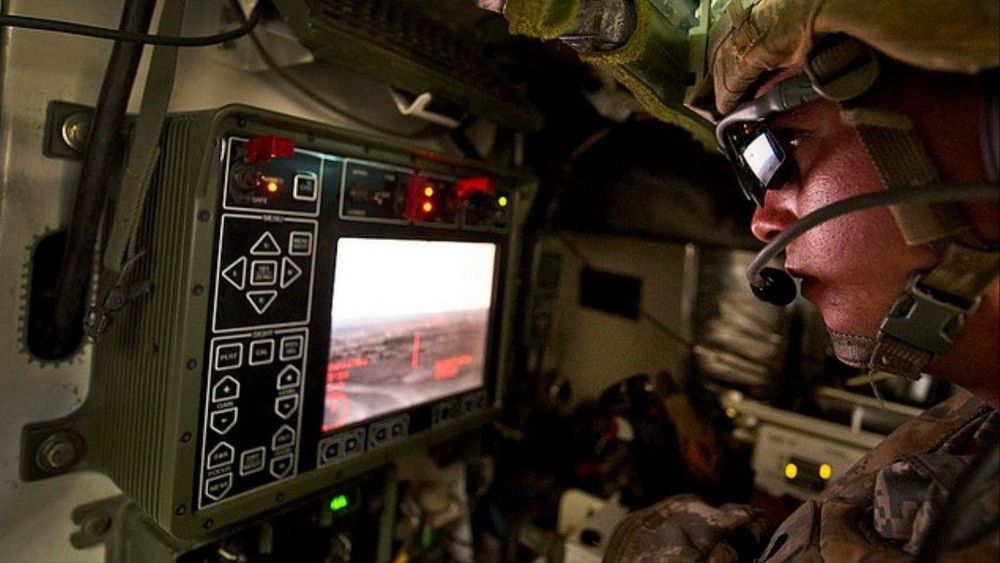
China is the world leader in facial recognition technology. But is the state using it to violate the human rights of its citizens?
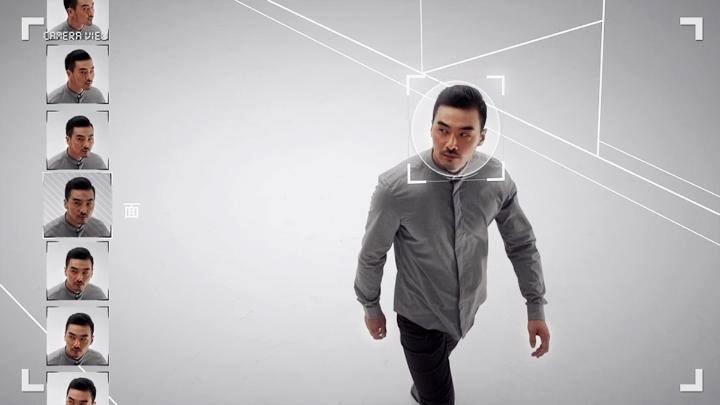


China is the world leader in facial recognition technology. But is the state using it to violate the human rights of its citizens?


Early this morning, I was asked this question at Quora. It’s a pretty basic request of network administrators, including parents, schools and anyone who administers a public, sensitive or legally exposed WiFi hot spot.
Is there a quick and easy way to view, log, or otherwise monitor the web sites visited by people on your home or office network?
Yes. It’s free and and it is pretty easy to do.
It gets a bit trickier, if the individual on your network is using a VPN service that they have configured on their device.[1] A VPN does not stop you from logging their browsing, but all of their activity will point to the VPN address instead of the site that they are actually visiting. In that case, there is another way to monitor their activity. See note #1, below.
Before getting into this, I should mention that I believe that using covert methods to monitor a family member’s online activity is a terrible method of parenting. In my opinion, there are better ways to deal with the issue—parenting techniques that don’t undermine trust as they deal with safety.

I can think of at least three methods for logging the websites that people on your network visit. In the explanation below, we will focus on #2. For more information, dig into the notes at the bottom of this answer.
You can either…
In the remainder of this quick tutorial, we focus on method #2..
Once you configure your router to use the two DNS servers at OpenDNS.com, create a free account on their web site. Then, enable the logging feature. It not only shows you visited domains, it maps them into actual domain names and subdomains—making it easy to search, sort or analyze traffic.
You can download a spreadsheets and sort by number of visits or by the domains visited. Logs are maintained for only two weeks. So, if you wish to maintain a history, you will need to visit OpenDNS and download them regularly. (Check their user forum. Someone has created a safe, single-line DOS command that downloads these activity logs to your PC).
[1] VPN, Onion Routing and Encryption
If an individual in your home or office is using a Virtual Private Network [VPN], they are effectively covering their tracks with method #3, above. You can see their connection to the VPN service, but that service is either trusted to destroy logs of visited web sites, or anonymize traffic, by routing it through a chain of users that have no way to back-trace and identify the requester’s address.
Since their traffic originates on your network, there are other things you can do to monitor their activities. For example, if they are not using end-to-end encryption, you can use method #3 yourself, to route data in and out through your own PC or service.
[2] Logging the IP address or domain of visited web sites is not a feature of all routers. I have three recent model routers — and only one of them has a feature to log traffic in and out of the network.
[3] OpenDNS cannot discriminate the individual device in your home or office that has accessed websites that it logs. The logs include the traffic for all HTTP access that originates through your internet service subscription.
But some remarkable feature of OpenDNS (other than it being completely free):
a) It speeds up your overall internet experience noticeably! Like Google’s free DNS service, it is more robust and more redundant than the default DNS settings recommended by your internet service provider.
b) It maps every IP address into a domain name. So when you log in to check your logs and statistics, you don’t need to figure what the numbers mean. You view a list that makes sense. You can even search for certain words or web sites.
c) It permits you to block websites based on a very rich set of 100 criteria, including violence, adult content, hate speech, etc.
d) It offers graphs of your network access including overall volume. An example is shown here:
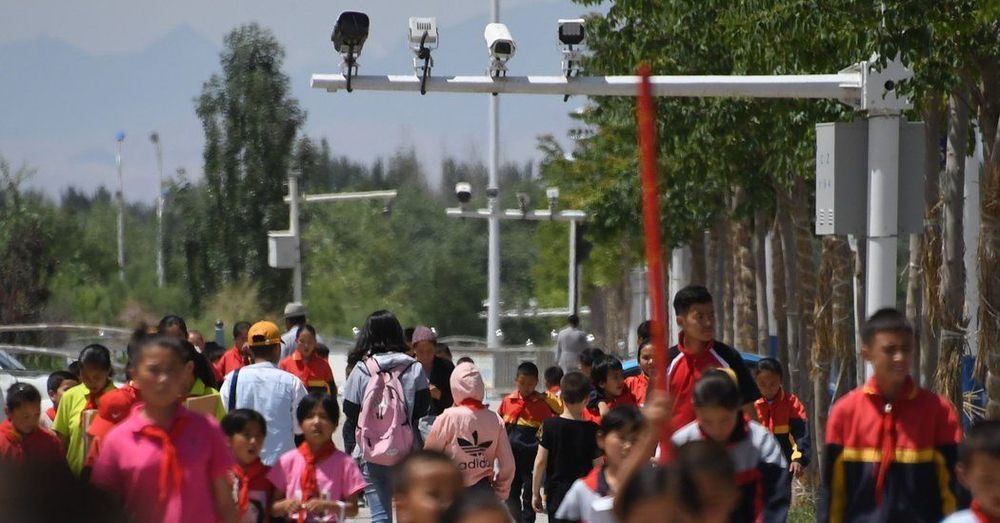

BEIJING — China has turned its western region of Xinjiang into a police state with few modern parallels, employing a combination of high-tech surveillance and enormous manpower to monitor and subdue the area’s predominantly Muslim ethnic minorities.
Now, the digital dragnet is expanding beyond Xinjiang’s residents, ensnaring tourists, traders and other visitors — and digging deep into their smartphones.
A team of journalists from The New York Times and other publications examined a policing app used in the region, getting a rare look inside the intrusive technologies that China is deploying in the name of quelling Islamic radicalism and strengthening Communist Party rule in its Far West. The use of the app has not been previously reported.

Betty Lim
Is a massive, planetary-wide, space surveillance system currently being constructed that aims to monitor you all the way down to your DNA. Officially, the Space Fence is, according to Wikipedia, a 2nd generation space surveillance system being built (started in 2014) by the US Air Force and Lockheed Martin to track artificial satellites and space debris. Its budget is US$1.594 billion, it’s expected to be operational in 2019 and the Space Fence facility will be located in the Marshall Islands along with an option for another radar site in Western Australia. The Space Fence is a resurrection of a program started by Reagan in the 1980s called SDI (Strategic Defense Initiative), commonly known by its nickname “Star Wars.” However, like many exotic weapons of the New World Order, it has a cover purpose and a real purpose. This article exposes the grander implications of the Space Fence – and how it connects to other technology that could be used to enslave you.
What is the Space Fence?
Although the USAF and Lockheed Martin tell us that the purpose of the Space Fence is to detect, track and catalog space debris, we must acknowledge that the MIC (Military Intelligence Complex) is at the helm of the New World Order and is routinely engaged in psychological operations against the rest of the population. The Space Fence is the answer to the prayers of a control-freak conspiratorial class. It will have the capacity to surveil everything on Earth. Like Skynet in the fictional Terminator films, it could become surveillance beyond comprehension. How? The Space Fence is designed to operate in LEO (Low Earth Orbit). It is designed to be one big interconnected machine, run by AI and joined to current (weaponized) technology by interacting with cell phone towers, Gwen Towers, Nexrad Towers, metal particulates and more to create a giant wireless network that manipulates us through the ionization of our atmosphere.
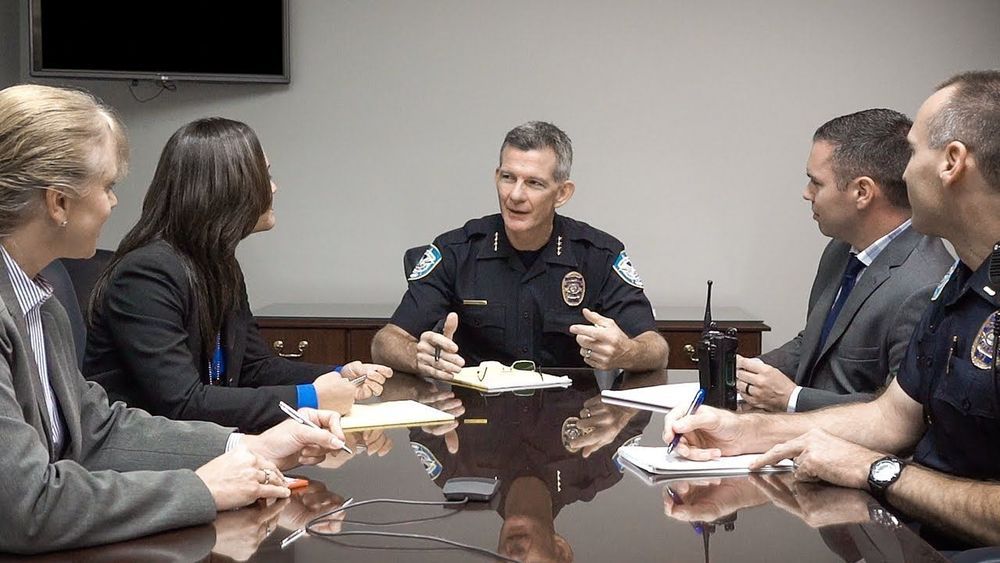

At some convenience stores, an A.I. system may bar the door if you look like the suspected criminals in its database, or if you’re wearing a mask. That’s part of the growing use of facial recognition and video analytics, a…

China isn’t the only country with a draconian “social credit score” system — there’s one quite a bit like it operating in the U.S. Except that it’s being run by American businesses, not the government.
There’s plenty of evidence that retailers have been using a technique called “surveillance scoring” for decades in which consumers are given a secret score by an algorithm to give them a different price — but for the same goods and services.
But the practice might be illegal after all: a California nonprofit called Consumer Education Foundation (CEF) filed a petition yesterday asking for the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to look into the shady practice.
New 3D-printed materials are going to space thanks to a recently funded partnership between Israel’s NanoDimension and Florida’s Harris Corp.
The companies plan to create new materials to reduce the manufacturing of small satellites, an exceedingly popular market right now for applications ranging from weather observations to remote surveillance.
They aim to fly their materials on an external platform of the International Space Station for a year. The goal is to better understand how 3D-printed components (such as circuits and materials) withstand the space environment, which includes extreme temperature swings and high radiation. The launch date of the project was not disclosed.

