I had to post this bigsmile couldn’t resist.



The brand new space opera novel Lightless is a fast-paced, gripping read, and like all good science fiction, explores the human side of cutting-edge scientific concepts. We talked to debut author C.A. Higgins about using real physics in her story.
In Lightless, a prototype spaceship on its maiden voyage on behalf of a totalitarian regime is infiltrated by escaped terrorists. And it’s up to Althea, a socially awkward computer scientist who prefers the company of the Ananke’s disturbingly sentient electronic system to that of her crewmates, to save the day as her well-ordered world begins to unravel.
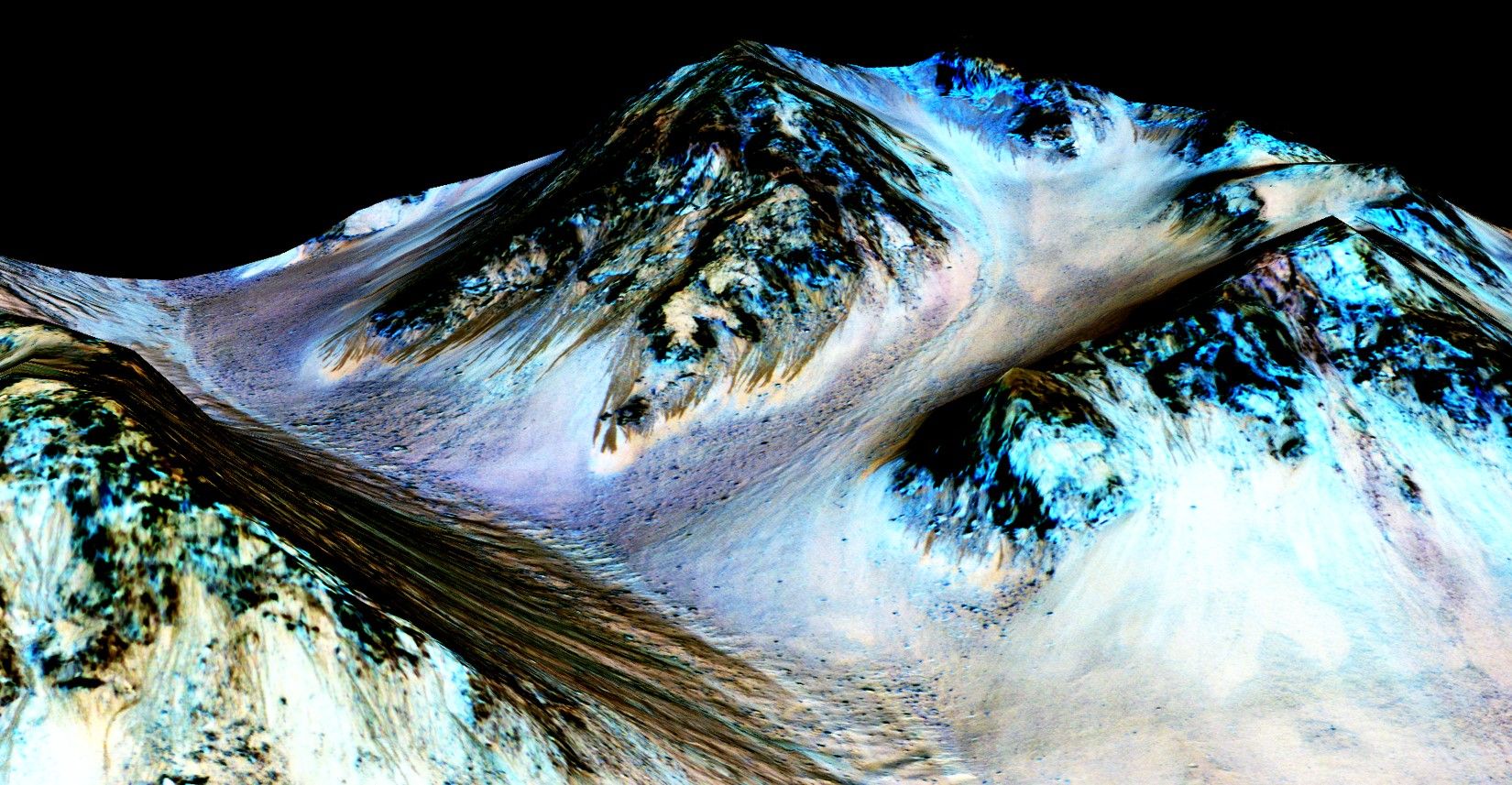

New findings from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) provide the strongest evidence yet that liquid water flows intermittently on present-day Mars.
Using an imaging spectrometer on MRO, researchers detected signatures of hydrated minerals on slopes where mysterious streaks are seen on the Red Planet. These darkish streaks appear to ebb and flow over time. They darken and appear to flow down steep slopes during warm seasons, and then fade in cooler seasons. They appear in several locations on Mars when temperatures are above minus 10 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 23 Celsius), and disappear at colder times.
“Our quest on Mars has been to ‘follow the water,’ in our search for life in the universe, and now we have convincing science that validates what we’ve long suspected,” said John Grunsfeld, astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. “This is a significant development, as it appears to confirm that water — albeit briny — is flowing today on the surface of Mars.”
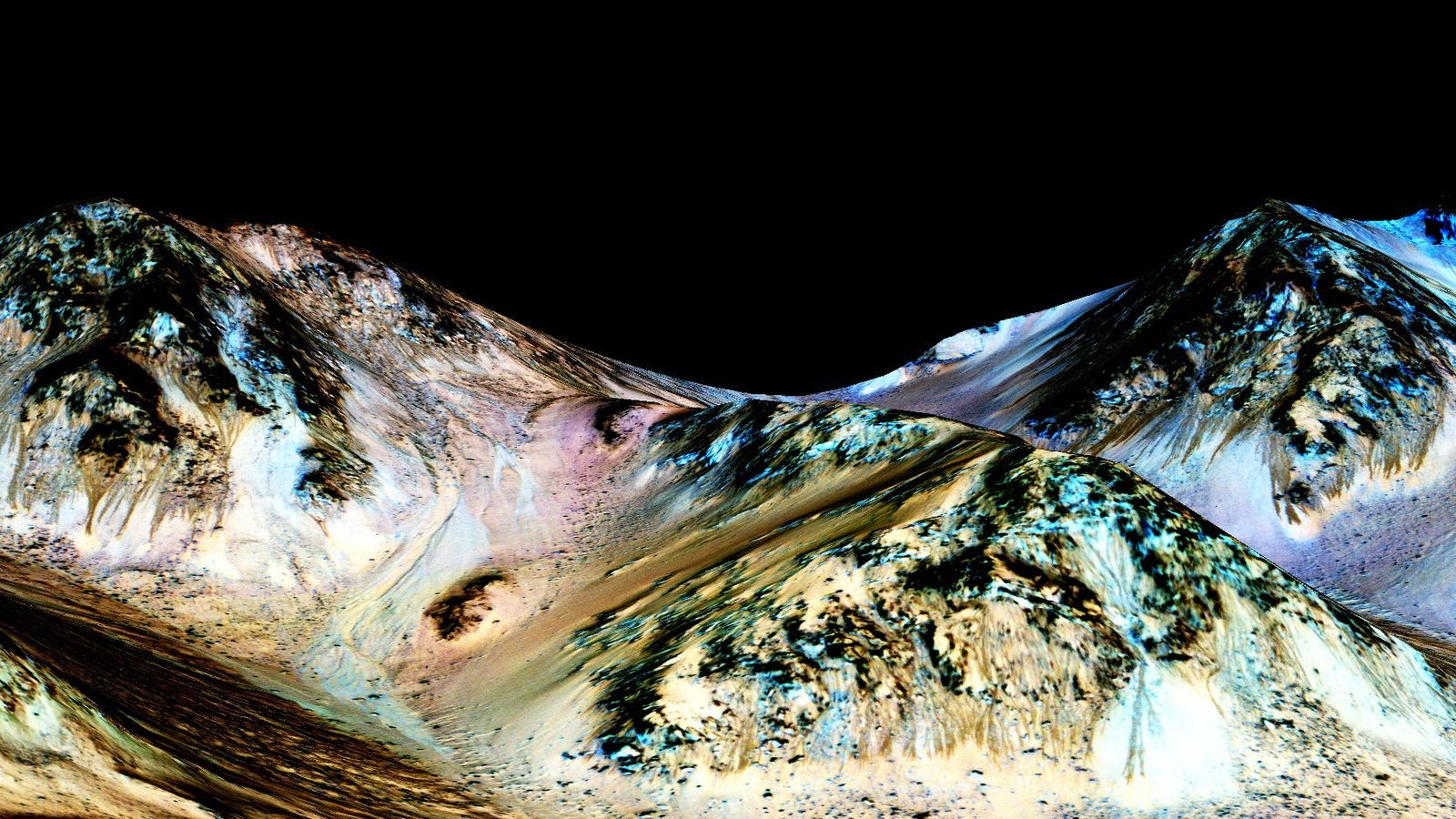

Liquid water exists on the surface of Mars during the planet’s warmer seasons, according to new research published in Nature Geosciences . This revelation comes from new spectral data gathered by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), a spacecraft that studies the planet from orbit. The orbiter analyzed the chemistry of weird dark streaks that have been known to appear and disappear seasonally on the Martian surface. The analysis confirms that these streaks are formed by briny — or salty — water flowing downhill on Mars.
NASA has advertised these findings as the solution to a major Mars mystery: does the Red Planet truly have liquid water on its surface? Researchers have known that water exists in ice form on Mars, but it’s never been confirmed if water can remain in a liquid state. The space agency is claiming that we now have that answer.
This isn’t the first study to suggest liquid water is present in some form on Mars. Scientists have theorized for years that Mars was once home to a large ocean more than 4 billion years ago. And recent findings from the Mars Curiosity rover suggest that liquid water exists just underneath the Martian surface. The discovery of water on Mars has almost become a joke among planetary scientists. Alfred McEwen, a planetary geologist at Planetary Image Research Laboratory who also worked on this research, wrote in Scientific American that the studies have become extremely commonplace: “Congratulations — you’ve discovered water on Mars for the 1,000th time!” he joked.

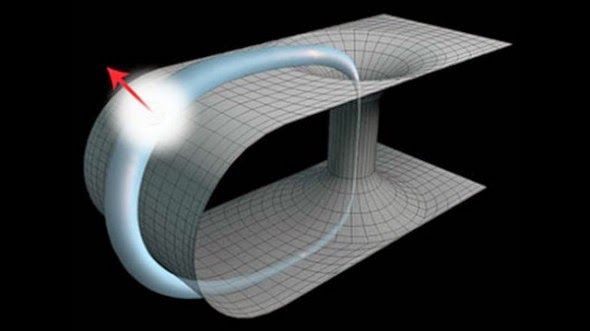
According to scientists photons can travel through time. They already have simulated directing quantum light particles to the past for the first time in the history. University of Queensland scientists learned that a simulation of two wormhole-travelling photons might interrelate; signifying hopping through time is conceivable at smallest scales. Their study might help to comprehend how time-travel could be conceivable in the quantum realm. PhD student Martin Ringbauer spoke to The Speaker: “For the first, ‘photon one’ would travel through a wormhole into the past and interact with its older version. In the second, ‘photon two’ travels through normal space-time but interacts with a photon that is stuck in a time-travelling loop through a wormhole, known as a closed timelike curve (CTC).”
Tim Ralph, UQ Physics Professor, said: “We used single photons to do this, but the time-travel was simulated by using a second photon to play the part of the past incarnation of the time travelling photon.”


Is NASA about to confirm flowing seasonal water on modern-day Mars?