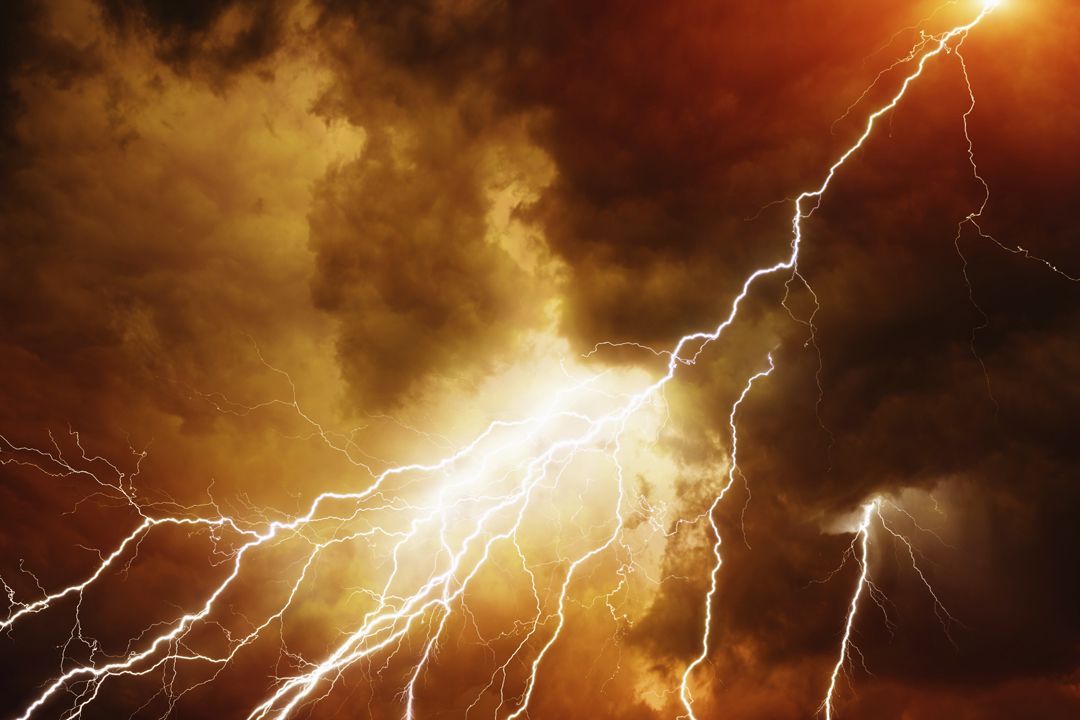
A terrifying few moments flying into the top of an active thunderstorm in a research aircraft has led to an unexpected discovery that could help explain the longstanding mystery of how lightning gets initiated inside a thunderstorm.
University of New Hampshire physicist Joseph Dwyer and lightning science colleagues from the University of California at Santa Cruz and Florida Tech describe the turbulent encounter and discovery in a paper to be published in the Journal of Plasma Physics.
In August 2009, Dwyer and colleagues were aboard a National Center for Atmospheric Research Gulfstream V when it inadvertently flew into the extremely violent thunderstorm—and, it turned out, through a large cloud of positrons, the antimatter opposite of electrons, that should not have been there.