Terraforming of Venus.



Figures.
New calculation shows that universal expansion appears to be 8 percent greater than expected, which isn’t good news.

The Space Solar Power Initiative (SSPI), a collaboration between Caltech and Northrup Grumman, has developed a system of lightweight solar power tiles which can convert solar energy to radio waves and can be placed in orbit to beam power to an energy-thirsty Earth.
One of the greatest challenges facing the 21st Century is the issue of power—how to generate enough of it, how to manufacture it cheaply and with the least amount of harmful side-effects, and how to get it to users.
The solutions will have to be very creative—rather like what the Space Solar Power Initiative (SSPI), a partnership between Caltech and Northrup Grumman, has devised.
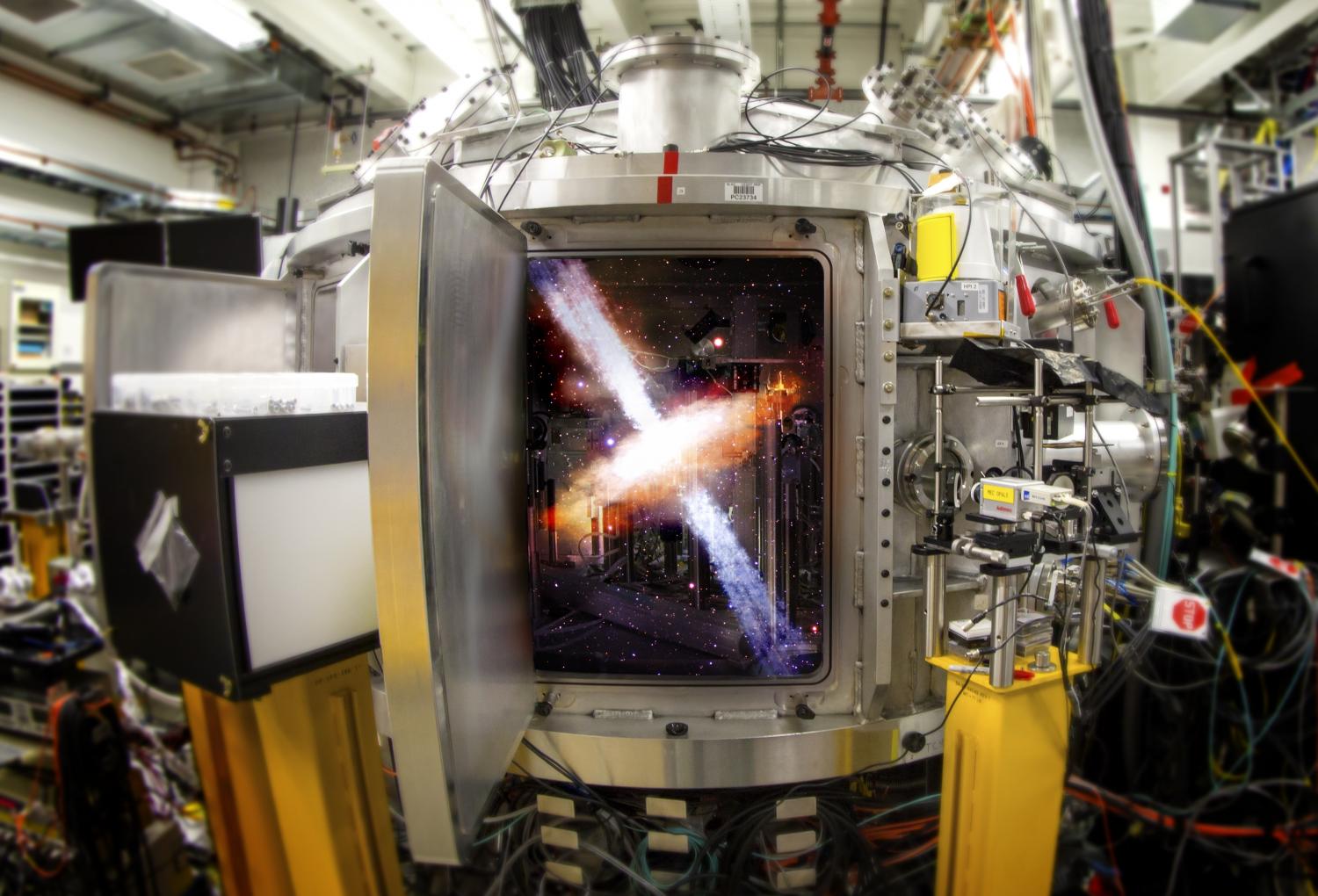
Conditions in the vast universe can be quite extreme: Violent collisions scar the surfaces of planets. Nuclear reactions in bright stars generate tremendous amounts of energy. Gigantic explosions catapult matter far out into space. But how exactly do processes like these unfold? What do they tell us about the universe? And could their power be harnessed for the benefit of humankind?
To find out, researchers from the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory perform sophisticated experiments and computer simulations that recreate violent cosmic conditions on a small scale in the lab.
“The field of laboratory astrophysics is growing very rapidly, fueled by a number of technological breakthroughs,” says Siegfried Glenzer, head of SLAC’s High Energy Density Science Division. “We now have high-power lasers to create extreme states of matter, cutting-edge X-ray sources to analyze these states at the atomic level, and high-performance supercomputers to run complex simulations that guide and help explain our experiments. With its outstanding capabilities in these areas, SLAC is a particularly fertile ground for this type of research.”




Hmm… That would explain Alzheimer disease — It’d be like some sort of unabashedly evil version of a smart phone data caps!
Or not.
wink
NEW YORK — Is the universe just an enormous, fantastically complex simulation? If so, how could we find out, and what would that knowledge mean for humanity?
These were the big questions that a group of scientists, as well as one philosopher, tackled on April 5 during the 17th annual Isaac Asimov Debate here at the American Museum of Natural History. The event honors Asimov, the visionary science-fiction writer, by inviting experts in diverse fields to discuss pressing questions on the scientific frontiers.
Neil deGrasse Tyson, director of the museum’s Hayden Planetarium and host of this year’s event, invited five intellectuals to the stage to share their unique perspectives on the problem: Zohreh Davoudi, a nuclear physicist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT); Max Tegmark, a cosmologist at MIT whose recent book probes the universe as mathematics; James Gates, a physicist at the University of Maryland who discovered strange, error-correcting codes deep in the equations of supersymmetry; Lisa Randall, a physicist at Harvard University who thinks the simulation question is more or less irrelevant; and David Chalmers, a philosopher at New York University who regularly questions the reality that conscious minds perceive. [7 Surprising Things About the Universe].

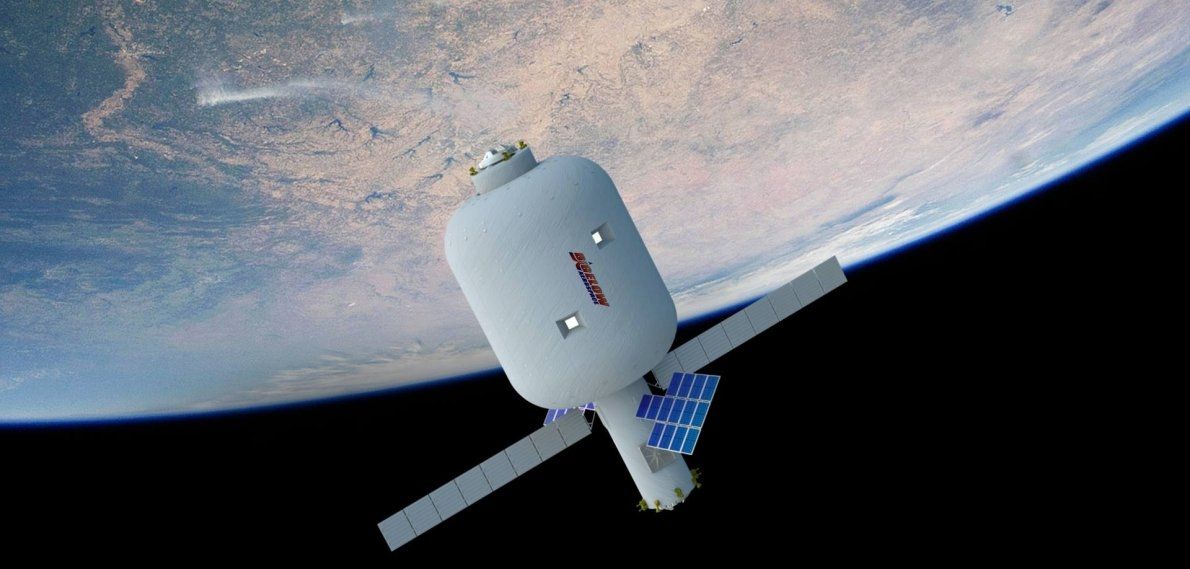
Colorado Springs, Colo., (April 11, 2016) – Bigelow Aerospace (BA) and United Launch Alliance (ULA) announced they are partnering to develop and deploy habitable volumes in Low Earth orbit (LEO). The volumes will be based on the Bigelow Aerospace B330 expandable module with the initial launch to orbit in 2020 on ULA’s Atlas V 552 configuration launch vehicle.
The B330 will have 330 cubic meters (12,000 cu ft) of internal space. The craft will support zero-gravity research including scientific missions and manufacturing processes. Beyond its industrial and scientific purposes, however, it has potential as a destination for space tourism and a craft for missions destined for the Moon and Mars.
“We are exploring options for the location of the initial B330 including discussions with NASA on the possibility of attaching it to the International Space Station (ISS),” said Robert Bigelow, founder and president of Bigelow Aerospace. “In that configuration, the B330 will enlarge the station’s volume by 30% and function as a multipurpose testbed in support of NASA’s exploration goals as well as provide significant commercial opportunities. The working name for this module is XBASE or Expandable Bigelow Advanced Station Enhancement.”