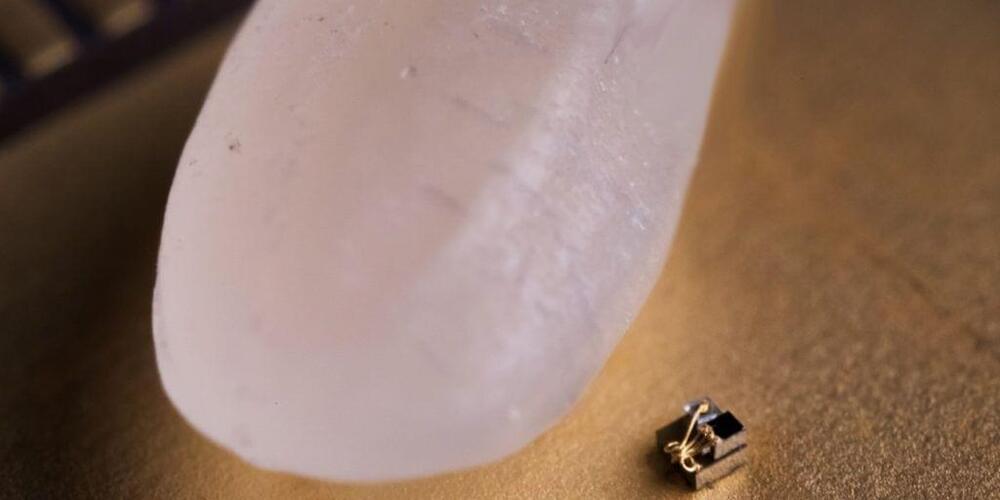
Circa 2018
Researchers at the University of Michigan just created the world’s smallest computer (again). Their previous micro-computer, the Michigan Micro Mote, measured 2x2x4mm. It was a complete, functioning system powered by solar cell batteries. But in March this year, IBM announced a new, smaller computer, which measured 1×1 mm, and was smaller than a grain of salt. It “raised a few eyebrows at the University of Michigan.”
After all, it’s unclear if the IBM computer even count as an actual microcomputer. The IBM device lost all its programming and data as soon as it turns off, unlike the Michigan Micro Mote, which retained its programming even when it wasn’t externally powered. “It’s more of a matter of opinion whether they have the minimum functionality required,” said David Blaauw, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at University of Michigan who helped develop the University of Michigan’s newest tiny device. If the IBM machine constituted a computer, then University of Michigan would work to gain back their title: their latest microdevice measures 0.3mm per side (1/10th the size of IBM’s computer), and is smaller than a grain of rice.
The device was designed to be a precision temperature sensor that can report temperatures in clusters of cells with an error of about 0.1 degrees Celsius. “When we first made our millimeter system, we actually didn’t know exactly all the things it would be useful for. But once we published it, we started receiving dozens and dozens and dozens of inquiries,” Blaauw said. It could, for instance, measure the temperature of tumors and conduct other cancer studies, monitor oil reservoirs, conduct audio or visual surveillance, or help in “tiny snail studies.”