We explore, or we expire. That is why we must get on with it.
The astronaut sees the Moon as a stepping stone.

We explore, or we expire. That is why we must get on with it.
The astronaut sees the Moon as a stepping stone.
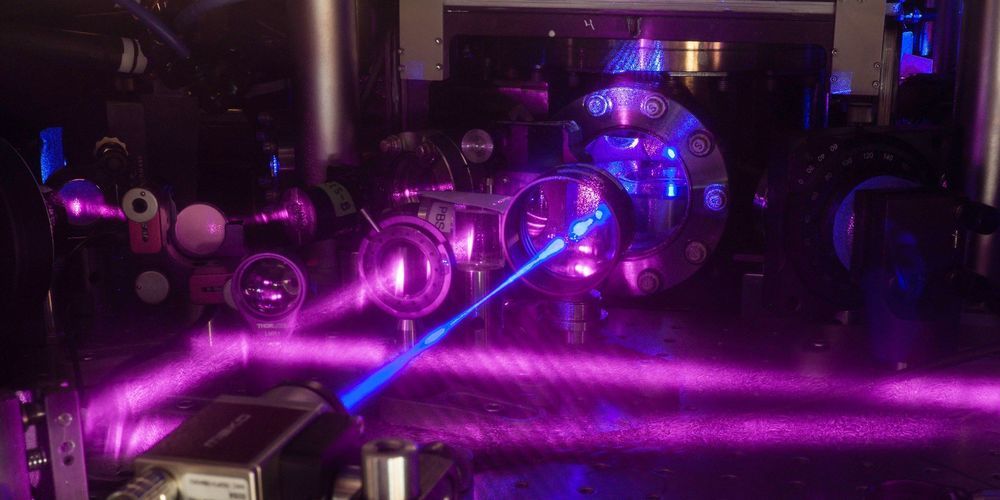
Insanely precise atomic clocks are letting astrophysicists image black holes, steer spacecraft, and maybe one day hunt for gravitational waves.


A fully-contained near-Earth asteroid retrieved to cislunar space can be used as a Research and Development destination for resource extraction and engineering tests as space-native material, unaltered by a radical change in environment, in industrial quantity, and in an accessible orbit.
As a geologist and data manager working in petroleum exploration, I’m not qualified to analyze an all-encompassing view of asteroid mining…but maybe I’m qualified to share what I see from my perspective. Rather than looking at all the reasons why asteroid mining is not currently happening, I’d like to dive deep into how changing decision-making perspectives may make a mission possible.
As human activity and accessibility to do business in space broadens, potential demand for resources delivered to space will also increase. Now is the time to start looking at alternative sources of materials to fuel this expansion. Rather than launching everything from Earth, some materials could be sourced from near-Earth asteroids that are energetically easier to reach than our Moon. While mining asteroids for bulk materials like water might be theoretically profitable compared to launch from Earth, the upfront costs so far have been prohibitive. We’ve already seen the first wave of asteroid mining startups come and go. The high cost of technology development and long timescales for return-on-investment have kept commercial asteroid mining missions grounded.
But even with existing research, achieving sustained fusion inside a reactor is still many years out.
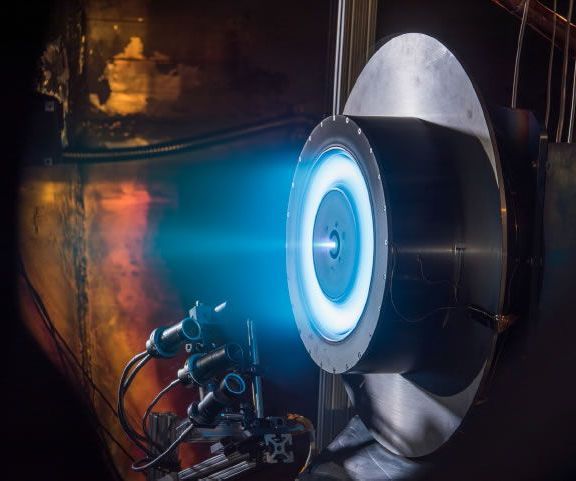

As NASA seeks cost-effective access to destinations across the inner solar system, including cislunar space and Mars, it also seeks to shorten the cycle of time to develop and infuse transformative technologies that increase the nation’s capabilities in space, enable NASA’s future missions and support a variety of commercial spaceflight activities.
NASA’s Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) project is developing critical technologies to extend the length and capabilities of ambitious new science and exploration missions. Alternative propulsion technologies such as SEP may deliver the right mix of cost savings, safety and superior propulsive power to enrich a variety of next-generation journeys to worlds and destinations beyond Earth orbit.
Energized by the electric power from on-board solar arrays, the electrically propelled system will use 10 times less propellant than a comparable, conventional chemical propulsion system, such as those used to power the space shuttles to orbit. Yet that reduced fuel mass will deliver robust power capable of propelling robotic and crewed missions well beyond low-Earth orbit — sending exploration spacecraft to distant destinations or ferrying cargo to and from points of interest, laying the groundwork for new missions or resupplying those already underway. Mission needs for high-power SEP are driving the development of advanced technologies the project is developing and demonstrating including large, light-weight solar arrays, magnetically shielded ion propulsion thrusters, and high-voltage power processing units.
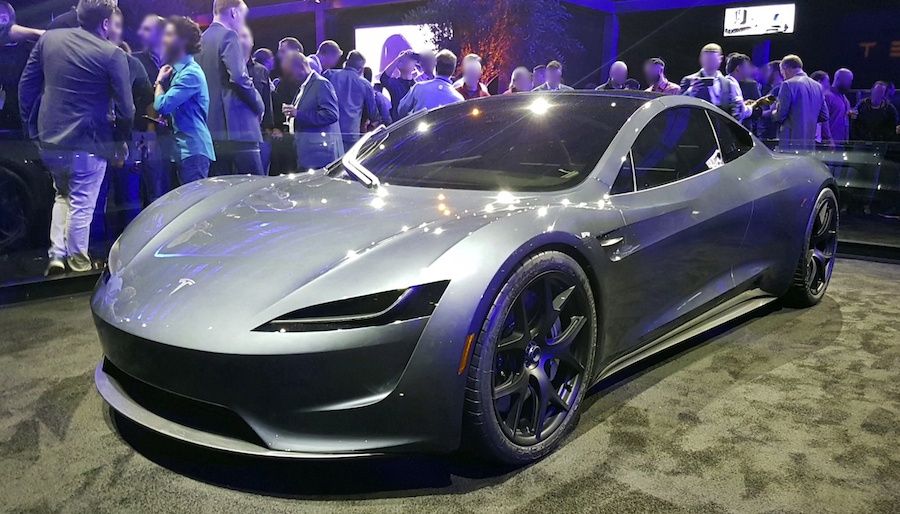

The previous Tesla Roadster Battery range of 1000 km was a conservative estimate. It is the range which users will get if they drive like a maniac. Who can blame them, when the car does 0–100 km/h in under 2 seconds.
Furthermore, Tesla fans also remember that a founders edition with cold gas thrusters is also coming in very limited numbers for hardcore electric car enthusiasts.
It is 2019 and the numbers provided by electric cars have already begun to eclipse the likes of Lamborghini Aventador and Bugatti Veyron. Lamborghini Aventador currently gives 10 MPG (Miles per gallon) or 4.25 km/l in the city, while the Bugatti Veyron delivers an embarrassingly low 7 MPG or 2.97 km/l.

China plans to build a scientific research station on the moon in “about 10 years,” according to the state news agency Xinhua.
The China National Space Administration (CSNA) intends to build the research station in the region of the moon’s south pole, Zhang Kejian, head of CSNA, said in a public statement, Xinhua reported. That’s a bit of a departure from the six successful NASA Apollo moon landings, which took place closer to the moon’s equator between 1969 and 1972.
Details of China’s long-term lunar plans are still sketchy, but CSNA has made significant steps toward lunar exploration. Earlier this year, the Chinese successfully landed the uncrewed Chang’e-4 on the far side of the moon, and have also placed astronauts aboard two temporary space stations, Tiangong-1 and Tiangong-2. Their space agency also plans to put a larger, more permanent station into orbit in the coming years.
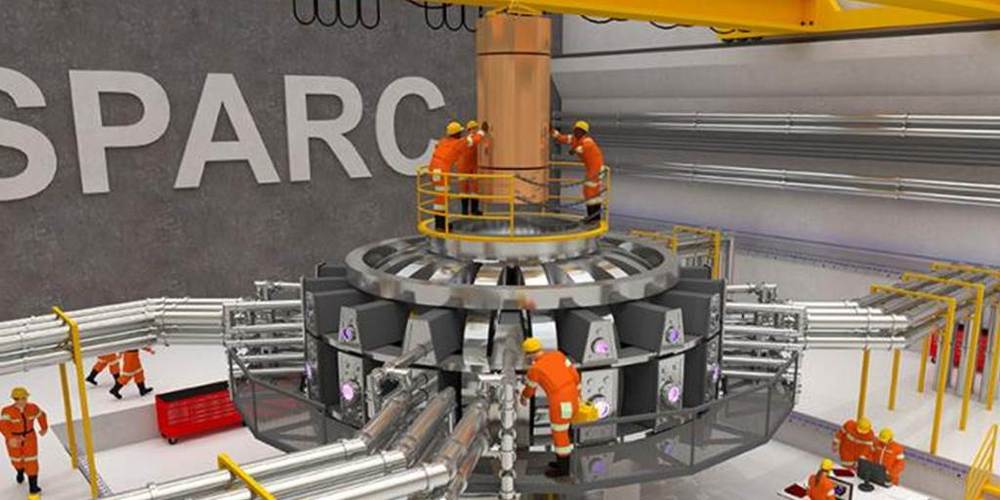


After decades of research and development, fusion may be poised for its “SpaceX moment.”
A visualization of SPARC, a compact, experimental fusion facility now under construction on MIT’s campus. Ken Filar / PSFC Research Affiliate.