Movano has unveiled its new smart ring, which can track steps, sleep, heart rate, heart rate variability, and several other important health metrics.
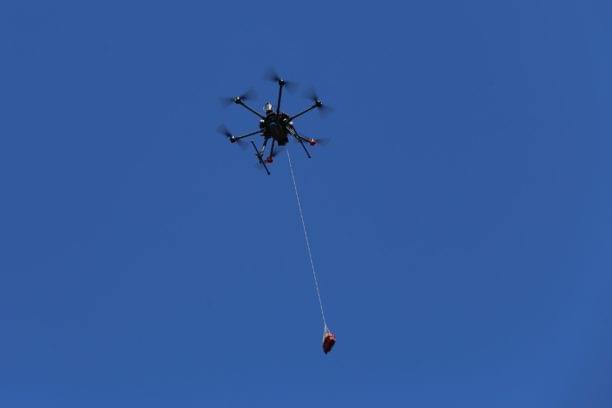



An autonomous drone delivers a defibrillator – and saves the life of a cardiac arrest patient. Swedish drone company Everdrone says it’s a medical history first – but the grateful patient says that it’s a technology that should be used everywhere.
For heart attack patients, seconds count: the minutes that an ambulance can take to reach a patient in cardiac arrest can mean the difference between life and death. Autonomous drones offer a game-changing solution. Autonomous drone specialists Everdrone operate the drone delivery system in Region Västra Götaland, supported by Vinnova, Swelife and Medtech4Health. Their innovative solution has been developed with Center for Resuscitation Science at Karolinska Institutet, SOS Alarm and Region Västra Götaland.
Now, the technology can claim a life saved. In Trollhättan, Sweden on December 92,021, an Everdrone autonomous drone delivered a defibrillator that helped save the life of a 71-year-old man.

From the fMRI scans, the researchers saw the same areas of the brain light up but with different activation patterns, depending on whether the dogs were hearing the story in their native language or a new one—suggesting that they were neurologically processing differences between the two languages.
Then the researchers tried to test whether the dogs were responding to specific characteristics intrinsic to each language. Were the animals reacting to actual changes in speech patterns—that Hungarian words put stress on the first syllable, for instance—or just responding to basic differences in fundamental auditory signatures between the two languages—alterations in tones that occur during vowel pronunciation? They tested this by playing recordings in which the speech from the story had been garbled, resulting in gibberish that “sounded” like Hungarian or Spanish. Again, the team saw different patterns in brain activity when a dog heard real human speech instead of speechlike gibberish, although the researchers cannot yet say whether this is evidence that dogs can recognize human speech as speech (sounds strung together in a meaningful way for humans to communicate with one another)—or whether their brain was just responding to the more natural sound when compared with the weird-sounding gibberish. There was no change in brain activity between hearing Spanish gibberish versus Hungarian gibberish, however, implying that the canines’ brain was not just responding to the different tonal qualities.”
A new study’s authors say their investigation represents the first time that a nonhuman brain has been shown to detect language.

South Africa’s space participation dates back to the 1960s when the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) first established its Deep Space Network Station, popularly known as DSS-51, in Hartebeesthoek. The station was established to assist NASA’s interplanetary missions. The facility was then operated by the South African Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR)… […].
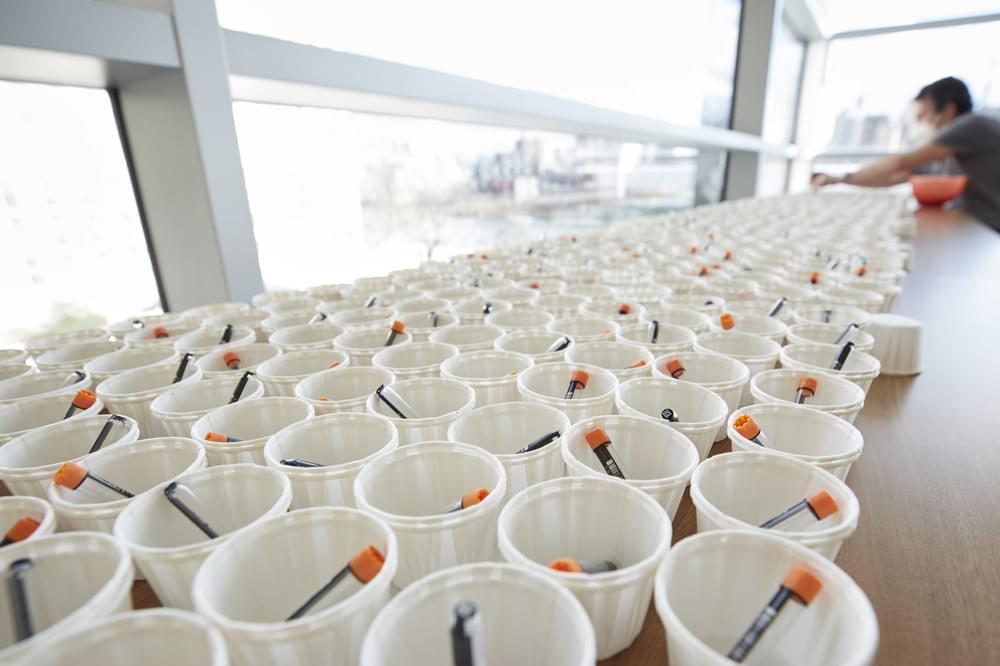

In the early days of the pandemic, with commercial COVID tests in short supply, Rockefeller’s Robert B. Darnell developed an in-house assay to identify positive cases within the Rockefeller community. It turned out to be easier and safer to administer than the tests available at the time, and it has been used tens of thousands of times over the past nine months to identify and isolate infected individuals working on the university’s campus.
Now, a new study in PLoS confirms that Darnell’s test performs as well, if not better, than FDA-authorized nasal and oral swab tests. In a direct head-to-head comparison of 162 individuals who received both Rockefeller’s “DRUL” saliva test and a conventional swab test, DRUL caught all of the cases that the swabs identified as positive—plus four positive cases that the swabs missed entirely.
“This research confirms that the test we developed is sensitive and safe,” says Darnell, the Robert and Harriet Heilbrunn professor and head of the Laboratory of Molecular Neuro-Oncology. “It is inexpensive, has provided excellent surveillance within the Rockefeller community, and has the potential to improve safety in communities as the pandemic drags on.”
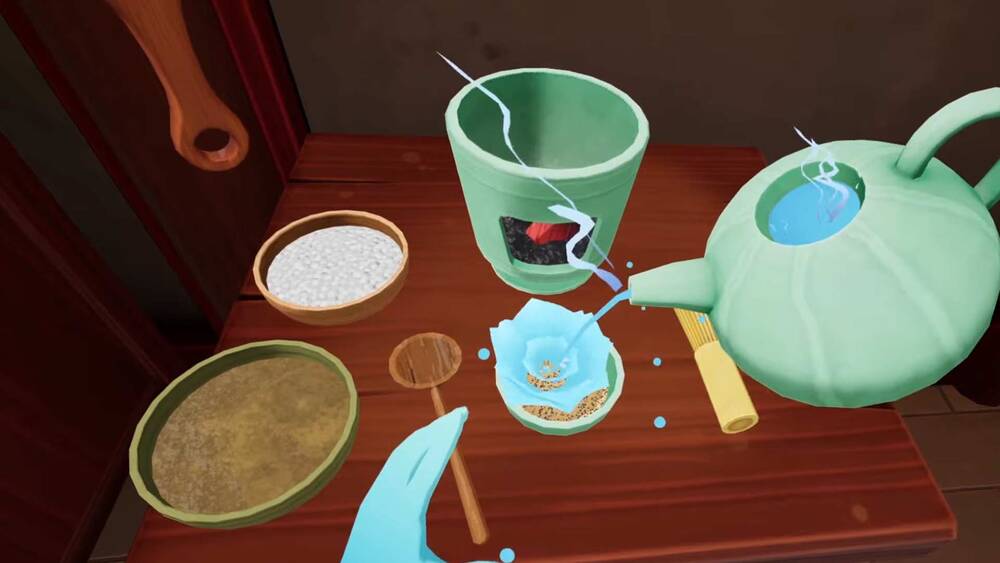

Schell Games today announced that Lost Recipes, its upcoming historical cooking sim, is set to release January 27th on the Quest platform, bringing with it the chance to cook ancient recipes in period accurate kitchens from around the world.
Arriving from the VR veterans known for I Expect You to Die, Until You Fall, and the upcoming VR adaptation of Among Us, Lost Recipes throws you into a time portal to recreate dishes from centuries past.
Schell Games says Lost Recipes teleports you to “historically-accurate kitchens, using authentic ingredients, utensils, and techniques.” Check out the announcement trailer below:
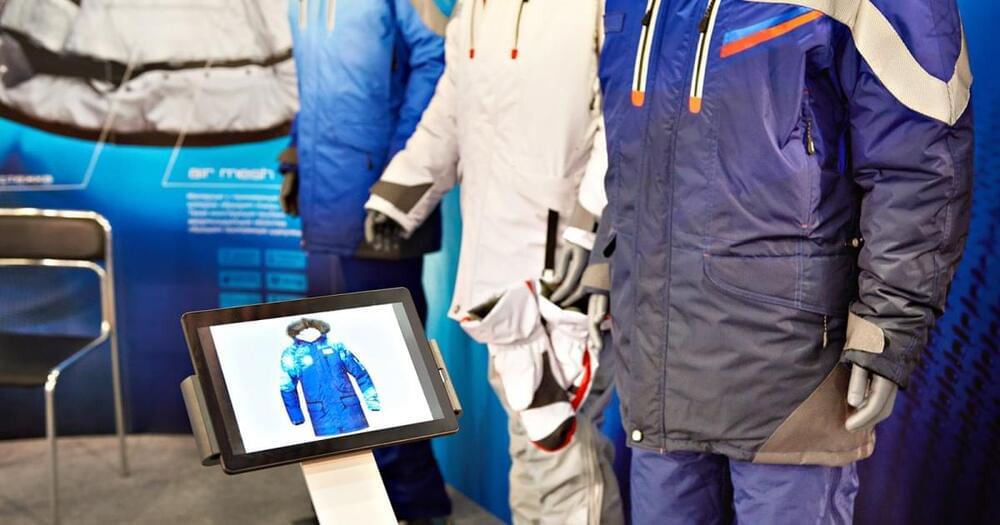

That’s the future that designers of E-textiles, or smart textiles, want to build.
Fashion trial and error: Smart textiles embed flexible electronics into clothing to give them similar tracking and monitoring capabilities as smartwatches. Today’s market, however, doesn’t have the same kind of demand as it has for the devices we wear on our wrists.
Many of these systems are kept out of equilibrium because individual constituents have their own power source — ATP for cells, gas for cars. But all these extra energy sources and mismatched reactions make for a complex dynamical system beyond the reach of statistical mechanics. How can we analyze phases in such ever-changing systems?
Vitelli and his colleagues see an answer in mathematical objects called exceptional points. Generally, an exceptional point in a system is a singularity, a spot where two or more characteristic properties become indistinguishable and mathematically collapse into one. At an exceptional point, the mathematical behavior of a system differs dramatically from its behavior at nearby points, and exceptional points often describe curious phenomena in systems — like lasers — in which energy is gained and lost continuously.
Now the team has found that these exceptional points also control phase transitions in nonreciprocal systems. Exceptional points aren’t new; physicists and mathematicians have studied them for decades in a variety of settings. But they’ve never been associated so generally with this type of phase transition. “That’s what no one has thought about before, using these in the context of nonequilibrium systems,” said the physicist Cynthia Reichhardt of Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico. “So you can bring all the machinery that we already have about exceptional points to study these systems.”

The uncertainty principle, first introduced by Werner Heisenberg in the late 1920’s, is a fundamental concept of quantum mechanics. In the quantum world, particles like the electrons that power all electrical product can also behave like waves. As a result, particles cannot have a well-defined position and momentum simultaneously. For instance, measuring the momentum of a particle leads to a disturbance of position, and therefore the position cannot be precisely defined.

❤️ Check out Weights & Biases here and sign up for a free demo: https://www.wandb.com/papers.
❤️ Their blog post is available here: https://www.wandb.com/articles/better-paths-through-idea-space.
📝 The paper “Emergent Tool Use from Multi-Agent Interaction” is available here:
https://openai.com/blog/emergent-tool-use/
❤️ Watch these videos in early access on our Patreon page or join us here on YouTube:
- https://www.patreon.com/TwoMinutePapers.
- https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCbfYPyITQ-7l4upoX8nvctg/join.
🙏 We would like to thank our generous Patreon supporters who make Two Minute Papers possible:
Alex Haro, Andrew Melnychuk, Angelos Evripiotis, Anthony Vdovitchenko, Brian Gilman, Bryan Learn, Christian Ahlin, Claudio Fernandes, Daniel Hasegan, Dennis Abts, Eric Haddad, Eric Martel, Evan Breznyik, Geronimo Moralez, James Watt, Javier Bustamante, John De Witt, Kaiesh Vohra, Kasia Hayden, Kjartan Olason, Levente Szabo, Lorin Atzberger, Lukas Biewald, Marcin Dukaczewski, Marten Rauschenberg, Matthias Jost„ Maurits van Mastrigt, Michael Albrecht, Michael Jensen, Nader Shakerin, Owen Campbell-Moore, Owen Skarpness, Raul Araújo da Silva, Rob Rowe, Robin Graham, Ryan Monsurate, Shawn Azman, Steef, Steve Messina, Sunil Kim, Taras Bobrovytsky, Thomas Krcmar, Torsten Reil.
https://www.patreon.com/TwoMinutePapers.
Splash screen/thumbnail design: Felícia Fehér — http://felicia.hu.
Károly Zsolnai-Fehér’s links:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/twominutepapers/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/twominutepapers.
Web: https://cg.tuwien.ac.at/~zsolnai/