WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – A new highly efficient power amplifier for electronics could help make possible next-generation cell phones, low-cost collision-avoidance radar for cars and lightweight microsatellites for communications.
Fifth-generation, or 5G, mobile devices expected around 2019 will require improved power amplifiers operating at very high frequencies. The new phones will be designed to download and transmit data and videos faster than today’s phones, provide better coverage, consume less power and meet the needs of an emerging “Internet of things” in which everyday objects have network connectivity, allowing them to send and receive data.
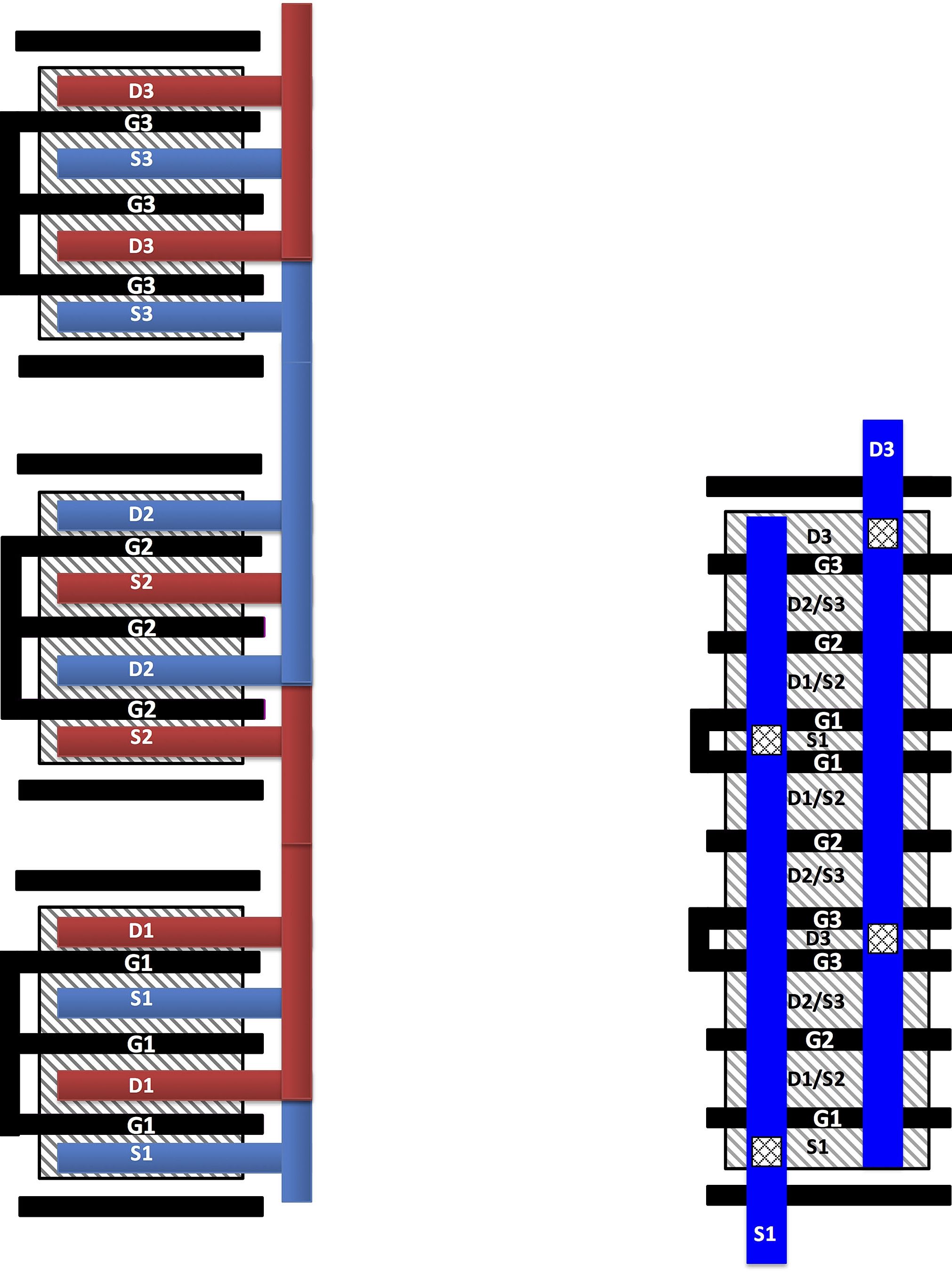
Power amplifiers are needed to transmit signals. Because today’s cell phone amplifiers are made of gallium arsenide, they cannot be integrated into the phone’s silicon-based technology, called complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS). The new amplifier design is CMOS-based, meaning it could allow researchers to integrate the power amplifier with the phone’s electronic chip, reducing manufacturing costs and power consumption while boosting performance.
Read more