When it comes to the future of space exploration, a number of new technologies are being investigated. Foremost among these are new forms of propulsion that will be able to balance fuel-efficiency with power. Not only would engines that are capable of achieving a great deal of thrust using less fuel be cost-effective, they will be able to ferry astronauts to destinations like Mars and beyond in less time.
This is where engines like the X3 Hall-effect thruster comes into play. This thruster, which is being developed by NASA’s Glenn Research Center in conjunction with the US Air Force and the University of Michigan, is a scaled-up model of the kinds of thrusters used by the Dawn spacecraft. During a recent test, this thruster shattered the previous record for a Hall-effect thruster, achieving higher power and superior thrust.
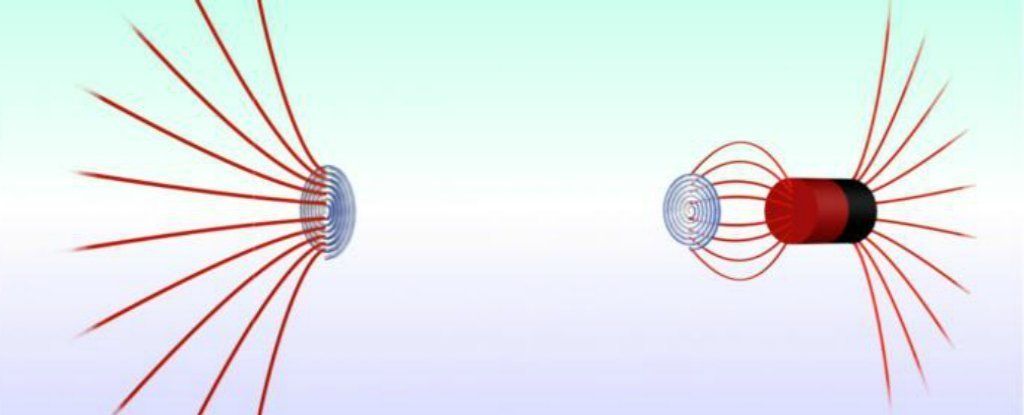
Hall-effect thrusters have garnered favor with mission planners in recent years because of their extreme efficiency. They function by turning small amounts of propellant (usually inert gases like xenon) into charged plasma with electrical fields, which is then accelerated very quickly using a magnetic field. Compared to chemical rockets, they can achieve top speeds using a tiny fraction of their fuel.
Read more