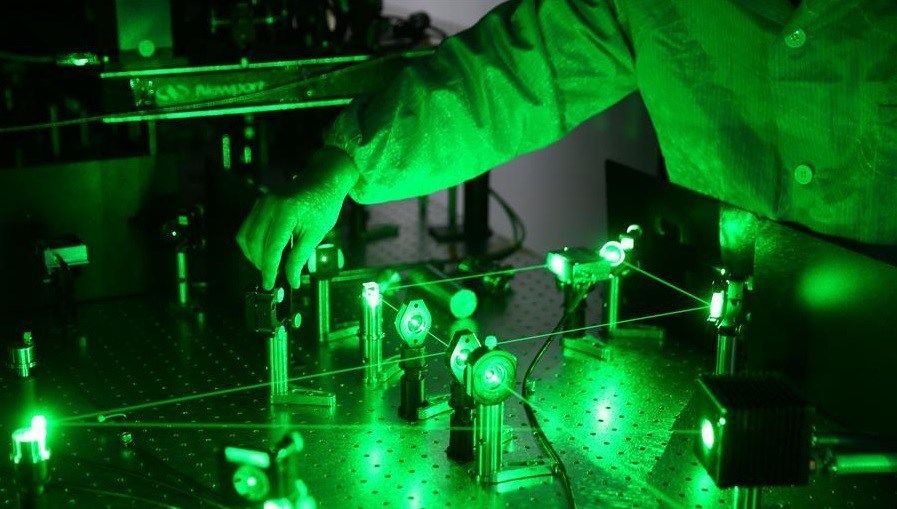
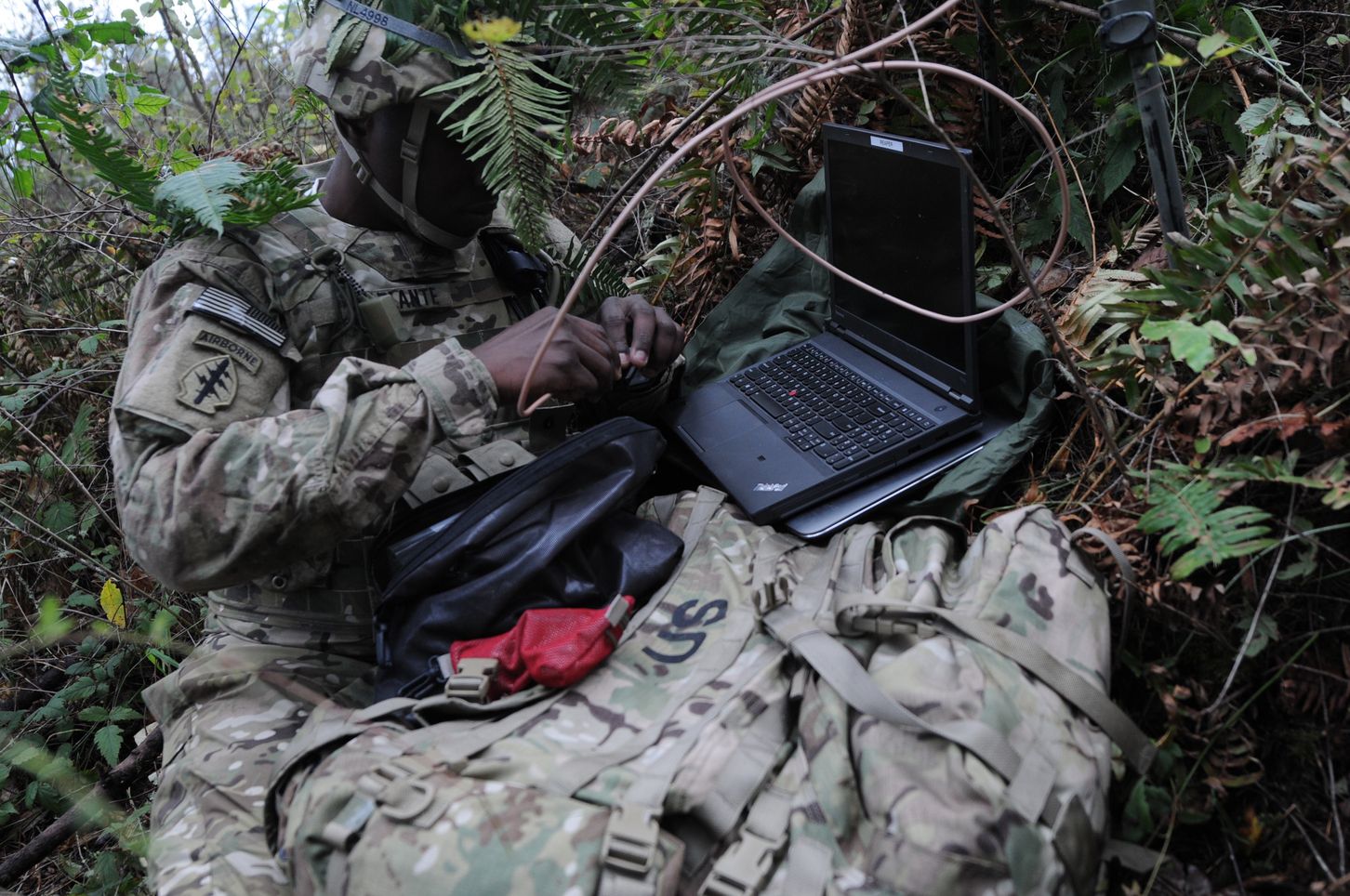
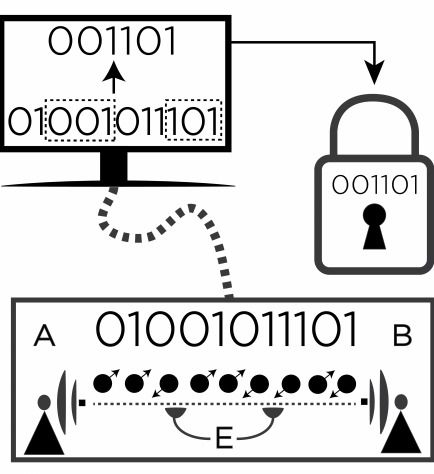
NSA meets with Silicon Valley execs to voice their concerns over legacy systems being hacked by Quantum technology. Glad they’re talking about it because with the recent advancements in Quantum means it will be available in devices, communications, and platforms a lot sooner than originally projected.
The National Security Telecommunications Advisory Committee (NSTAC) brought together Silicon Valley executives with federal officials at the advisory committee’s annual meeting on Wednesday in Santa Clara, California.
U.S. military and intelligence officials, including Department of Defense Secretary Ash Carter, Department of Homeland Security Secretary Jeh Johnson, and Department of Commerce Secretary Penny Pritzker, attended the advisory committee.
“Today’s era relies on technological innovation in our field such as speed and agility,” said Defense Secretary Carter at the meeting. During his presentation, he introduced Raj Shah, CEO/co-founder of Morta Security, Air Force Reservist, and former F-16 pilot, to lead the Defense Department’s Defense Innovation Unit Experimental (DIUX) initiative. The DoD is restructuring the DIUX program, a Silicon Valley outreach initiative, with Carter calling the revised program “DIUX 2.0.” Shah’s security firm, Morta Security, was acquired by Palo Alto Networks in March 2014.
Read more