With new research, scientists have the most accurate measurement ever of one of the fundamental constants of the universe.
🤯 Get unlimited access to the weird world of Pop Mech.
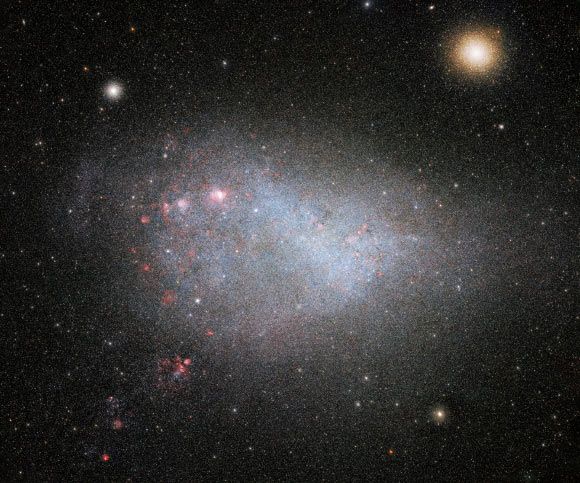

New images, taken with the 520-megapixel Dark Energy Camera (DECam) on the Víctor M. Blanco 4-m Telescope at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, represent a portion of the second data release from the Survey of the MAgellanic Stellar History (SMASH), the deepest, most extensive survey of the Magellanic Clouds (high-resolution images: the Large Magellanic Cloud and the Small Magellanic Cloud).
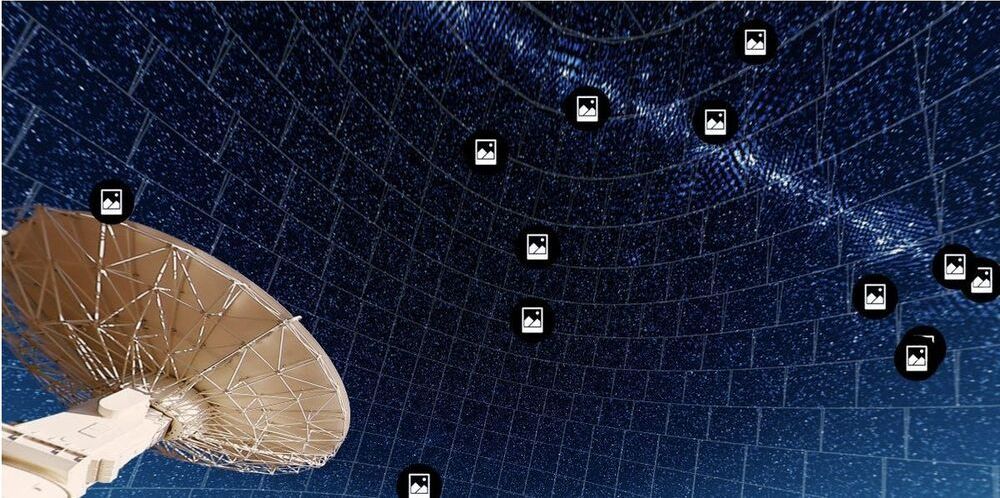

Astronomers have mapped about a million previously undiscovered galaxies beyond the Milky Way, in the most detailed survey of the southern sky ever carried out using radio waves.
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey (or RACS) has placed the CSIRO’s Australian SKA Pathfinder radio telescope (ASKAP) firmly on the international astronomy map.
While past surveys have taken years to complete, ASKAP’s RACS survey was conducted in less than two weeks — smashing previous records for speed. Data gathered have produced images five times more sensitive and twice as detailed as previous ones.
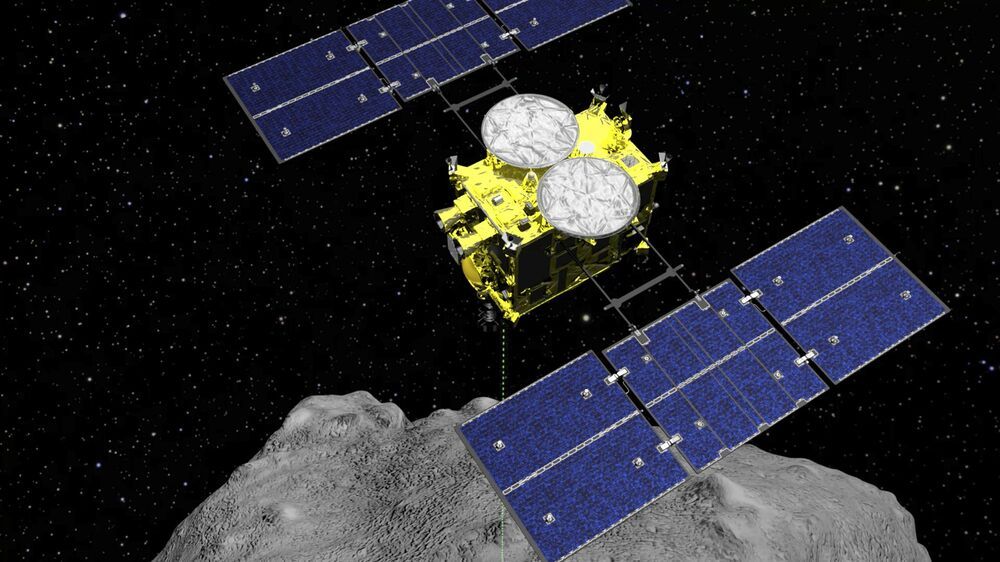
TOKYO (AP) — Japanese space agency officials said Friday the Hayabusa2 spacecraft is on its intended trajectory as it approaches Earth to deliver a capsule containing samples from a distant asteroid that could provide clues to the origin of the solar system and life on Earth.
The spacecraft left the asteroid Ryugu, about 300 million kilometers (180 million miles) away, a year ago. The capsule is to be released 220,000 kilometers (136,700 miles) away in space and land in a remote, sparsely populated area of Woomera, Australia, on Sunday.
Hayabusa2 is flying smoothly according to plan, Yuichi Tsuda, project manager at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, said at a briefing ahead of the critical separation of the capsule from the spacecraft on Saturday.

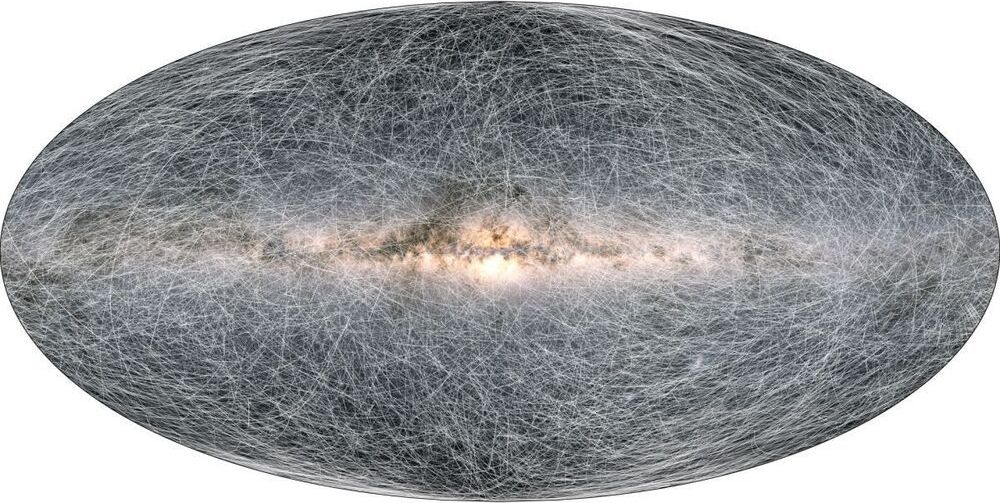
Europe’s Gaia spacecraft has produced the best-yet map of the Milky Way with measurements of 1.8 billion objects.



This is the episode for all those with questions about what we know about Mars. Specifically, how Mars went from being potentially habitable to the desert we see today. Guest Bruce Jakosky, the Principal Investigator for NASA’s MAVEN Mars orbiter explains it all.
NASA’s MAVEN orbiter has arguably done more to document how and why Mars lost its atmosphere and much of its water than any spacecraft ever sent to the red planet. The mission’s principal investigator, planetary scientist Bruce Jakosky is this week’s featured guest and we discuss the current paradigm on why Mars went so horribly wrong. Jakosky offers a candid and inside look at how such missions work and what we can expect from Mars science in the next few years.
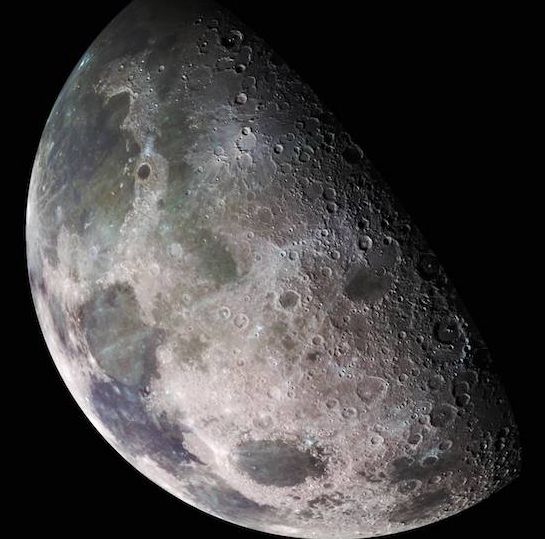

New research indicates that if even a moderate amount of the water delivered by asteroids to the Moon was sequestered, the lunar poles would contain gigaton deposits (1 billion metric tons) of ice in sheltered craters and beneath its surface.
By modeling over 4 billion years of the Moon’s impact history, researchers were able to track the origin and potential quantity of ice that might be obscured from view beneath the lunar surface.
“We looked at the entire time history of ice deposition on the Moon,” said Kevin Cannon, a planetary scientist at the Colorado School of Mines in Golden and lead author of the new study in the AGU journal Geophysical Research Letters.