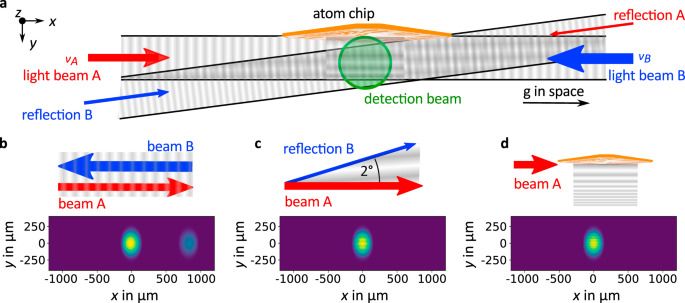
Conducting atom-optical experiments in space is interesting for fundamental physics and challenging due to different environment compared to ground. Here the authors report matter-wave interferometry in space using atomic BECs in a sounding rocket.


NASA hopes to score a 21st-century Wright Brothers moment on Monday as it attempts to send a miniature helicopter buzzing over the surface of Mars in what would be the first powered, controlled flight of an aircraft on another planet.
Landmark achievements in science and technology can seem humble by conventional measurements. The Wright Brothers’ first controlled flight in the world of a motor-driven airplane, near Kitty Hawk, North Carolina, in 1903 covered just 120 feet (37 meters) in 12 seconds.
A modest debut is likewise in store for NASA’s twin-rotor, solar-powered helicopter Ingenuity.

Massive solar storms in space can be picked up by iOS and Android smartphones, meaning billions of people have a personal geomagnetic storm detector — but the signals threaten to interfere with future location-based applications.
Hoping to get the public more involved in science, study author Sten F. Odenwald, an astronomer at the NASA Goddard Spaceflight Center, published a paper on the topic April 2 in Space Weather. It indicates that even through the unavoidable interference caused by other smartphone components, the phone’s built-in magnetometers can detect geomagnetic storms.
“Smartphones — at least theoretically — should be able to detect some of the strongest storms, pretty easily in fact,” Odenwald told The Academic Times. “Especially if you happen to live up in the northern latitudes — in Minnesota or in Canada, or places like that where it really rocks and rolls.”


Circa 2020 o.o
The NASA Perseverance Rover has a device aboard called MOXIE that will convert the air available on Mars into oxygen. The device is a test, and if the technology was used on a larger scale could produce oxygen for humans to breathe on the Red Planet and could be used for rocket fuel. NASA knows that one of the most challenging parts of putting people on Mars will be getting them off the planet and back to Earth.
Two get a crew for off Mars would require 55000 pounds of oxygen to produce thrust from 15000 pounds rocket fuel. Rather than send all of the oxygen needed from Earth to Mars, scientists want to enable the astronauts to create the rocket fuel on Mars. MOXIE is a first-generation oxygen generator meant to test technology that could create the required oxygen.
MOXIE stands for Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment and is an experiment that is entirely separate from the Perseverance’s primary science mission. One of the main missions of Perseverance is to recover rock samples that can be returned to earth that might have signs of ancient microbial life. MOXIE is focused on the engineering required for future human exploration efforts.

Thermoelectrics directly convert heat into electricity and power a wide array of items—from NASA’s Perseverance rover currently exploring Mars to travel coolers that chill beverages.
A Clemson University physicist has joined forces with collaborators from China and Denmark to create a new and potentially paradigm-shifting high-performance thermoelectric compound.
A material’s atomic structure, which is how atoms arrange themselves in space and time, determines its properties. Typically, solids are crystalline or amorphous. In crystals, atoms are in an orderly and symmetrical pattern. Amorphous materials have randomly distributed atoms.



