Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

The Longevity Reporter: The Weekly Newsletter on Aging (05th September, 2015)
Checkout the latest Longevity Reporter Newsletter (05th September, 2015), covering this week’s top news in health, aging, longevity.
This week: Dramatic Advances In Super-Resolution Imaging; This Stunning 3-D Model Provides A Fresh Perspective On Cancer; Want A Long Lifespan? You Need Stable Gene Networks; The Future Of Health: Precision Medicine; And more.

Squishy transistors—a device concept for fast, low-power electronics
An international team of researchers from the National Physical Laboratory (NPL), IBM, the University of Edinburgh and Auburn University have shown that a new device concept — a ‘squishy’ transistor — can overcome the predicted power bottleneck caused by CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) technology reaching its fundamental limits.
Moore’s law predicted that the number of transistors able to fit on a given die area would double every two years. As transistor density doubled, chip size shrank and processing speeds increased. This march of progress led to rapid advances in information technology and a surge in the number of interconnected devices. The challenge with making anything smaller is that there are fundamental physical limits that can’t be ignored and we are now entering the final years of CMOS transistor shrinkage.
Furthermore, this proliferation is driving an increase in data volume, accompanied by rising demands on energy to process, store and communicate it all; as a result, IT infrastructure now draws an estimated 10 % of the world’s electrical power. Previous efforts have focused on remediation by reducing the amount of energy per bit. However, soon we will hit a power barrier that will prevent continued voltage scaling. The development of novel, low-power devices based on different physical principles is therefore crucial to the continued evolution of IT.

The World in 2025: 8 Predictions for the Next 10 Years
In 2025, in accordance with Moore’s Law, we’ll see an acceleration in the rate of change as we move closer to a world of true abundance. Here are eight areas where we’ll see extraordinary transformation in the next decade:

The Longevity Dividend
Investments in Longevity Could Really Pay Off
With a ‘silver tsunami’ ahead, tackling aging makes all kinds of sense — and could reap rich rewards.
This Presidential Candidate Is Promising Immortality
AOL running an energetic 2-min video on transhumanism and longevity on their morning show:
Zoltan Istvan of the Transhumanist Party is running for President on one platform: longevity.

The Genomics Revolution: Building An App Store For Genomes
Your DNA contains a huge amount of information, and it’s getting cheaper and easier to sequence it every day. The problem now is not the sequencing, but what you can actually learn from the information — if you can at all. We’re pretty good at reading off the code nowadays, but the vast majority of it is still a mystery. While there are many companies that will sequence your DNA for a relatively cheap fee, there’s no unified platform directing you to companies who can actually make sense of the code for you; after all there’s not much use having information if you have no idea what it means. Starting with a $100 million investment and partners including Illumina (a world leader in sequencing), new company Helix aims to change this by building a sort of genome ‘App store’ — putting you in touch with your DNA.
Helix wants to act like a hub, connecting you with the right companies and enabling you to find out information you want on your very own genome. As sequencing expands, buoyed by the precision medicine drive, we’re learning more and more about our DNA. This platform hopes to bring all these developments together so that discoveries can trickle through to individuals at home trying to decipher their own genomes.
”Genomics is reaching an inflection point in cost, volumes, and knowledge, creating a significant opportunity to unlock information that is currently not widely accessible to individuals”
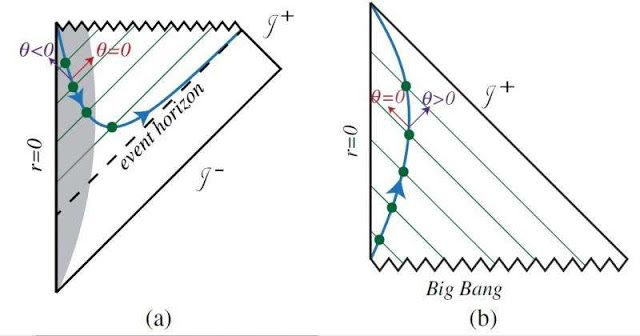
New General Relativity Area law theory suggests time runs backward inside a blackhole
Black holes are known to have many strange properties, such as that they allow nothing—not even light—to escape after falling in. A lesser known but equally bizarre property is that black holes appear to “know” what happens in the future in order to form in the first place. However, this strange property arises from the way in which black holes are defined, which has motivated some physicists to explore alternative definitions.
They reported a new area law in general relativity that is based on an interpretation of black holes as curved geometric objects called “holographic screens.”
“The so-called teleology of the black hole event horizon is an artifact of the way in which physicists define an event horizon: the event horizon is defined with respect to infinite future elapsed time, so by definition it ‘knows’ about the entire fate of the universe,” Engelhardt told Phys.org. “In general relativity, the black hole event horizon cannot be observed by any physical observer in finite time, and there isn’t a sense in which the black hole as an entity knows about future infinity. It is simply a convenient way of describing black holes.”
VASIMR: Here’s How we Might Reach Mars in 39 Days
The first VASIMR experiment was conducted at MIT in 1983 on their magnetic mirror device plasma device, and in 1998 ASPL created the first VASIMR rocket, the VX-10. By 2005 the ASPL had created the VX-50, which was capable of up to 50kW of plasma discharge. So, what’s so significant about this design?