A team of researchers affiliated with several institutions in France has observed a phase transition in an artificially created flock. In their paper published in the journal Physical Review Letters, the group describes how they created their artificial flock and the events that led to a phase transition.
Scientists trying to understand crowd behavior generally create computer models meant to mimic human behavior under crowded conditions—but such simulations are limited by the parameters that are used to create them. Most in the field agree on the need to recreate crowd or flocking behavior physically in a lab. In this new effort, the researchers have built on prior work with an artificial crowd, and have found that under certain conditions it underwent a phase transition similar to water freezing to an ice state.
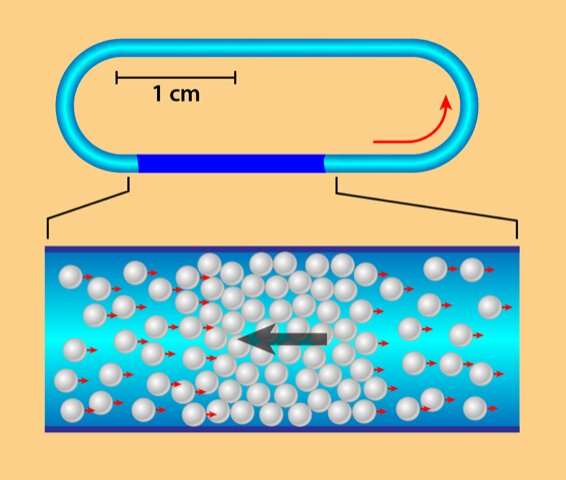
Working on a prior effort, some of the team members created an artificial crowd consisting of millions of beads suspended in a liquid between two plates of glass. The plates were joined in a way that allowed the beads to move around the outer edges of an oval—similar to cars on a partially three-dimensional race track. The beads were forced to move in one direction by applying an electric field—the Quincke effect spun the beads, which pushed them through the liquid in the same direction. Also, due to a dipole effect, the beads did not adhere to one another—instead, they moved around the track, seemingly of their own accord. The prior team showed that increasing density of the beads could set off a Vicsek-like transition in which randomly moving particles exhibit flock-like behaviors. In this new effort, the researchers used the same setup with the beads to create a flock and then watched what would happen as density was increased.