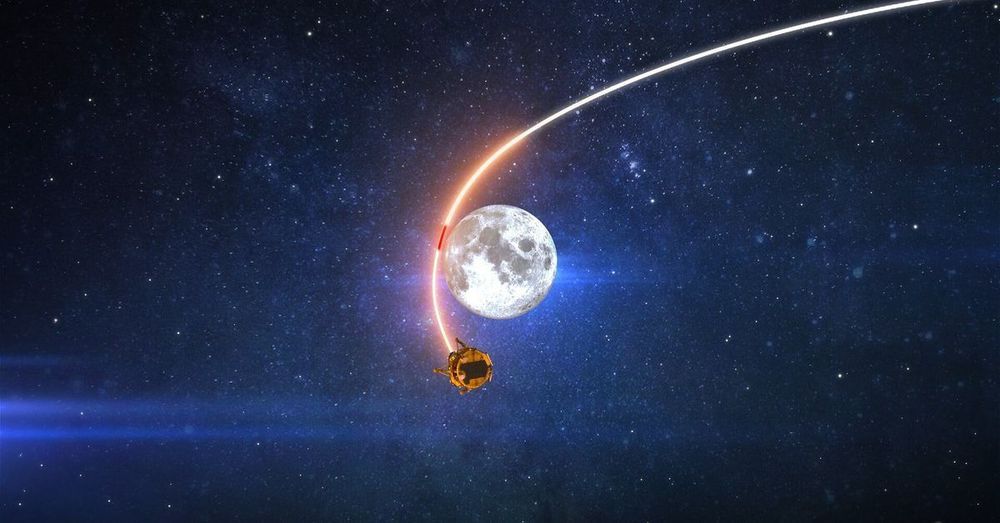
It probably slammed into the lunar surface.
Beresheet probably slammed into the lunar surface.


From smog-sucking bikes to electric taxis and paint made of car exhaust, designers and architects are stepping up to address air pollution—the world’s single largest health risk. But a new air filter making the rounds in Oslo, Paris, Brussels, and Hong Kong shows that nature may be our best ally in this battle.
Essentially a moss-covered wall, each CityTree removes CO2, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter from the air while also producing oxygen. A single tree is able to absorb 250 grams of particulate matter a day and remove 240 metric tons of CO2 each year—a level roughly on par with the air purification impact of 275 urban trees. Thirteen feet tall, with a metal frame, the CityTrees are easily installed in a public space, and they even have built-in seating at their base.

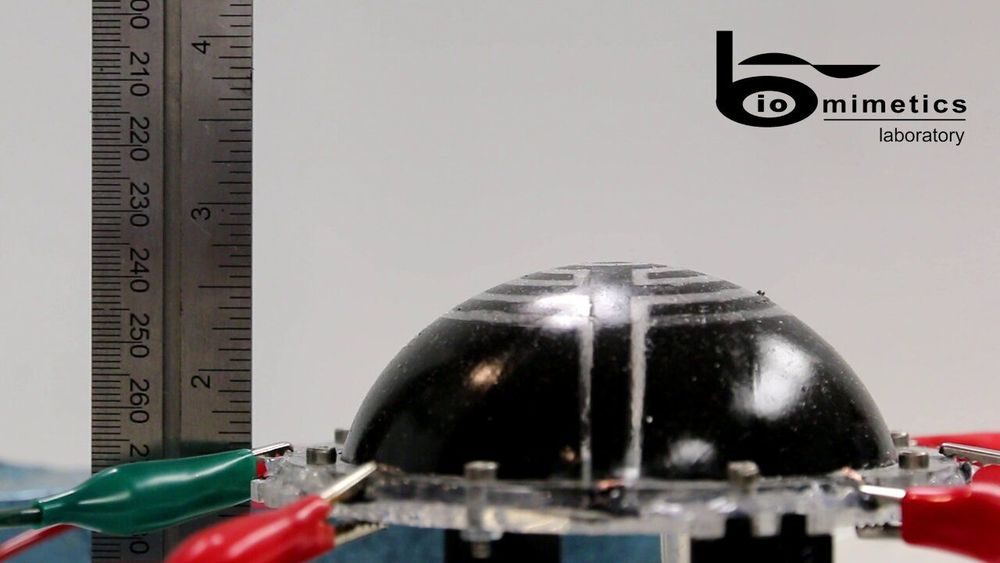
Researchers at the Auckland Bioengineering Institute and Technische Universit\xE4t Dresden have recently designed a new type of inflatable robot for space navigation. These robots, presented in a paper published in SPIE Digital Library, were created using dielectric elastomer transducers (DETs), which are essentially electrical capacitors made from soft rubbery materials.
“Current space technology is limited by its mass and volume. It takes thousands of dollars to launch even a single kilogram into orbit,” Joseph Ashby, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “Our research aims to replace or augment current technology with lighter smart-material replacements combined with inflatable structures.”
If they are integrated with inflatable structures, DETs could aid the development of soft and low-mass robots, which have high packaging efficiency and are easy to deploy. In fact, DETs deform when a voltage is applied to them, due to the Maxwell stress generated by the electric field.

Georgia is immensely proud of its ancient wine-making tradition, claiming to have been the first nation to make wine. Now it wants to be the first to grow grapes on Mars.
Nestling between the Great Caucasus Mountains and the Black Sea, Georgia has a mild climate that is perfect for vineyards and has developed a thriving wine tourism industry.
Now Nikoloz Doborjginidze has co-founded a project to develop grape varieties that can be grown on Mars.
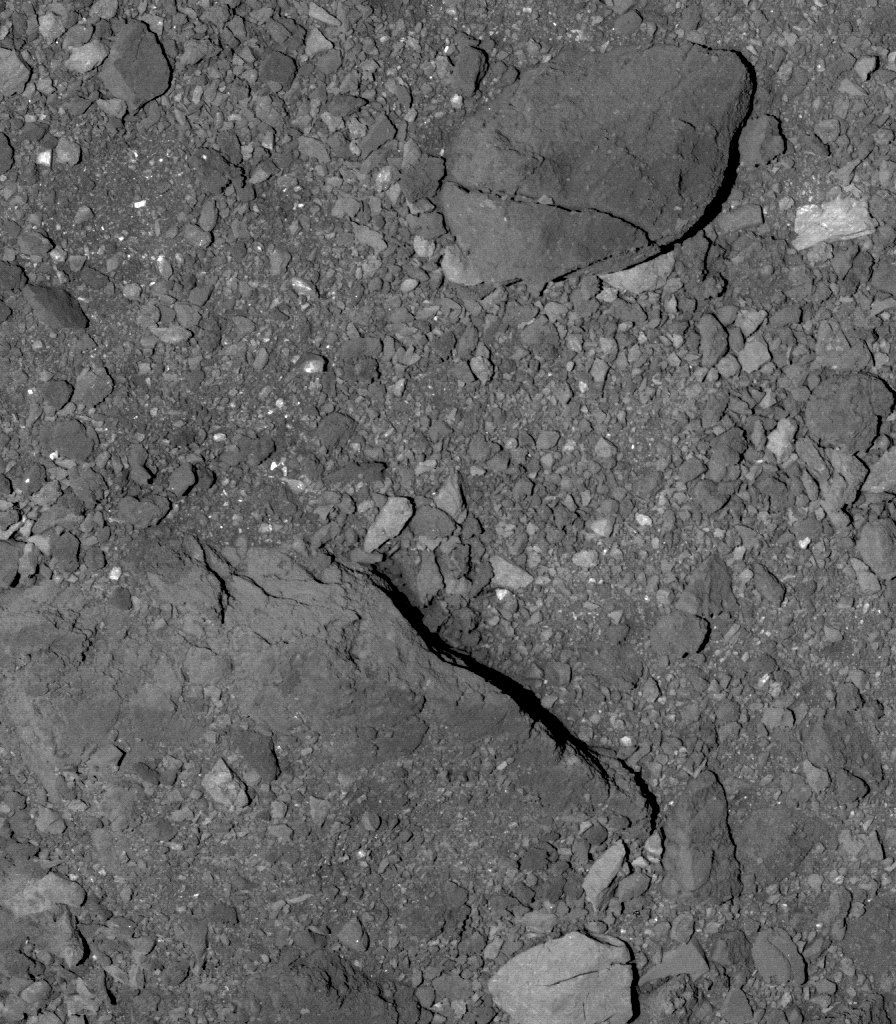

This image from Flyby 1 of Detailed Survey: Baseball Diamond phase shows the rocky surface of Bennu just south of the asteroid’s equator. The PolyCam camera on NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft took the image on March 7 from a distance of 3 miles. For scale, the cracked rock at the top is 69 ft long, about the length of 4 parallel parking spots.
More details on the image: bit.ly/2IpIKSG


Plants are naturally amazing little machines – so giving them a bionic leg-up could unlock a whole new range of abilities. Now a team of researchers from the University of Melbourne has developed a new way to turn plants into nanomaterial factories, which could allow them to act as chemical sensors or even allow them to survive in harsh environments, such as in space or on Mars.

