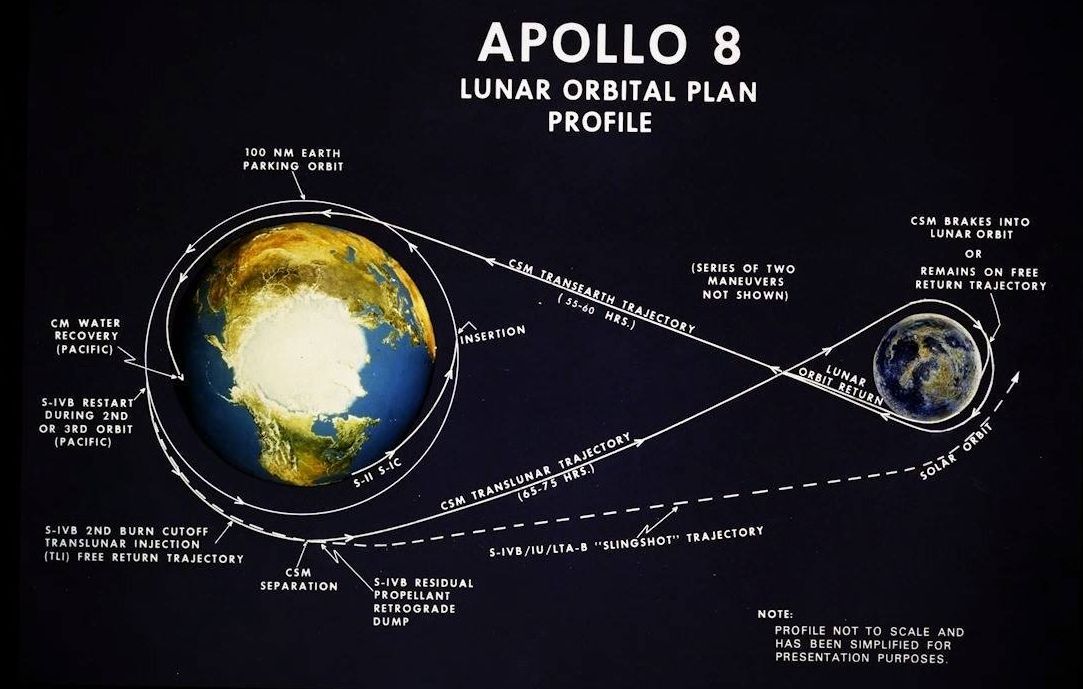
50 years ago this Christmas, we orbited the Moon for the first time. 1 out of every 4 people on Earth watched the crew’s broadcast on Christmas Eve. This is the story of Apollo 8:
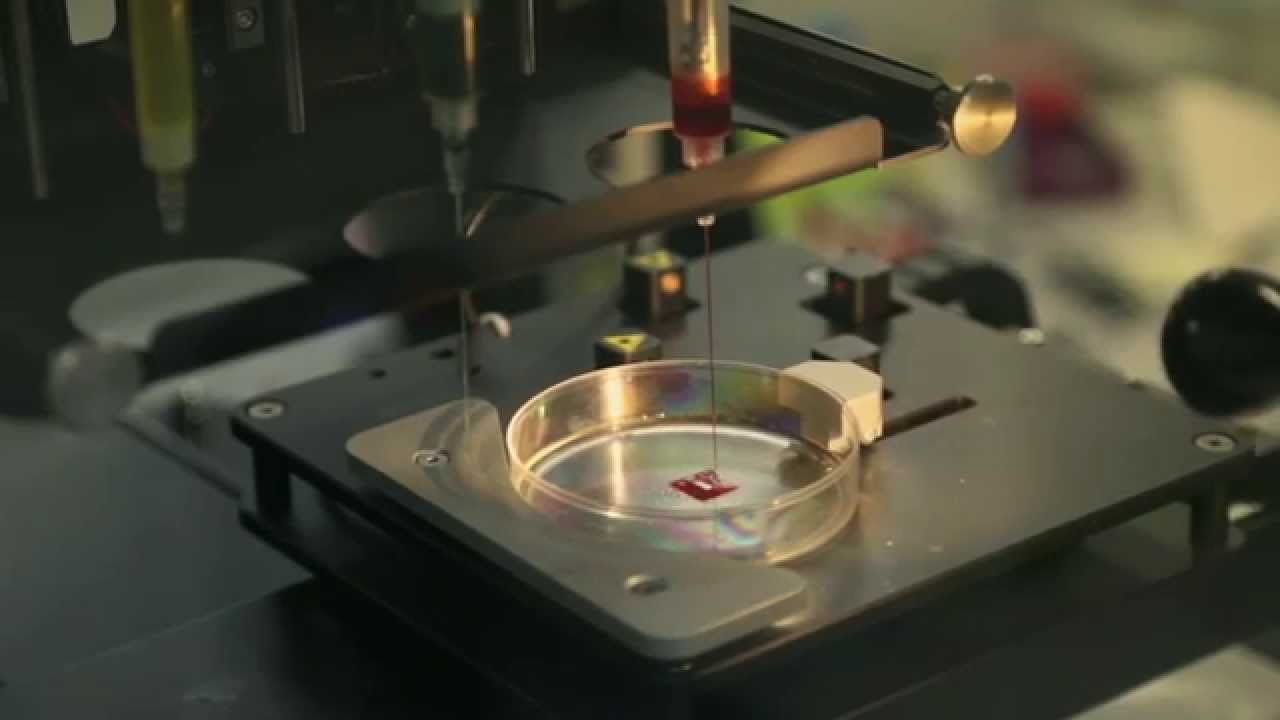


Medical research has taken a leap into the future as Russian scientists have managed to grow a mouse’s thyroid in zero gravity using a 3D bioprinter on the International Space Station (ISS). And human organs may be next in line.
The breakthrough device dubbed Organaut was delivered to the ISS by a Soyuz MS-11 spacecraft on December 3 by Expedition 58.
In what is no longer a plot of a sci-fi movie, the innovative device created a mouse’s thyroid in zero gravity. And the result was a success. Invitro, whose subsidiary 3D Bioprinting Solutions built the printer, told Ria Novosti: “We received photos from space. The camera clearly shows a living construction of a mouse’s thyroid being assembled.”
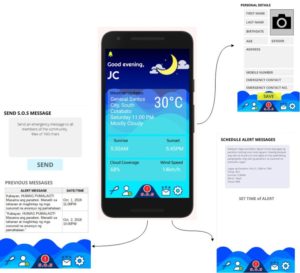
MANILA, Philippines — Among the 2,729 teams in 200 locations all over the world who participated in the NASA Space Apps Challenge, an app made by Filipino innovators was nominated first time by NASA scientists and experts to become a finalist at the global level. Altogether, they will join the top 25 in competing for the six winners of the biggest hackathon in the universe.
The winning app seeking to communicate scientific data to fishermen even without Internet connection was made by IT professionals Revbrain G. Martin, Marie Jeddah Legaspi, and Julius Czar Torreda from team iNON, which stands for “It’s now or never.” Named ISDApp, from the Tagalog word “isda” meaning fish, it sends useful information to fishermen such as real-time weather, sunrise and sunset, wind speed, and cloud coverage to plan their fishing activities in catching more fish using the NASA GLOBE Observer app, a data collection from citizen scientists around the world used in concert with NASA satellite data to identify or communicate information, and educating the public about planet Earth. Fishermen will receive SMS notifications from the Amazon Web Services gateway while local government officials would manage their details using a smartphone app connected to the cloud. NASA scientists and experts consider this fisherfolk app made by Pinoys as one of the solutions “with the most potential to improve life on Earth or in the universe,” therefore nominated as global finalist for Galactic Impact.

The fishermen app won in the local level on Friday-Sunday, October 19–21, 2018 at De La Salle University, Malate, Manila, Philippines, in collaboration with the Embassy of the United States of America to the Philippines and PLDT. US Embassy deputy chief of mission John C. Law, PLDT Enterprise Core Business Research and Development head Leandro T. Santos, DOST-Philippine Council for Industry, Energy and Emerging Technology Research and Development deputy executive director Engr. Raul C. Sabularse, Department of Information and Communications Technology senior planning officer Yvette M. Cabrera, and Animo Labs executive director Federico C. Gonzalez served as jurors at the local level.
An emergency checklist kit app designed for disaster preparedness also won at the local level developed by students Jeorge Loui P. Delfin, Bluen Ginez, Samuel Jose, Rainier G. Narboneta, and Eugenio Emmanuel A. Araullo. Other projects and solutions developed during the hackathon are games using images from the Hubble Space Telescope, augmented reality mobile app to tell a story of the changes in the Arctic and Antarctic ice, artificial intelligence app helping scientists confirm the habitability of exoplanets, and story-based game using NASA Earth imagery. They joined together with teams of coders, scientists, developers, designers, storytellers, makers, builders, technologists, thinkers, entrepreneurs, and everyone around the globe working together in a 48-hour sprint to develop solutions to some of the most pressing challenges on Earth and in space, using NASA resources and data.
https://www.facebook.com/ArchersNetwork/videos/281167132522644
A day-long data bootcamp was held to learn new concepts, strategies and skills from keynote speakers, panelists, and mentors. Michael Carroll from Urban Engine in Huntsville, AL and NASA Earth Science Division senior advisor Dr. Patricia Jacobberger introduced Space Apps through a virtual talk while NASA astronaut Drew Feustel, orbiting aboard the International Space Station welcomed everyone to the event. US Embassy science fellow Dr. Anondo Mukherjee and US Fulbright fellow Sarah Marie Hartman gave an online lecture about the Earth’s environment. DOST-Advanced Science and Technology Institute acting director Dr. Joel Joseph S. Marciano, Jr. and PHL-Microsat program leader Dr. Marc Caesar R. Talampas discussed microsatellite development and advanced technologies in the Philippines.
Several mentors coming from different backgrounds such as YSEALI alumni Ryan Madrid and Malcolm Flores, De La Salle University professors Jordan Aiko P. Deja and Neil Patrick A. Del Gallego, PHL-Microsat engineers Ariston N. Gonzalez, Lorenzo Sabug, Jr., Benjamin Joseph D. Jiao, and Carlo D. Pastoral, Amazon Web Services developers John Luis Garcia, Dennis Magsajo, and Randy Bardaje, Animo Labs incubatee and MachiBox CEO Simon Gregory Mabanta, VR Philippines lead Cristopher David, Mobility IT 4 Youth lead Art Polo Gabriel III, nuclear physicist Dr. Jasmine Albelda, and entrepreneur Ibba Bernardo guided participants in creating their winning apps and solutions to solve problems on Earth and space. Department of Information and Communications Technology undersecretary Monchito B. Ibrahim gave an inspiring message to the participants. IdeaSpace and Animo Labs looked upon promising projects and solutions that might have a business potential.

During the hackathon period, teams are expected to find solutions to themed challenges put forth by NASA. They work together with the rest of the world on hackathon weekend to devise creative and innovative solutions to these challenges. Projects do not have to be apps and anyone does not need to become a computer programmer to participate. Participants collaborate to build anything — from open-source software, hardware, data visualizations, and citizen science platforms, to videos, art, and other communications solutions — aimed at addressing global challenges. The overarching theme of the 2018 challenges is “Earth and Space,” underscoring the connections between major challenges, and the potential solutions to them, both on Earth and in space. The 2018 mainstage Space Apps event was hosted by Urban Engine in the US Space and Rocket Center at Huntsville, AL, also known as “The Rocket City.”
Since its inception in 2012, the International Space Apps Challenge has become the world’s largest global hackathon, engaging thousands of global citizens to collaborate in building innovative solutions to complex challenges using NASA’s open data. Hackathons are technology development marathons that draw on the talents and initiative of bright-minded people. Space Apps inspires local innovation communities to convene, cooperate, and create.
The 2018 hackathon was organized by Matt T. Keener, Jeanie M. Duwan, Randolf D. Mariano, and Xavier E. Lara from the American Spaces Philippines of the US Embassy and Kai Shan L. Fernandez, Christine M. Abrigo, Donna Lyn G. Labangon, Kevin Anthony Y. Kaw, and Dr. Rafael A. Cabredo from De La Salle University. Another hackathon was organized at Makati-Bonifacio Global City by Womensphere. In the past years, Tzar C. Umang brought Space Apps in Dagupan, Pangasinan on 2016 while Art Polo Gabriel III, Wilson Censon, and Tito Mari Francis Escaño organized one in PLDT InnoLab in Mandaluyong, Metro Manila. De La Salle — College of Saint Benilde also hosted Space Apps on 2017 by Dr. Edward M. Moises, Norman Lee, and Catherine Valdellon-Mojado.
Lead organizer Michael Lance M. Domagas is very thankful that NASA scientists and experts recognized the skills and talents of Filipinos in building projects and open-source solutions that address real-world problems, on Earth and in space, and hoping that Filipinos would win the competition.

Being in space can have weird and sometimes harmful effects on the human body, and we’ll have to work through those issues if we’re to make it out to Mars and beyond, and stay healthy.
But it looks like we have finally found one feature of the human body that’s untroubled by microgravity — and it’s a part of our all-important immune system.
Based on a study of blood samples from International Space Station (ISS) crew members, a few months in space don’t affect B-cell immunity — the number of white blood cells in our bodies ready to fight off infection by producing antibodies.
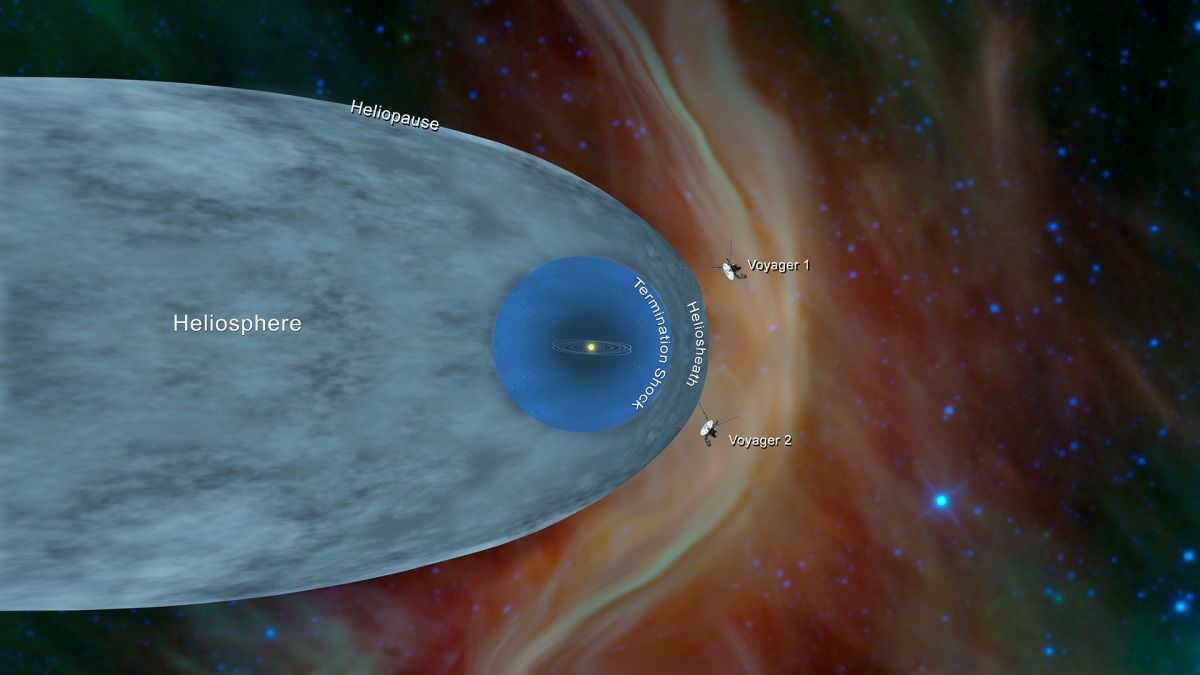
It’s pretty cool how NASA knows the spacecraft is in interstellar space.
It’s only the second object made by humans to ever reach this distance, following Voyager 1 in 2012.
The long journey: Since launching more than 40 years ago back in 1977, the probe has traveled 11 billion miles to get to cross into interstellar space. While it launched before Voyager 1, its flight path put Voyager 2 on a slower path to reach this milestone.
What does that mean? No, Voyager 2 hasn’t left the solar system. Our solar system is huge and goes way beyond its last planet. Instead, it means Voyager 2 has left the heliosphere, the pocket of particles and magnetic fields created by our closest star. Solar wind, the charged plasma particles that come out from the sun, generates this bubble.
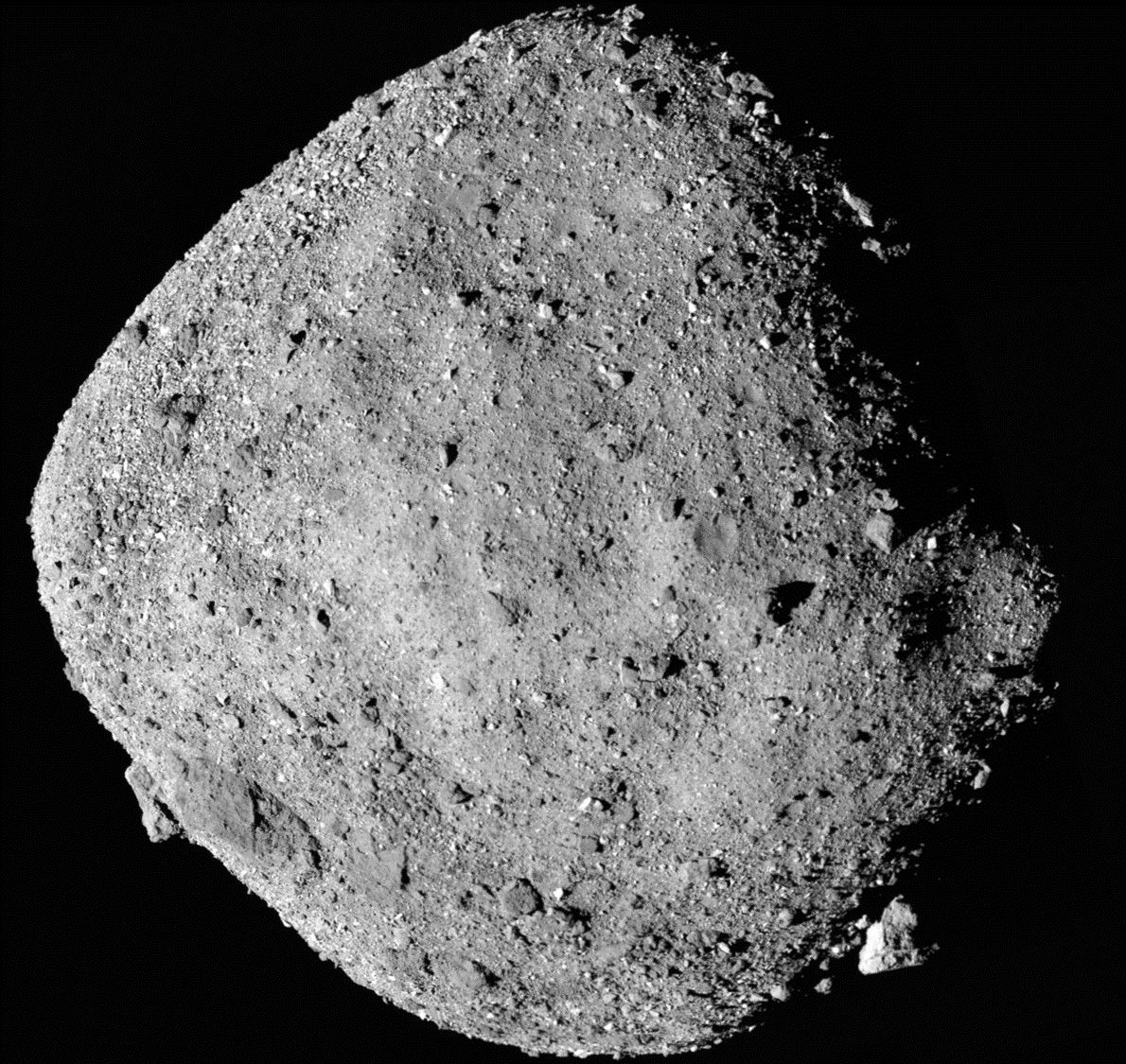

We’ve discovered water on the asteroid Bennu! Our OSIRIS-REx mission has revealed water locked inside the clays that make up Bennu.
Recently analyzed data from NASA’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) mission has revealed water locked inside the clays that make up its scientific target, the asteroid Bennu.
During the mission’s approach phase, between mid-August and early December, the spacecraft traveled 1.4 million miles (2.2 million km) on its journey from Earth to arrive at a location 12 miles (19 km) from Bennu on Dec. 3. During this time, the science team on Earth aimed three of the spacecraft’s instruments towards Bennu and began making the mission’s first scientific observations of the asteroid. OSIRIS-REx is NASA’s first asteroid sample return mission.
Data obtained from the spacecraft’s two spectrometers, the OSIRIS-REx Visible and Infrared Spectrometer (OVIRS) and the OSIRIS-REx Thermal Emission Spectrometer (OTES), reveal the presence of molecules that contain oxygen and hydrogen atoms bonded together, known as “hydroxyls.” The team suspects that these hydroxyl groups exist globally across the asteroid in water-bearing clay minerals, meaning that at some point, Bennu’s rocky material interacted with water. While Bennu itself is too small to have ever hosted liquid water, the finding does indicate that liquid water was present at some time on Bennu’s parent body, a much larger asteroid.
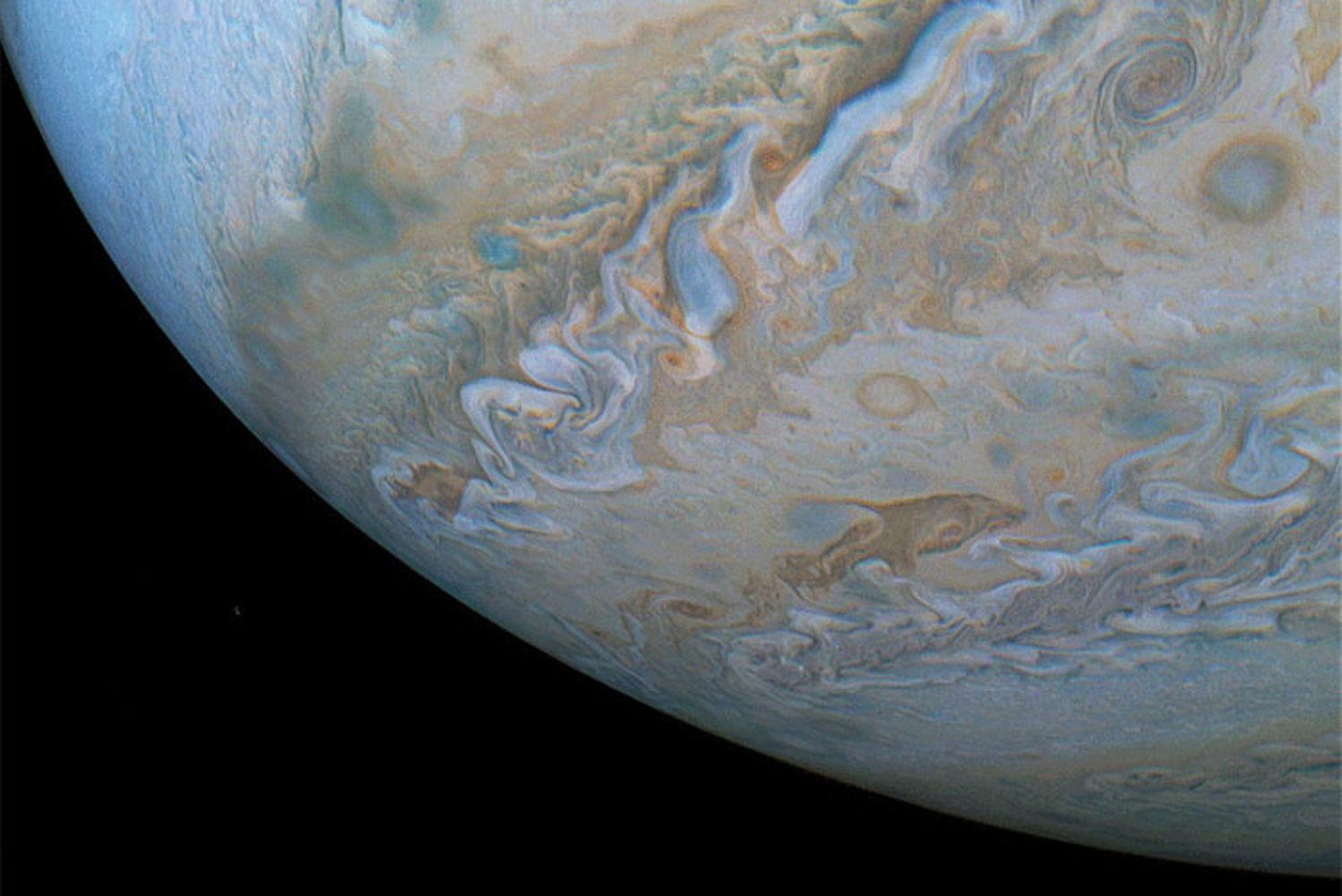
Try to spot a dolphin swimming through a sea of Jovian clouds.
In a phenomenon called pareidolia, humans can find shapes in what is otherwise just random data. Is Flipper actually splashing across Jupiter’s atmosphere? Obviously not. But a new series of images that showcase a dolphin-shaped cloud moving across Jupiter’s southern belt is really enjoyable to look at.
Citizen-scientists Brian Swift and Sean Doran made the images using data from the JunoCam imager, an instrument on board NASA’s Juno spacecraft. On Oct. 29, the spacecraft performed its 16th close flyby of Jupiter.

If it’s quiet solitude and beauty you seek, there is no better place than the surface of Mars has earned its moniker as the red planet, but the HiRISE camera aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) can transform the subtle differences of soils into a rainbow of colours. 
For 10 years, HiRISE has recorded gorgeous – and scientifically valuable – images of Mars. Its photos are so detailed that scientists can examine the planet’s features at the scale of just a few feet, including the recent crash site of Europe’s Schiaparelli Mars lander.
We combed through 2,054 of the camera’s latest pictures, released in August, September, and October, to bring you some of the best – and hopefully help you temporarily escape Earth.

