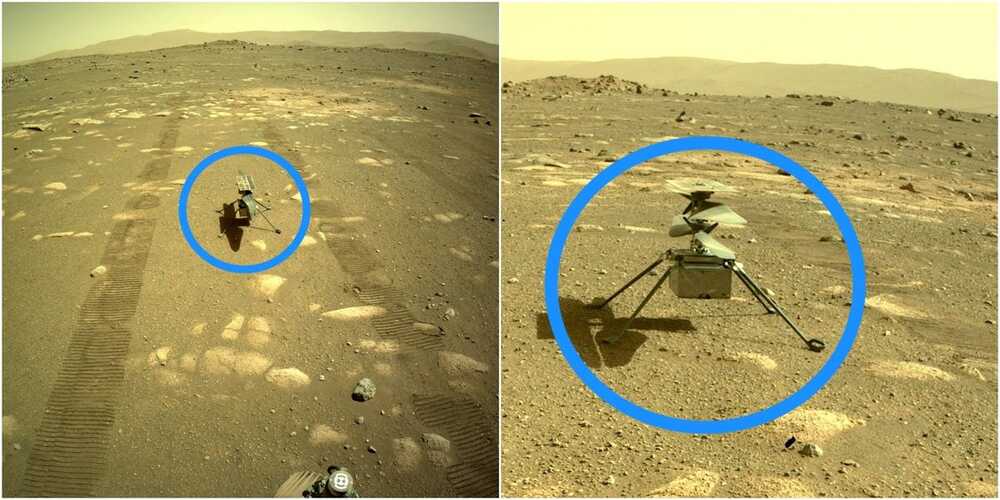
For 50 years, AeroVironment has advanced UAV development. Today, the company is a Technology Solutions Provider at the intersection of four future-defining technologies: robotics, sensors, analytics and connectivity. Its culture of experimentation and R&D dates back to its founder, Dr. Paul MacCready Jr., whose achievements earned him the nickname “the father of human-powered flight”. From deploying the world’s most popular sUAS to designing the helicopter that’s en route to fly in Mars’ thin atmosphere, AeroVironment’s collective accomplishments provide a case study of imagination, innovation and collaboration — one that has and will bring effective solutions to frontlines, farms and frontiers, yesterday, today and tomorrow.
For 50 years, AeroVironment has advanced UAV development. Today, the company is a Technology Solutions Provider at the intersection of four future-defining technologies: robotics, sensors, analytics and connectivity. Its culture of experimentation and R&D dates back to its founder, Dr. Paul MacCready Jr., whose achievements earned him the nickname “the father of human-powered flight”. From deploying the world’s most popular sUAS to designing the helicopter that’s en route to fly in Mars’ thin atmosphere, AeroVironment’s collective accomplishments provide a case study of imagination, innovation and collaboration — one that has and will bring effective solutions to frontlines, farms and frontiers, yesterday, today and tomorrow.
Leading the Way: UAS Capabilities – Onward and Upward
From solar-powered aircraft to the first hand-launched small UAS (sUAS) for military reconnaissance, AeroVironment literally launched the era of small aerial vehicles for environmental, commercial and defense purposes. For 35 years, the company has made its UAVs smaller and simpler, yet with multiple and ever-more-innovative functionality.