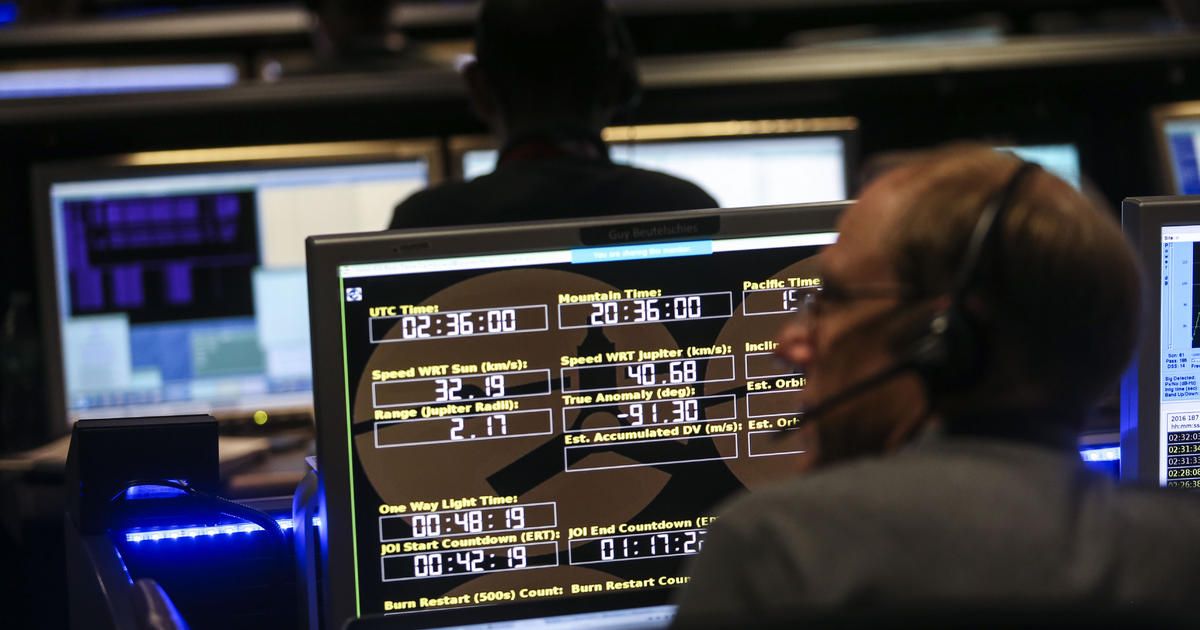
Translated this intriguing article for English readers about our soon to occur Mars-Colonisation, and prospective announcements at the upcoming SpaceX Event!
In our analysis of end 2015 (available on our website, and its summary in the English section) we tried to discern what might look like the project SpaceX Mars Colonization Transportation (MCT), Elon Musk has finally unveiled Sept. 27 at the next International Astronautical Congress. This year included the meagre clues gleaned from the various statements of the contractor, some alter the previous information (eg abandonment of multi-body launcher formula type Falcon Heavy) or, coercion, seemed to confirm the fundamental options such as refuelling earth parking orbit by a second launcher, the total reuse and descent of March of the entire interplanetary shuttle ( “landing the whole thing”). Since then, other indications of various origins have appeared on fans forums. Examine their possible significance.
The choice single-body launcher recoverable and we had driven to approach the performance target (100 T Payload deposited on Mars) to increase the diameter of the drive bay 15 m, although it seemed sufficient to limit that of upstairs itself to 12.5m (pm the first two stages of the Saturn 5 moon had a diameter of 10 m). This configuration allowed to stay a maximum of 31 engines of 300 T thrust and achieve take-off weight (GLOW) 7750 T. Unfortunately, the shape flared rear of the first floor, certainly favourable to the stability phase of ascent, is very unfavourable for the return (flight in opposite direction), especially since it has less then effective ways to stabilise the trajectory. Since it is difficult to imagine that we can reduce the GLOW and therefore the take-off thrust, the solution is to increase the diameter of the whole floor to 15 m. Now it is one of the rumours on forums “MCT-geeks”; SpaceX had solicited tooling suppliers for this diameter.
At the time, it evoked a Raptor 250 Tf thrust (optimal size for mass according SpaceX). Wishing nevertheless not to increase the number of engines (compared to what is allowed with the Falcon Heavy), we considered it necessary to increase the engine thrust to 300 Tf, that remained liveable in the 15 m the Bay. The problem is that even with this power, the desired performance is not achieved (unless we assume our assumptions about the structure of the masses too pessimistic shuttle); Indeed there were 90 T CU (referred to 100) and more in the most favourable conditions: Mars at perihelion and transfer long (Hohmann). But a noise is that SpaceX would work on a Raptor 700 Tf! This level of unit thrust would exceed the planned takeoff thrust, reached with 13 of these engines easily Lodgeable. Given the performance deficit, we can imagine that SpaceX, once the diameter of 15 m admitted, will seek to accommodate the maximum engine.
Read more