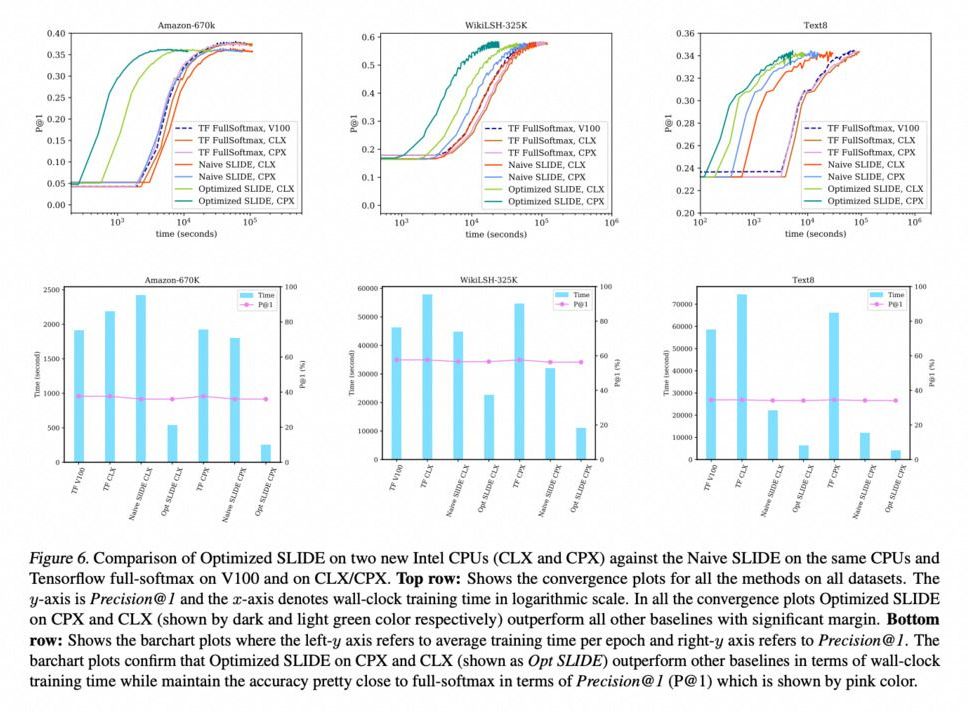
Computer scientists from Rice University have displayed an artificial intelligence (AI) software that can run on commodity processors and train deep neural networks 15 times faster than platforms based on graphics processors.
According to Anshumali Shrivastava, an assistant professor of computer science at Rice’s Brown School of Engineering, the resources spent on training are the actual bottleneck in AI. Companies are spending millions of dollars a week to train and fine-tune their AI workloads.
Deep neural networks (DNN) are a very powerful type of artificial intelligence that can outperform humans at some tasks. DNN training is a series of matrix multiplication operations and an ideal workload for graphics processing units (GPUs), which costs nearly three times more than general-purpose central processing units (CPUs).