Scientists literally pulled this out of thin air.
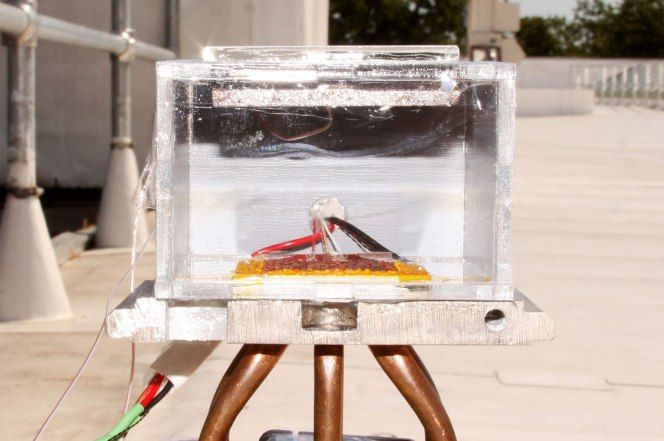
Engineers at MIT and the University of California Berkeley have designed a system, powered by sunlight, that can turn air into liters of drinkable water.
This box has the potential to help drought-stricken communities, desert explorers or — someday — astronauts traveling to dry, dusty planets. The report was a href=” http://science.sciencemag.org/content/early/2017/04/12/science.aam8743” target=”_blank”