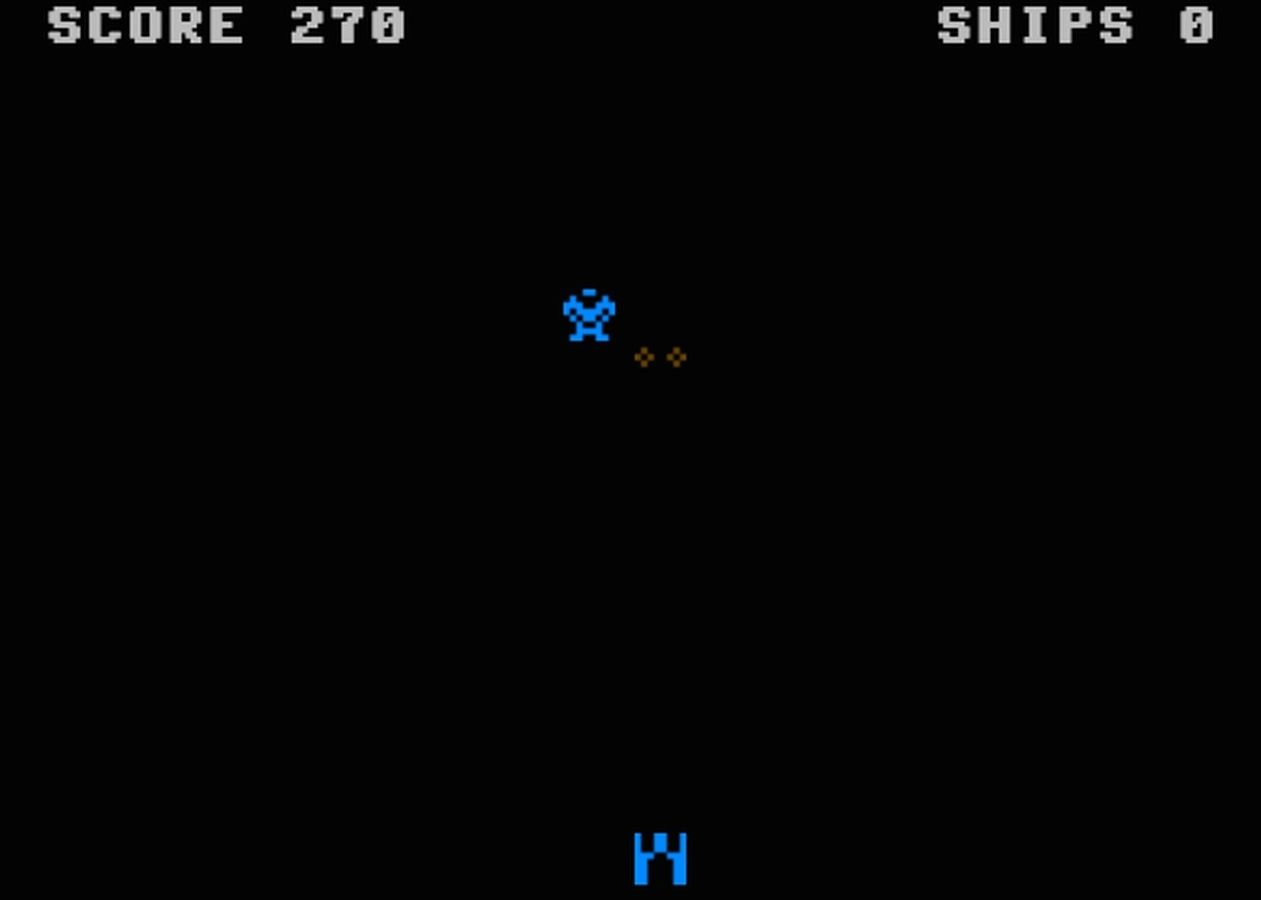
Elon Musk is obsessed with space. At age 30, he founded SpaceX. At age 41, he oversaw the first cargo mission to the International Space Station by a private company. And at age 12, as a kid living in South Africa, he made a space-themed PC game called Blastar. Now, thanks to the power of the internet, you can play that game.
Musk sold the code for Blastar for $500 to the magazine PC and Office Technology, and a reproduction of the page it appeared on was published in Ashlee Vance’s biography Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic Future. From there, Tomas Lloret Llinares — a software engineer at Google — took the code and rebuilt the game to work in HTML5.
Your mission, as the game’s lonely space pilot, is to “destroy [the] alien freighter carrying deadly hydrogen bombs and status beam machines.” Blastar is mostly a mix of Space Invaders and Asteroid, though it’s much more basic. There is never more than two ships on the screen, there are few sound effects, and — like many games of its time — it really has no ending. It’s almost unimpressive; that is, until you remember that it was made by a 12-year-old in 1984.
Read more






 .
.