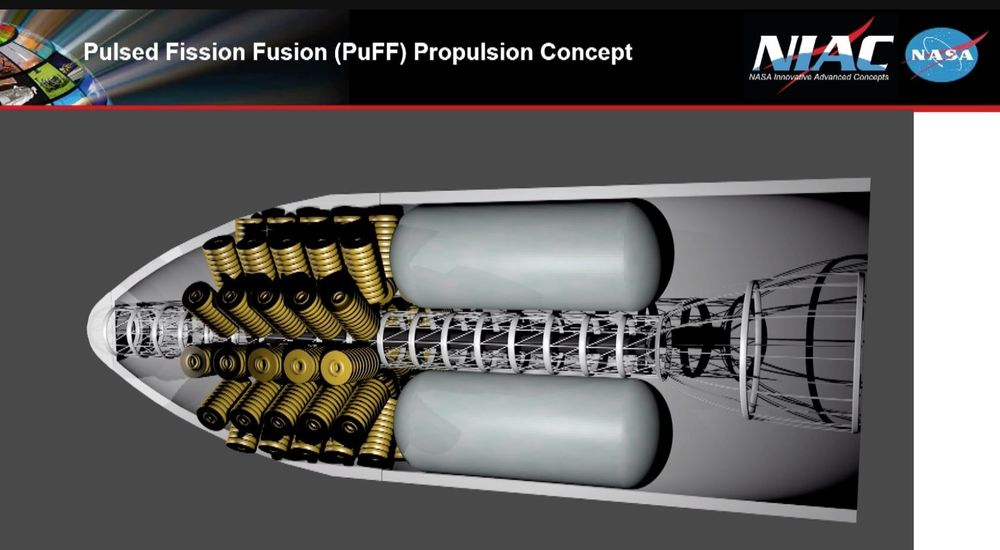
Robert Adams updated the work on a phase 2 Pulsed Fission-Fusion (PuFF) Propulsion Concept. Robert works at the NASA Marshall Space Flight Center. This system should be able to achieve 15 kW/kg and 30,000 seconds of ISP. This will be orders of magnitude improvement over competing systems such as nuclear electric, solar electric, and nuclear thermal propulsion that suffer from lower available power and inefficient thermodynamic cycles. Puff will meet an unfilled capability needed for manned missions to the outer planets and vastly faster travel throughout the solar system.
A tiny lithium deuteride and uranium 235 pellet will be fired into a shell of structure that will complete a circuit and generate high voltages and pressures that will compress the pellet and cause fission and fusion to occur.