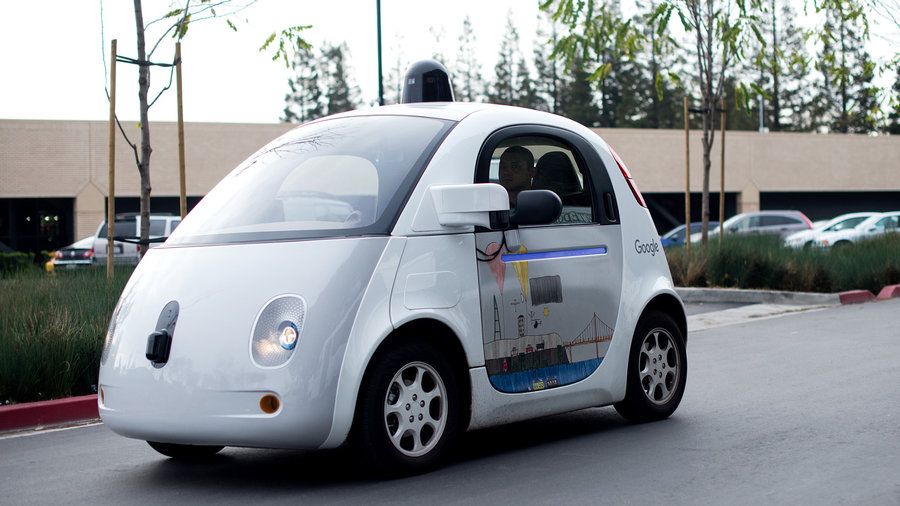
In a major step forward for self-driving cars and the industry seeking to manufacture them, US highway authorities have informed Google that its autonomous vehicle systems could qualify as a “driver” in the eyes of the law.
A letter addressed to the company from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) last week suggests that if self-driving vehicles (SDVs) can satisfy a number of safety standards, the fact that artificial intelligence (AI) is controlling the car – in the absence of any human controls – would not be a barrier to the car legally driving on US roads.
“We agree with Google its SDV will not have a ‘driver’ in the traditional sense that vehicles have had drivers during the last more than one hundred years,” writes chief counsel for the NHTSA, Paul A. Hemmersbaugh. “If no human occupant of the vehicle can actually drive the vehicle, it is more reasonable to identify the ‘driver’ as whatever (as opposed to whoever) is doing the driving. In this instance, an item of motor vehicle equipment, the [SDS Self-Driving System], is actually driving the vehicle.”