Why the world’s most ambitious array of submillimeter antennas continues to reap astronomical dividends.



🏺Super Pink Moon
Fyodor R., Credits article input Oscar Cainer, photography taken in North America, yesterday, by Richard S., one of our members.
Every April, sandwiched between the Worm Moon of March and the Flower Moon of May, the Pink Moon rises to hang like a great glowing orb in the sky, almost impossibly large, bright and full.


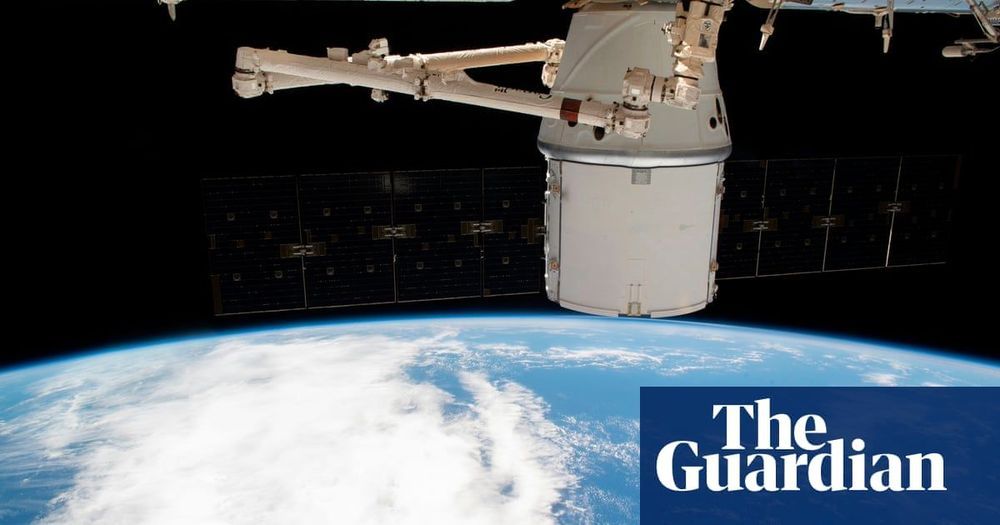
Boeing flubbed the first mission of the CST-100. Seemingly a routine mission for SpaceX after completing over 20 deliveries to the International Space Station, Boeing showed how not to do it. During the December 2019 Demo flight for the Boeing Starliner CST-100, the Starliner did not reach its planned orbit. Nor did the Starliner dock to the International Space Station as planned. Boeing was able to complete a number of mission objectives during the flight to comply with the milestones related to NASA’s Commercial Crew.
On the ULA Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20, the Boeing Starliner launched from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Boeing has a long rich history in both aviation and spaceflight. This mission, already three years behind in schedule, should have been a slam dunk.
After launching to the incorrect orbit, Boeing was able to successfully recover the Starliner. NASA shared that Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft did successfully complete the first land touchdown of a human-rated capsule at the White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico at 7:58 a.m. EST (5:58 a.m. MST) on December 22, 2019. The landing followed a deorbit burn for the botched flight, separation of the spacecraft’s service module, and successful deployment of its three main parachutes and six airbags. Boeing’s approach to the Starliner is unique as the prior US-made capsules, including the SpaceX Dragon, are water recoveries.
The NASA and Boeing investigation into the spaceflight was disclosed in Early March 2020. The recommendations included a list of corrections that needed to be addressed prior to the Starliner launching again. The investigation documented 61 “corrective actions” for the company’s Starliner spacecraft. This type of test did do what it was supposed to do. Find issues before people are exposed to potentially dangerous situations. This human risk reduction is a hallmark of the NASA Commercial Crew Program which was put in place to alternatives to the Space Shuttle and Soyuz spacecraft. NASA associate administrator Doug Loverro shared with reporters on a conference call that he expected it months for Boeing to work through the list to be ready for another test flight.

Hey all! I have recently made a video on how rich humanity can get from asteroid mining and how humanity can potentially eradicate poverty if it were to begin asteroid mining efforts. I have posted a link to the video here. If you find it worthy, please consider liking and subscribing!
Ever dream of becoming a billionaire? Well, believe it or not, space is the way to get rich. With billions of dollars worth of metals in each asteroid, asteroid mining is one of the most lucrative way for humanity to gather material resources. In this video, I talk about how humanity can potentially use asteroid mining to eradicate poverty and possibly make every single person alive rich.
Please like and follow our facebook page at: https://www.facebook.com/The-Futurist-Tom-104401617815917
For business inquires, please contact [email protected]
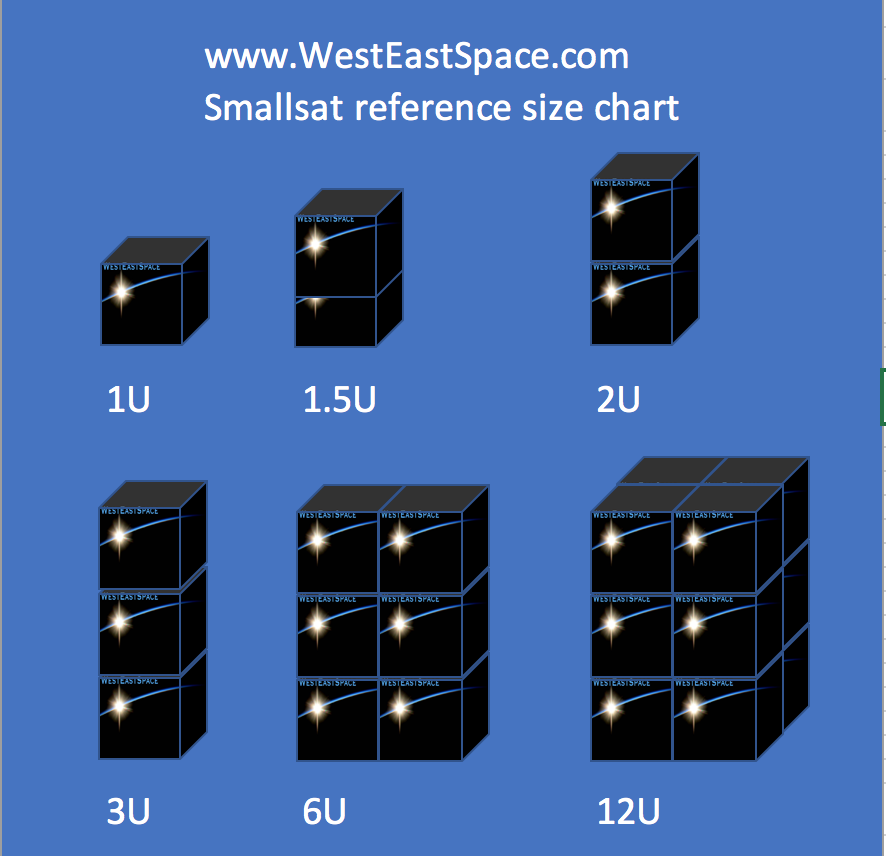
Satellites come in all sizes and shapes. A small satellite or SmallSat is commonly considered to be a satellite that weighs less than 500 kg.
As a basic application of various satellite sizes by mass, the common distinction:
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit(kg) | Classification | Examples |
| 1000 | Large satellites | Hubble Space Telescope / Inmarsat-4A F4 | |
| 500 | 1000 | Medium satellites | O3b |
| 0 | 500 | Small satellites | SpaceX StarLink |
CubeSats are smaller yet.
CubeSats need to conform to specific criteria including shape, size, and mass. At this point, most people have become aware or are at least heard of CubeSats. (Cube Satellites). CubeSats (cube satellite, cube satellite) are a type of nanosatellites defined by the CubeSat Design Specification (CSD) or otherwise commonly known by the unofficial term “CubeSat standard”. Cubesats are small, and start off at the 1U size of 10xm x 10 cm x 11.35 cm ( yes not exactly a cube, but very close) Here are some standard CubeSat dimensions:
1U CubeSat is 10 cm × 10 cm × 11.35 cm.
2U CubeSat is 10 cm × 10 cm × 22.70 cm.
6U CubeSat is 20 cm × 10 cm × 34.05 cm.
12U CubeSat is 20 cm × 20 cm × 34.05 cm.
The CubeSat Project began as a collaborative effort of several professors at California Polytechnic State University (Cal Poly) and Stanford University’s Space Systems Development Laboratory (SSDL). Prof. Jordi PuigSuari(Cal Poly), San Luis Obispo(SSDL), and Prof. Bob Twiggs(SSDL) started the CubeSat Project in 1999 and since the inception, the CubeSat Project gained wide acceptance. The development of CubeSats has advanced into a subindustry of space satellite development and launch. Numerous government, industry and academic organizations collaborate increased capabilities. The program has expanded to be an international collaboration of over 100 universities, high schools, and private firms developing CubeSats containing scientific, private, and government payloads.

O’Connell’s previous book, To Be a Machine, was an inspired journalistic exploration of “transhumanism”, the subculture that wants to fast-forward to a technological future in which man becomes part-machine. This one is haunted by the idea that, unless we change our ways, or even if we change our ways, our species does not have much of a future at all. For O’Connell, those fears had been sharpened by recent fatherhood.
A timely study of the world’s growing sense of doom ranges from tourists in Chernobyl to Elon Musk’s plan to colonise Mars.

Global warming is a complex problem that is not easy to solve. While world leaders seem to be dragging their feet over the issue, Yotam Ariel, founder of Bluefield, believes he might have at least one piece of the puzzle sorted. Methane monitoring from space. By leveraging a network of microsatellites with a proprietary sensor, Bluefield plans to deliver alerts and analytics to oil and gas clients to help combat the inadvertent release of methane gas
Methane, a greenhouse gas, is leaking into the atmosphere. One might ask, “Why bother with methane, isn’t carbon dioxide the problem?” Well, according to the IPCC (https://www.ipcc.ch/), methane is 84 times more potent than carbon dioxide, which is clearly a bad thing for global warming. Methane is believed to be responsible for 25% of global warming and knowing who is emitting, when, and how much, would be a massive step towards reversing climate change. Since between 50 and 65% of total global methane emissions come from human activities, being able to identify and stop leaks is crucial to lowering greenhouse gases in our atmosphere.
Bluefield plans to specialize in methane gas detection and not try and solve all problems all at once and thereby reducing complexity. Further reduction in complexity is achieved by leveraging outside suppliers where applicable that complement the Bluefield plans. By reducing the complexity, Bluefield can focus on its core mission and specialty. Areas outside of detection such as the satellite parts, ground stations, the launch, and other services will be outsourced. This will allow Bluefield to quickly move through its development stages. Whereas it might take up to 10 years for a space agency like NASA, JAXA or ESA, to fund, design, test and launch a custom satellite, Bluefield aims to accomplish this as early as next year.
In fact, the prototype for the first microsatellite design has already been completed. Bluefield shortlisted several suppliers and the final selection will be made soon. The company is well on its way to testing its technology in orbit after completing both field tests and high-altitude balloon tests this year. By mounting its newly developed sensor on several backpack-sized microsatellites, Bluefield will be able to collect enough raw data to provide methane emission monitoring at a previously unthinkable level in terms of global coverage, high resolution and at a price point well below what is currently available.
Astronomers have detected two stellar corpses whirling around each other, and they might be producing gravitational waves.
White dwarf stars are what become of stars like our sun after they run out of fuel and turn into leftover hot cores. For many years, researchers have predicted that there should be binary, or two-object, systems made up of white dwarf stars. According to general relativity, two such masses orbiting each other should emit energy in the form of gravitational waves, which are ripples or disturbances in the fabric of spacetime.
