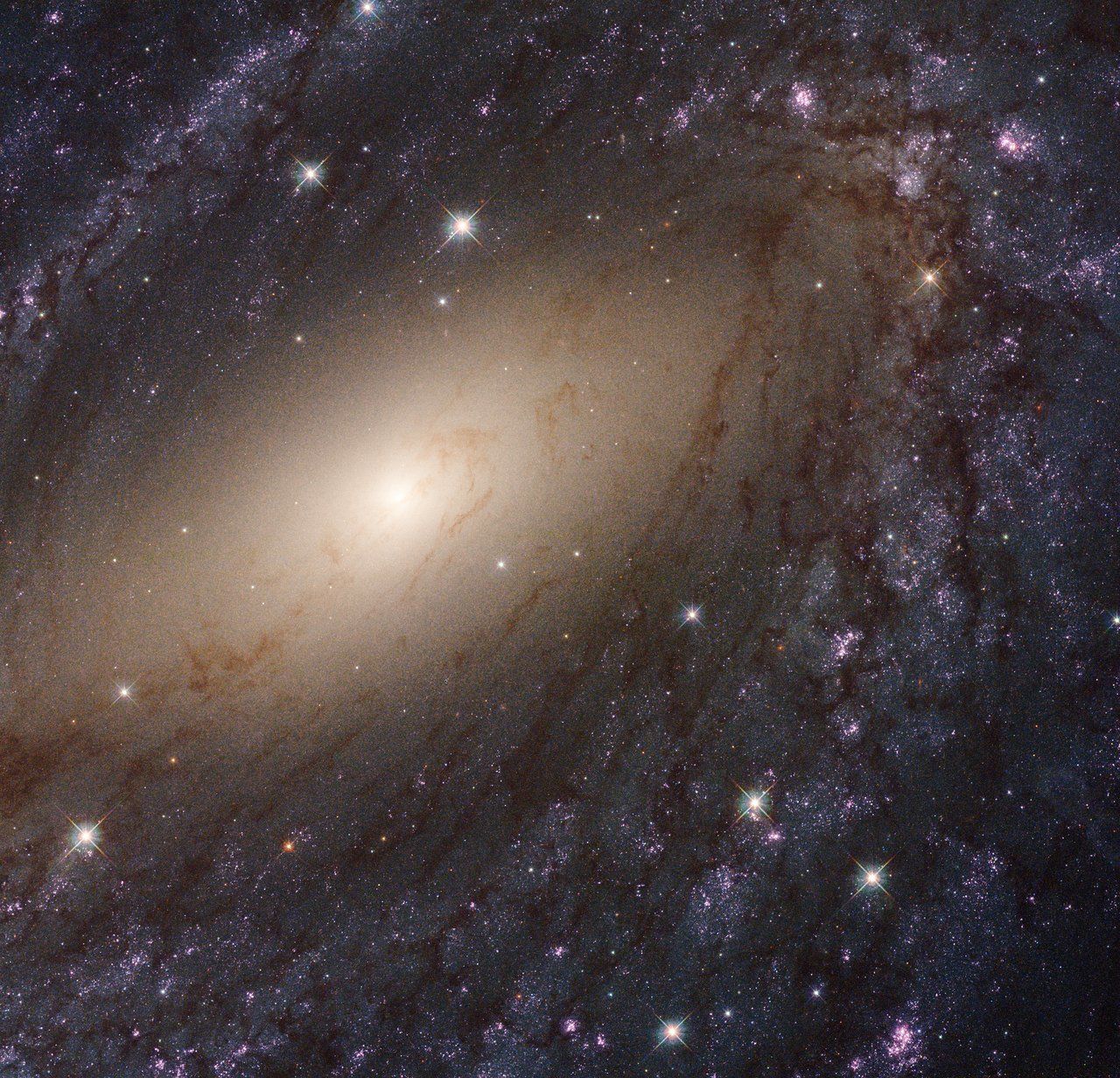
Capitalizing on the unparalleled sharpness and spectral range of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, an international team of astronomers is releasing the most comprehensive, high-resolution ultraviolet-light survey of nearby star-forming galaxies.
The researchers combined new Hubble observations with archival Hubble images for 50 star-forming spiral and dwarf galaxies in the local universe, offering a large and extensive resource for understanding the complexities of star formation and galaxy evolution. The project, called the Legacy ExtraGalactic UV Survey (LEGUS), has amassed star catalogs for each of the LEGUS galaxies and cluster catalogs for 30 of the galaxies, as well as images of the galaxies themselves. The data provide detailed information on young, massive stars and star clusters, and how their environment affects their development.
“There has never before been a star cluster and a stellar catalog that included observations in ultraviolet light,” explained survey leader Daniela Calzetti of the University of Massachusetts, Amherst. “Ultraviolet light is a major tracer of the youngest and hottest star populations, which astronomers need to derive the ages of stars and get a complete stellar history. The synergy of the two catalogs combined offers an unprecedented potential for understanding star formation.”