Blockchain is used both by NASA and startups hoping to democratize space.
Analysis.


This article is part of a series about how OS Fund (OSF) companies are radically redefining our future by rewriting the operating systems of life. Or as we prefer to think about it: Step 1: Put a dent into the universe. And Step 2: Rewrite the universe. You can see the full OSF collection here and read more about Building a Biological Immune System.
In contemplating the future, I love imagining how our daily lives today will be thought of in the future. What appears sci-fi to us today but will be “normal” 50 years from now? What inefficient and boneheaded things do we do today that future generations will look back and laugh at?
Seeing beyond what’s possible is a rare skill. Being able to design and build beyond what’s possible is even more rare. Put together, this is the unique set of skills and abilities that OSF founders all have in common. Most importantly, they’ve chosen to focus their abilities to tackling the biggest problems humanity faces.

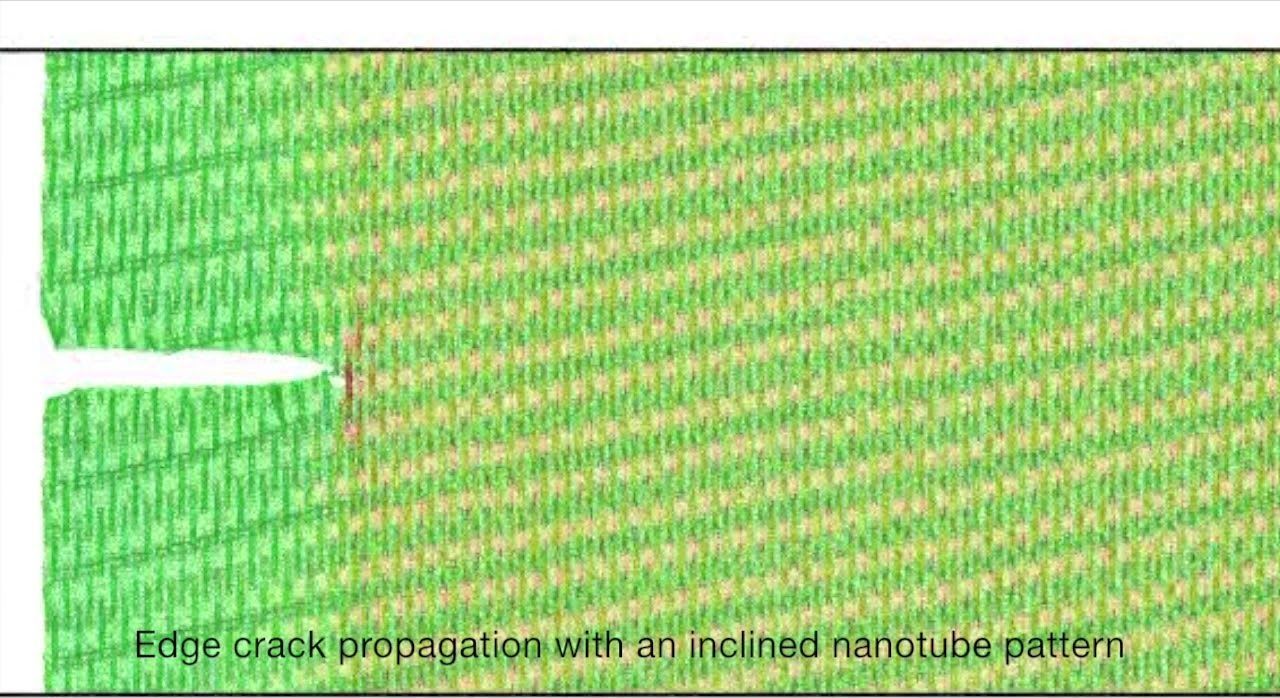
You may know graphene as a pseudo-legendary substance that could potentially revolutionize science and space travel and all sorts of things. If you don’t, you should get educated is pretty ridiculous. Simply made from carbon arranged into perfect one atom thing sheets makes the material one of the strongest ever observed. And, now, researchers at Rice University have found that so-called “rebar” graphene is dramatically tougher.
Graphene is much stronger than steel. In fact, an elephant could stand on a pencil and that pressure couldn’t break through a thin sheet of the material. But, because it is arranged in sheets, it can still be ripped if damaged from the right angle. But the researchers figured that reinforcing the structure, as we do with steel bars in concrete structures, l could help prevent damage.
The new research, published in the ACS Nano, a journal run by the American Chemical Society, Rice materials scientist Jun Lou and lead author Emily Hacopian examined the properties of rebar graphene under stress. Cracked and tears in the structure that otherwise would have spread across the sheet are stopped by the reinforcement while also staying stretchy and pliable.


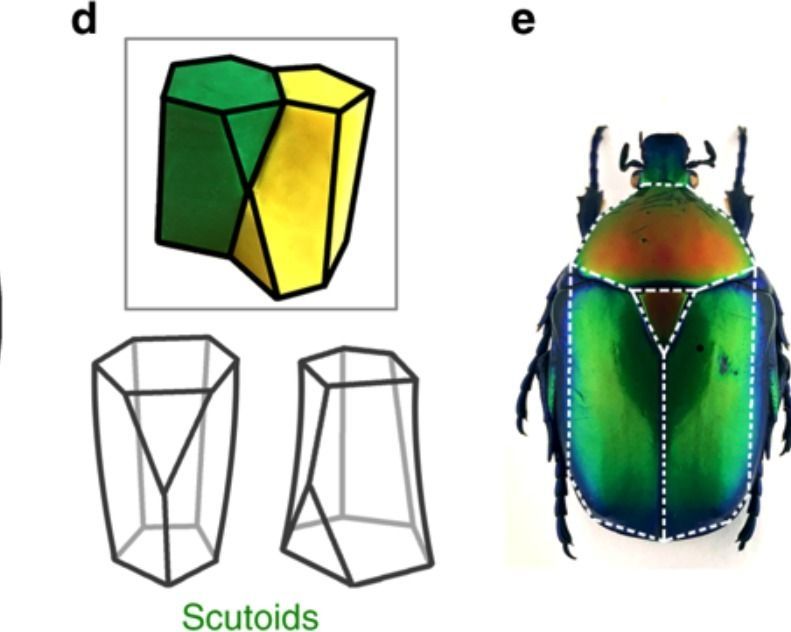
Science news is filled with fresh discoveries of all kinds of things. It seems like every day there’s a new dinosaur, planet, or ancient creature being brought back to life. Now, researchers are announcing the discovery of another new thing, but this time it’s a new… shape.
Just like the other “new” things that science brings us, the term “new” itself is relative. Just like the long-dead dinosaurs and incredibly-old planets being discovered on a regular basis, this new shape has been around for a while, but researchers are just now studying and describing it in detail. It’s called a “scutoid” and it’s actually pretty cool.
Don’t Miss : Hurry: AirPods are back in stock with a very rare discount on Amazon.

Bishop on the Moon?
It might sound strange, but in addition to encompassing nine counties and hundreds of cities, the Diocese of Orlando, Florida also has jurisdiction over an otherworldly object: the Moon. Why might you ask? The answer involves an obscure rule from 1917 and the Apollo 11 space mission.
On June 18th, 1968 the Roman Catholic Diocese of Orlando, Florida was established. It would encompass much of the greater central Florida area, along with Cape Canaveral (We’ll get back to that later). William Donald Borders was ordained the first Bishop of Orlando. One year later, Bishop Borders would also become the first Bishop of the Moon.
The Apollo 11 space mission began with the launch from Cape Canaveral on July 16, 1969. The mission fulfilled the national goal proposed by President John F. Kennedy in 1961 of “landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth, before this decade is out.” However, when Apollo 11 made its famous flight from Cape Canaveral to ultimately fulfill that goal, they inadvertently made Bishop Borders the first Bishop of the Moon thanks to an obscure rule from the 1917 Code of Canon Law in effect at the time.
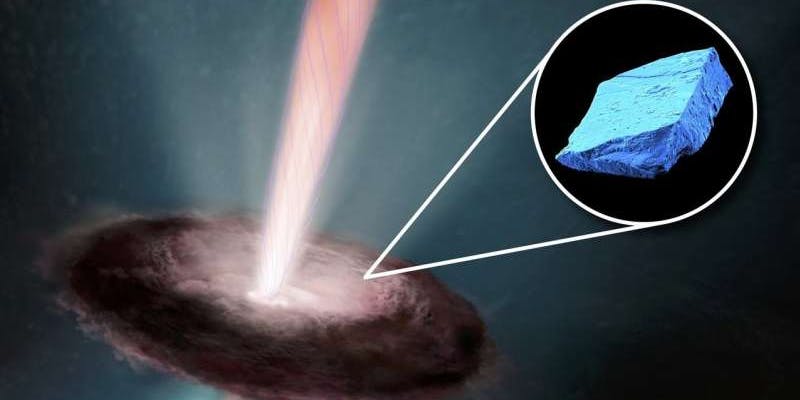

According to a study released Monday in Nature Astronomy ancient blue crystals unearthed from meteorites are the key to understanding what the sun was like during it’s earliest days. Scientists removed these microscopic crystals, technically called hibonites, from the chunk of the Murchison meteorite.
