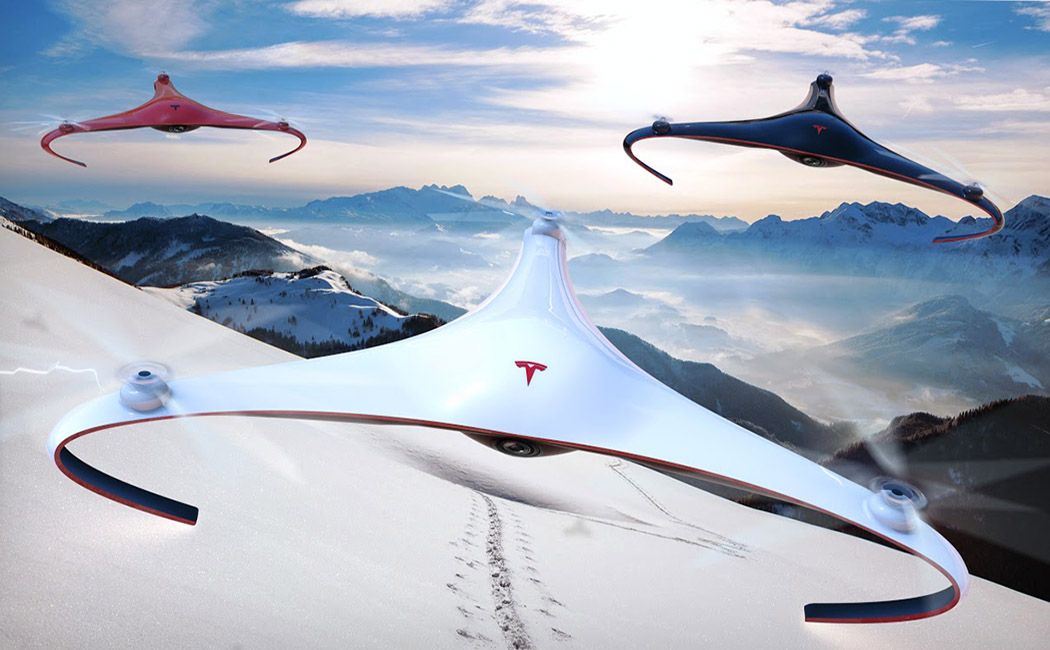
Did you know that Nikola Tesla patented a drone before there were drones?! Over 100 years ago he called these imagined vessels as being used to carry packages, establish communication with inaccessible regions, and “many other scientific purposes.” Drones are basically in the brand’s DNA, so it’s no wonder that there is so much hype around what a Tesla drone might be like! In this concept, called Aurora, Tesla’s electric motor technology is applied to a tricopter design to facilitate long-range, extended-time camera capability.
Operating either autonomously or controlled manually, it’s ideal for reconnaissance, checking on out-of-reach machinery, routine structure inspections, or simply for capturing vivid photography and video for fun. The three rotor design allows for larger propellers. This results in less required rotations and less energy to fly, making it more efficient with up to 35% more battery life. Because of the size of the propellers, it also has greater acceleration and better maneuverability. As far as looks go, it’s carefully considered and beautifully executed sculpting that’s probably the e-drone concept most closely in line with the Tesla aesthetic.
Designer: Alberto Esses