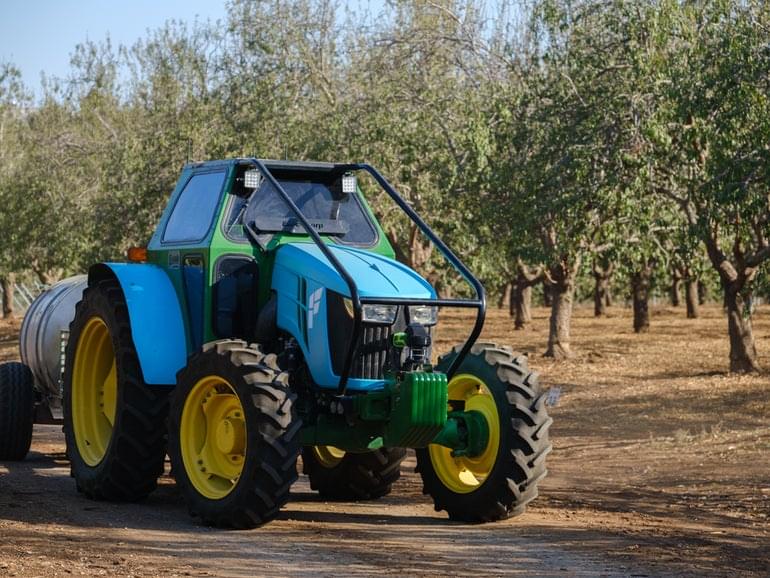
Move over manufacturing; agriculture is fast approaching the lights-out farm.
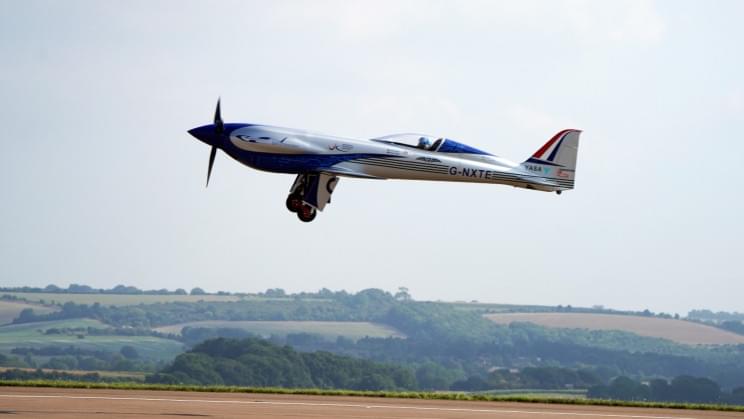



Welcome to a world with electric skies.
Rolls-Royce claims that its all-electric aircraft, called “Spirit of Innovation”, reached a top speed of 387.4 mph (623km/h), making it the fastest electric vehicle in the world, a press statement reveals.
Rolls-Royce believes it has set three new world records, with the top speed for an electric aircraft, the fastest time to climb to 3,000 meters with a time of 202 seconds, and the fastest speed over 9.3 miles (15 kilometers) at 182 m… See more.
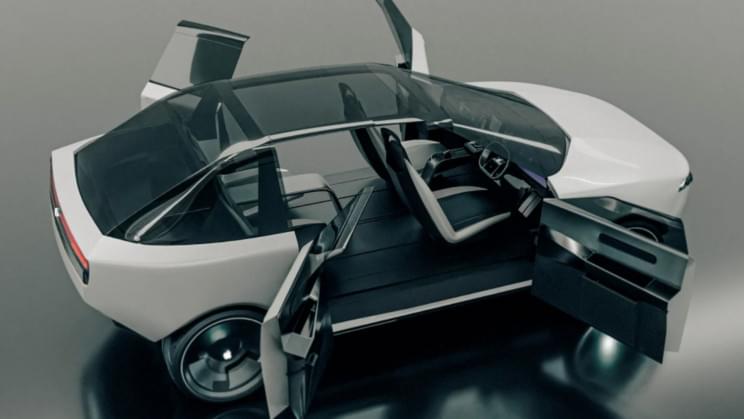

The team has set an internal deadline of 2025.
In a move that could peg it against electric vehicle market leader, Tesla, Apple has begun working aggressively on its fully autonomous electric car, Bloomberg reported. Developing a car has been on Apple’s agenda since 2014 but recent moves within the company signal a push towards making an Apple car a reality.
Given Apple’s history of taking regularly used products and transforming them into their must-have versions using excellent design, it is hardly a surprise. With Steve Jobs at the helm of affairs, Apple made the iPod even when music players were ubiquitous. Then the company revealed the iPhone when Nokia was still selling resistive touch screens as its premium product. And recently, the Apple Watch has become the “it” wearable even though there are other smartwatch options in the market. During a time where electric vehicles are in a surge, it only seems natural that the electric car is Apple’s next target.
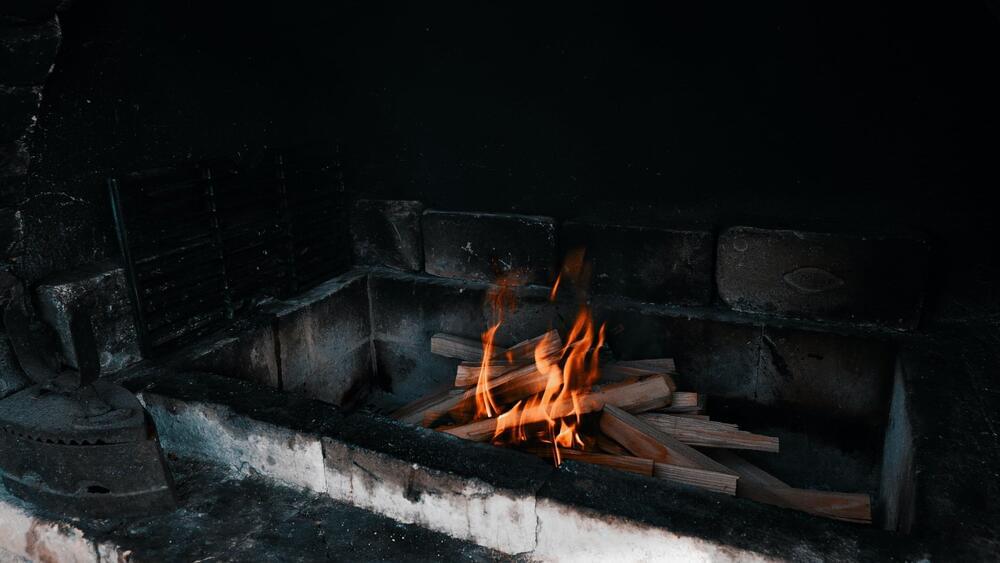

Soot is one of the world’s worst contributors to climate change. Its impact is similar to global methane emissions and is second only to carbon dioxide in its destructive potential. This is because soot particles absorb solar radiation, which heats the surrounding atmosphere, resulting in warmer global temperatures. Soot also causes several other environmental and health problems including making us more susceptible to respiratory viruses.
Soot only persists in the atmosphere for a few weeks, suggesting that if these emissions could be stopped then the air could rapidly clear. This has recently been demonstrated during recent lockdowns, with some major cities reporting clear skies after industrial emissions stopped.
But soot is also part of our future. Soot can be converted into the useful carbon black product through thermal treatment to remove any harmful components. Carbon blacks are critical ingredients in batteries, tires and paint. If these carbons are made small enough they can even be made to fluoresce and have been used for tagging biological molecules, in catalysts and even in solar cells.
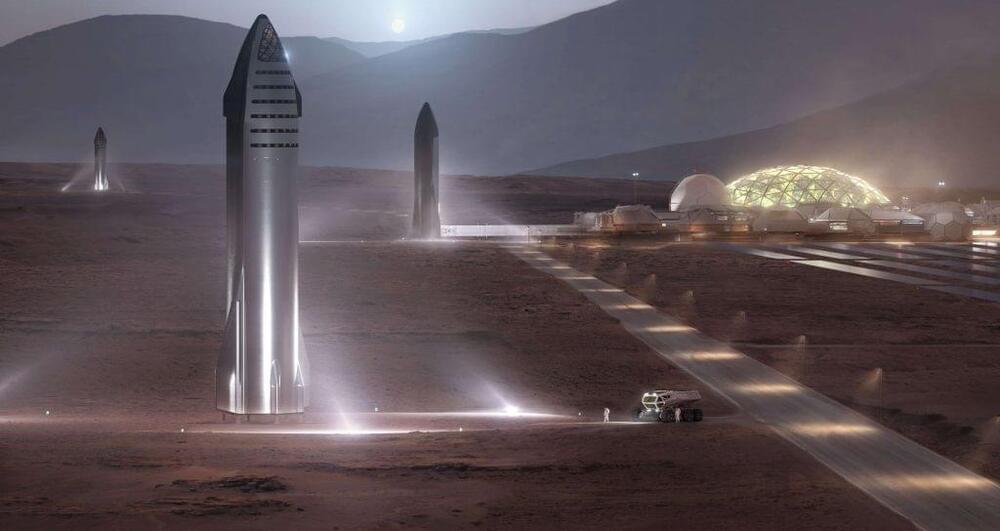

For the first time, SpaceX has teamed up with researchers from NASA and several other US institutions to publicly discuss how it plans to use Starship to build Mars Base Alpha.
Save for a handful of comments spread around the periphery of SpaceX and CEO Elon Musk’s main focus, Starship itself, the company and its executives have almost never specifically discussed how the next-generation fully-reusable rocket will be used to create a permanent human presence on Mars. For the most part, that clear focus on near-term hurdles is hard to fault. Half a century of mostly theoretical analysis has made it abundantly clear that a permanent and sustainable extraterrestrial human outpost is impossible without a radical reduction in the cost of access to space. For decades, NASA has studied and studied and studied slight variations of a plan that would cost hundreds of billions of dollars to send a few astronauts to Mars for a few months at a time.
Put simply, without a revolution in space transport, even a temporary presence on Mars where inhabitants are mostly dependent on imported goods is infeasible unless Mars exploration is made a national or international priority on the order of tens of billions of dollars per year. Over the 80–90 years that spaceflight has been seriously pondered, dozens of groups and papers and studies and space agencies have imagined what that revolution might look like and SpaceX is not unique for proposing a solution to that longstanding problem. However, SpaceX is the first of that long list of contenders to propose a solution and both invest significant resources and put hammer to metal in an attempt to make that vision real.
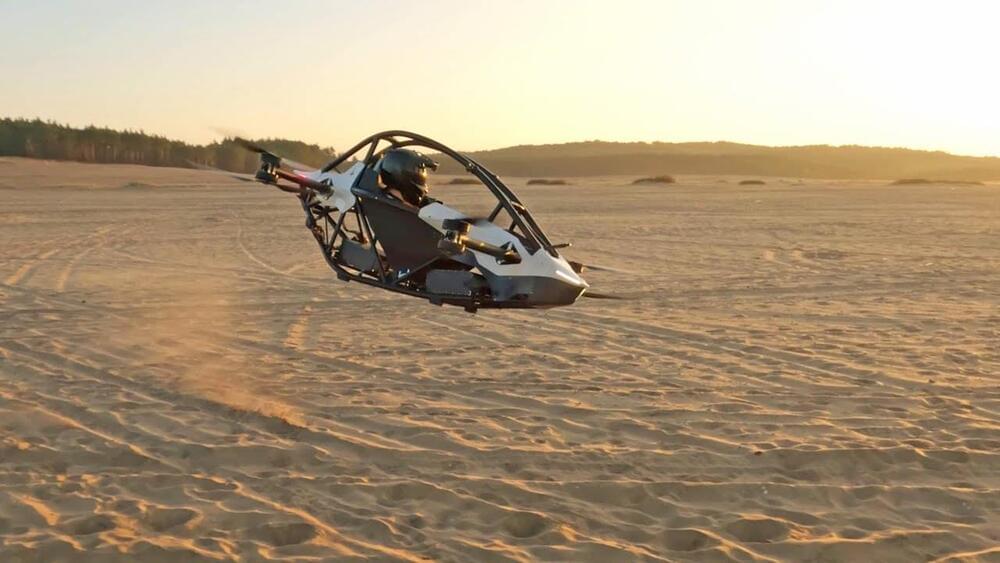

On October 21, Sweden’s Jetson Aero launched the Jetson One, a single-seat flying car with 20-minute flight times and a top speed of about 63 mph. It has already sold all 12 of the electric vehicles in its first production run (to be delivered in fall 2022), and it’s now taking orders for 2023.
The vehicles will be delivered about 50% assembled, and customers must finish putting them together themselves.
More than 150 companies are developing flying cars. Here’s why they’re aren’t yet off the ground and darting across city skies.


Rumors that Tesla is indeed making a smartphone were bolstered after the world-famous design studio ADR released concept images (in a video). This made people wonder: Is Tesla going to go after the iPhone — or simply create an entirely new market segment, such as a true-to-form satellite phone that works where traditional WiFi or 5G services are absent, and able to mine cryptocurrencies anywhere, including on the planet Mars?While speculations abound, there are numerous unanswered questions, such as: how much would it retail for? Does it have a sim card? What’s the monthly charge for using Starlink? Can I buy one, without first buying a Tesla EV? Its release date is a closely-guarded secret. A Starlink antenna is being taken out of the box. Tech publications have leaked images of the new device supposedly out of the EV maker, including some details of what it can do.
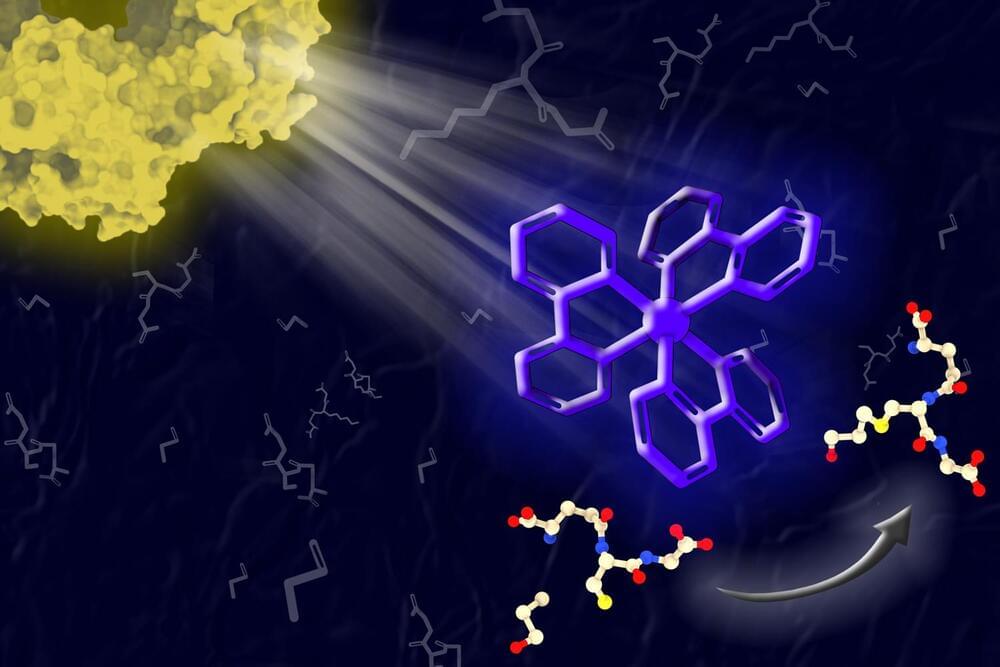
The new type of catalyst, known as a biohybrid photocatalyst, contains a light-harvesting protein that absorbs light and transfers the energy to a metal-containing catalyst. This catalyst then uses the energy to perform reactions that could be useful for synthesizing pharmaceuticals or converting waste products into biofuels or other useful compounds.
“By replacing harmful conditions and reagents with light, photocatalysis can make pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and fuel synthesis more efficient and environmentally compatible,” says Gabriela Schlau-Cohen, an associate professor of chemistry at MIT and the senior author of the new study.
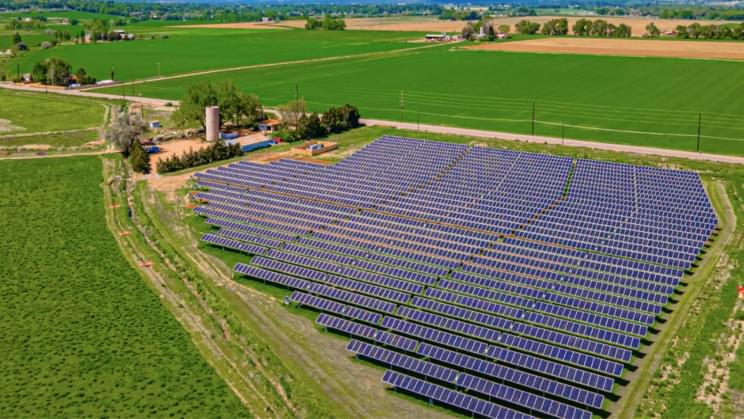

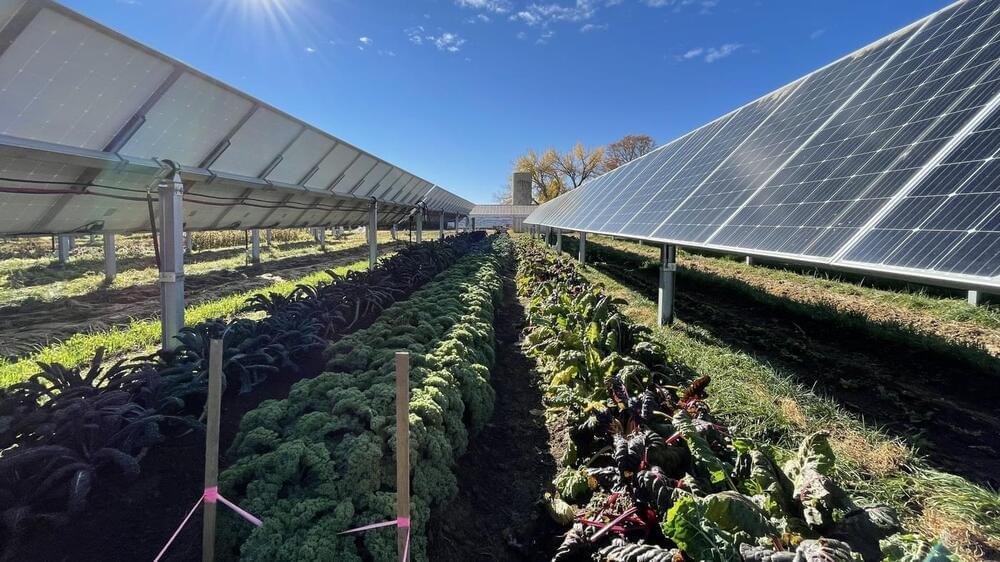
This solar farm in Colorado thinks so.
The farming industry is using way too much energy both for its own and the Earth’s sake. To put it in numbers, agriculture uses approximately 21 percent of food production energy, which equals 2.2 quadrillions of kilojoules of energy each year. What’s more, about 60 percent of the energy used in agriculture goes toward gasoline, diesel, electricity, and natural gas.
That’s where agrivoltaics come in. A system where solar panels are in… See more.