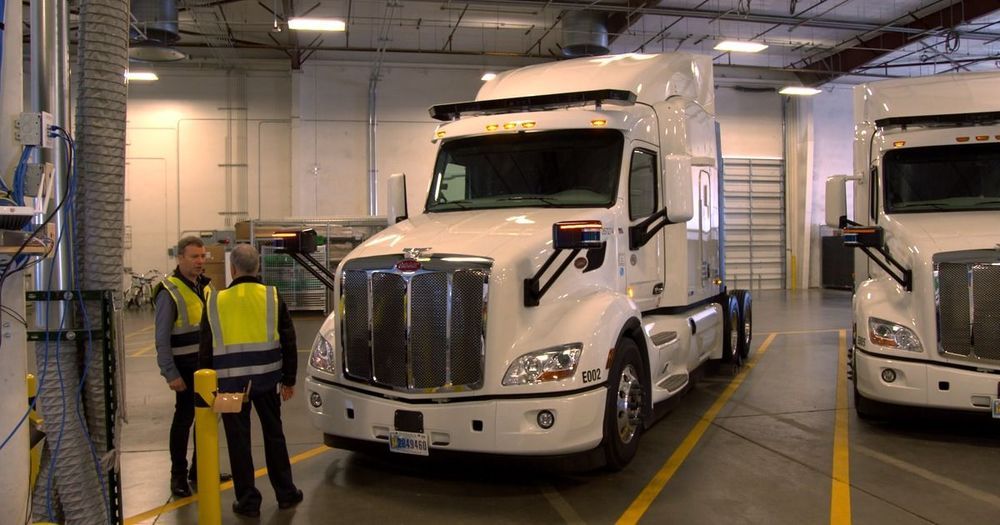
Companies are already testing driverless trucks on America’s roads. The technology will bring untold profits, but it may cost thousands of truckers their livelihoods.
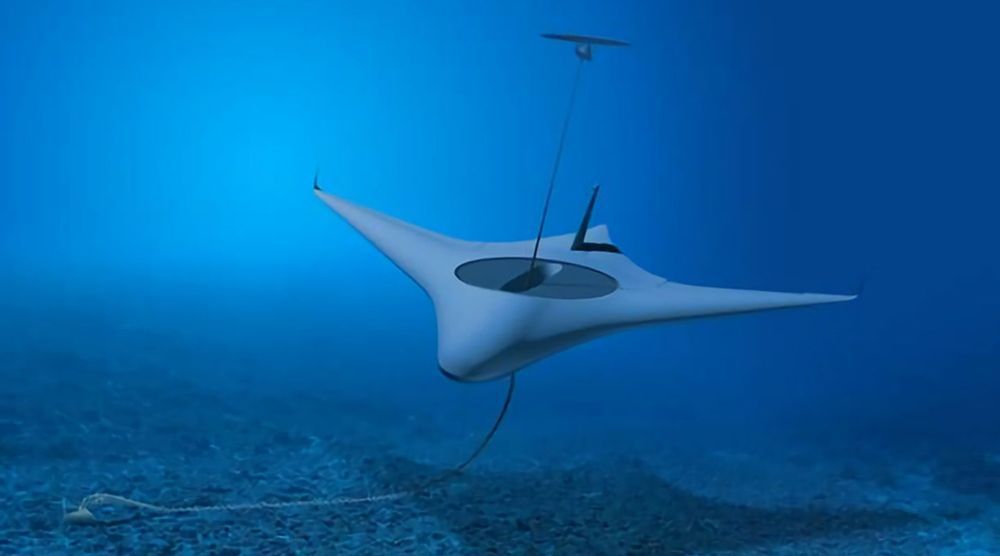





DARPA has announced the four companies it has selected to work under its Manta Ray Program. Three of the companies will be tasked with developing ‘an integrated solution’ for the program’s operational and technology areas, according to DARPA. The fourth company will instead focus on the topic of undersea energy harvesting options capable of working at the depths DARPA has planned.

Based on myth and such it could a definite possibility that this tale is true.
Amelia Earhart was one of the first female pilots in Earth history. She had been on expeditions all over the world, and recalled seeing people doing all kinds of strange things to their bodies. In the mid–20th century she became famous for being the first woman to fly across the Atlantic Ocean. In 1937 she attempted to fly around the world, and on July 2nd, she and her navigator, Fred Noonan, took off from New Guinea and headed east, around the equator.
However, while over the Pacific Ocean, their Lockheed L-10 Electra airplane ran low on gas. They began looking for an atoll to set down on, and tried to send out an SOS. Suddenly, they saw a huge light behind them. The plane stopped dead, and then started moving backwards towards the light. That was the last Earhart remembered of the event. They were in fact being abducted by an alien species, the Briori. To the outside world, it appeared that the plane just vanished somewhere in the South Seas.
Unbeknownst at the time was that the mission was financed by her government and was part of an intelligence operation to gather information about the Japanese. Rumors about this emerged after the Pearl Harbor attack in 1941, and it later became part of established history.

Diving into the autonomous submarine race, DARPA has awarded contracts to three companies as part of its Manta Ray Program. Intended to support a new generation of long-duration, long-range Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs), the end goal is to produce robotic vehicles that can operate for months without maintenance or human logistics support.
UUVs have advanced so far and so fast in the past 20 years that today major navies like those of the US and the UK are developing vehicles that are so large and so long-range that they are essentially unmanned versions of conventional submarines with the crew spaces removed.
The problem is that sailors are aboard their boats for a reason, which means that future UUVs need to be able to maintain themselves and do without humans to provide logistical support like refueling. This would mean that commanders would have more capabilities at their disposal without being hampered by the UUVs being dependent on manned vessels and ports that would reduce the hosts’ flexibility and availability.

The unique Icon A5 seaplane can turn any lake into an airport! ✈🌊.
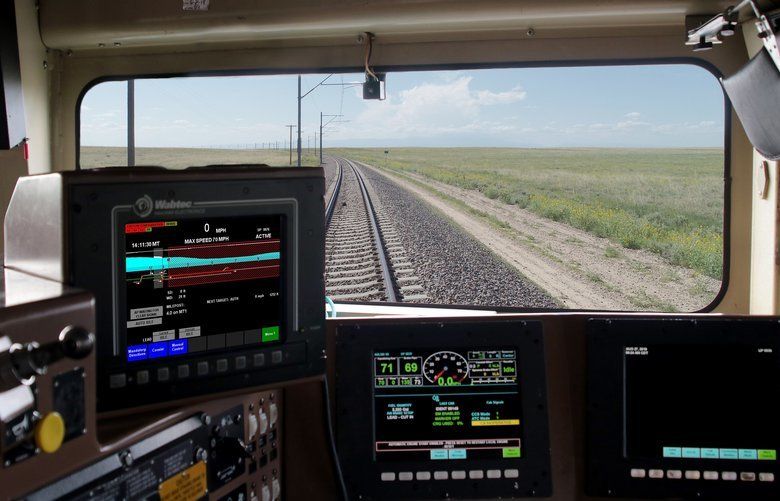

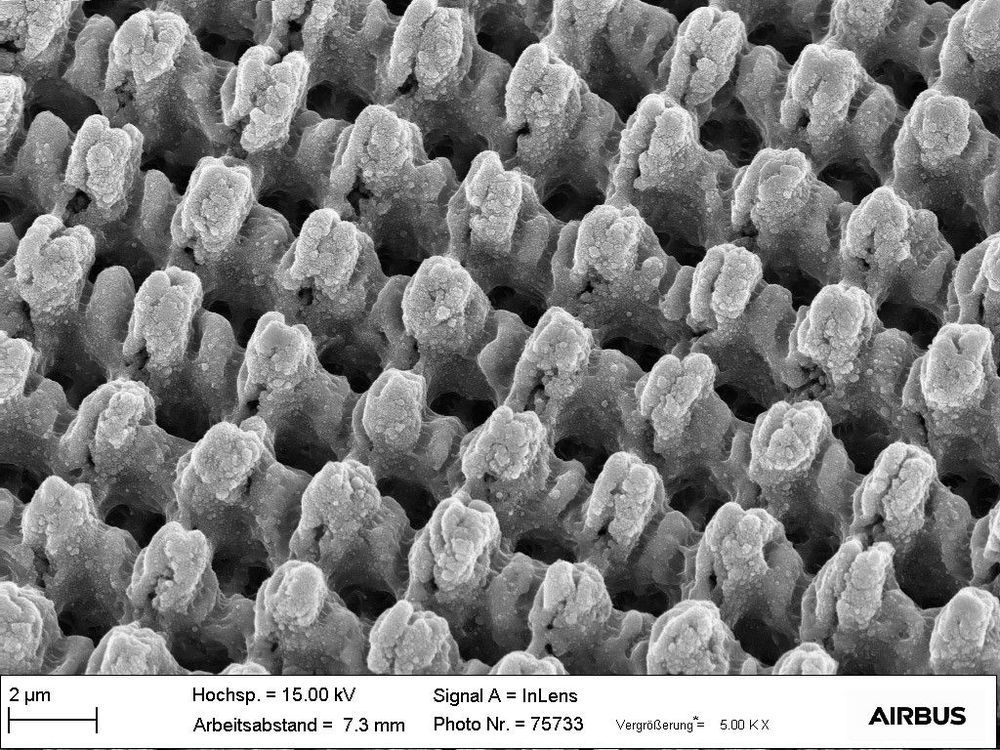
While it’s important to keep the wings of aircraft ice-free, the application of chemical deicers before takeoff can be problematic. German scientists are working on something that could help, in the form of an ice-repelling laser-based treatment for flight surfaces.
As many people will know from firsthand experience, waiting for an airliner to be sprayed with copious amounts of deicer is a hassle, potentially delaying takeoff. What’s more, the chemicals used can be quite expensive, plus they’re typically not very eco-friendly.
In order to allow smaller amounts of deicer to do the same job, some aircraft now incorporate heating elements in key areas of their fuselage, or they use setups that divert hot air from their engines to those same areas. The new system is intended to further minimize the need for deicers, perhaps even making them completely unnecessary.