Trek, which can move “faster than light”.
Meet The Anti-Death Presidential Candidate
My 4 min interview on transhumanism and longevity with BuzzFeed came out as a stand-alone video. About 800 comments under the YouTube video:
Because we all deserve a chance at immortality!
Editing humanity
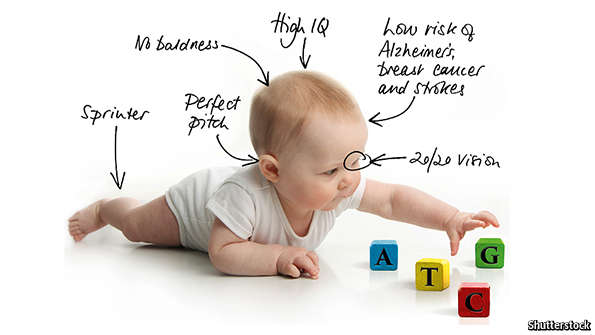
THE genome is written in an alphabet of just four letters. Being able to read, study and compare DNA sequences for humans, and thousands of other species, has become routine. A new technology promises to make it possible to edit genetic information quickly and cheaply. This could correct terrible genetic defects that blight lives. It also heralds the distant prospect of parents building their children to order.
The technology is known as CRISPR-Cas9, or just CRISPR. It involves a piece of RNA, a chemical messenger, designed to target a section of DNA; and an enzyme, called a nuclease, that can snip unwanted genes out and paste new ones in. Other ways of editing DNA exist, but CRISPR holds the promise of doing so with unprecedented simplicity, speed and precision.

Gene That Controls the Internal Clock Discovered
The circadian rhythm is a subject of many studies, yet it remains a mystery in many ways. While scientists have identified many of the cell proteins involved in circadian rhythm and several genes that contribute to a healthy rhythm, the ‘master clock’ gene remained elusive. However, a recent chronobiology study on rats indicates that the Zfhx3, or Zinc Finger Homeobox 3, gene may be the master gene that dictates this important biological rhythm.

US pushes pedal on car-to-car communication
V2V communication is a viable way to mitigate accidents amongst autonomous vehicles.
Engineers have known for some time that if cars could only “talk” to each other, they could avoid a lot of accidents.
Vehicles could be driven more safely with information about another car, obstacle or pedestrian around a blind curve, for example.
But the hurdles to implementing these systems are numerous: they require a legal framework and the allocation of wireless spectrum to enable vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communications.