You can now protect your home with this security drone! 😃
This security system deploys a drone when it senses intruders.


AI designed to be aware of it’s own competence.
Ira Pastor, ideaXme life sciences ambassador interviews Dr. Jiangying Zhou, DARPA program manager in the Defense Sciences Office, USA.
Ira Pastor comments:
On this episode of ideaXme, we meet once more with the U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), but unlike the past few shows where we been spent time with thought leaders from the Biologic Technology Office (BTO), today we’re going to be focused on the Defense Sciences Office (DSO) which identifies and pursues high-risk, high-payoff research initiatives across a broad spectrum of science and engineering disciplines and transforms them into important, new game-changing technologies for U.S. national security. Current DSO themes include frontiers in math, computation and design, limits of sensing and sensors, complex social systems, and anticipating surprise.
Dr. Jiangying Zhou became a DARPA program manager in the Defense Sciences Office in November 2018, having served as a program manager in the Strategic Technology Office (STO) since January 2018. Her areas of research include machine learning, artificial intelligence, data analytics, and intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) exploitation technologies.
Prior to joining DARPA, Dr. Zhou was a senior engineering manager in the Information Sciences Division at Teledyne Scientific and Imaging, LLC. During her more than ten-year tenure at Teledyne, Dr. Zhou worked on many contract R&D programs from U.S. government funding agencies as well as commercial customers in the areas of sensor exploitation, signal and image processing, and pattern recognition. Dr. Zhou also served as director of R&D of Summus Inc., a small start-up company specializing in contract engineering projects for U.S. Department of Defense and commercial customers in the areas of video and image compression, pattern recognition, and computer vision. Dr. Zhou began her career as a scientist at Panasonic Technologies, Inc., Princeton, New Jersey, where she conducted research in the areas of document analysis, handwriting recognition, image analysis, and information retrieval.
Dr. Zhou received a Bachelor of Science and a Master of Science, both in computer science, from Fudan University. She received a doctorate in electrical engineering from the State University of New York at Stony Brook.
Dr. Zhou is a member of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Society and also a member of the Upsilon Pi Epsilon international honor society for the computing and information disciplines.
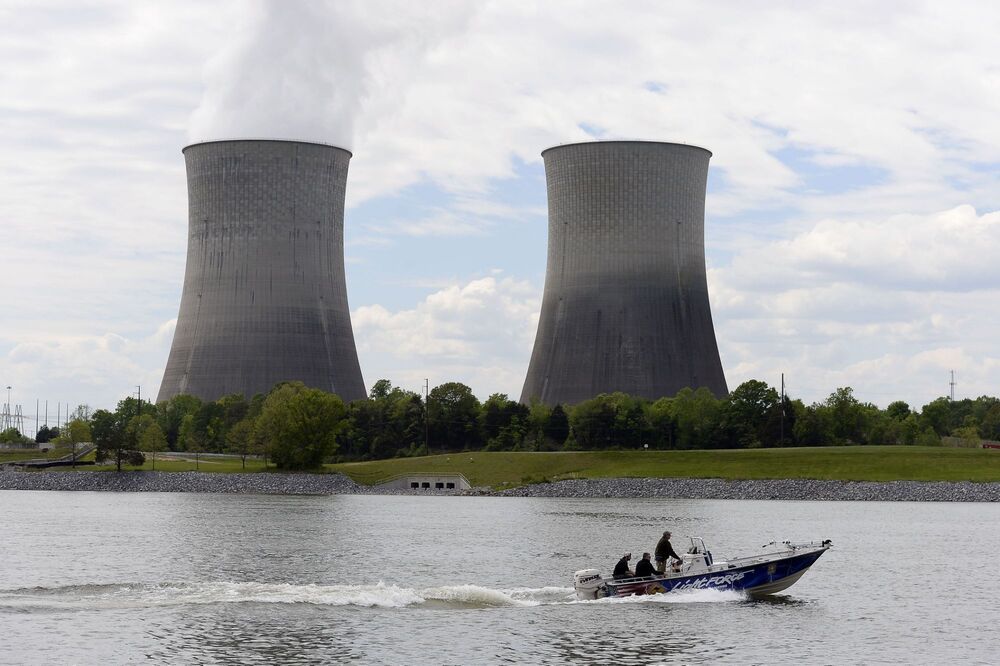

Federal regulators have fined the nation’s largest public utility more than $900,000 for violating procedures during the startup of a Tennessee nuclear reactor and subsequently misleading investigators. Two managers and a plant operator who worked at the Tennessee Valley Authority’s Watts Barr Nuclear Plant in Spring City were also issued violations by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission.
Howard Hall, director of the University of Tennessee’s Institute for Nuclear Security, said the notice of violation to TVA points to “a systemic problem in management.”
“As someone who has worked in this field essentially my entire life, I would have been appalled to receive such a letter,” Hall said.

When landing Apollo 11 in 1969, astronauts looked out the window for distinguishing features that they recognized from maps of the Moon and were able to steer the lander to avoid a disastrous touchdown on top of a rocky area. Now, 50 years later, the process can be automated. Distinguishing features, like known craters, boulders, or other unique surface characteristics, provide insight into surface hazards to help avoid them while landing.
NASA scientists and engineers are maturing technology for navigating and landing on planetary bodies by analyzing images during descent – a process called terrain relative navigation (TRN). This optical navigation technology is included on NASA’s newest Mars rover, Perseverance, which will test TRN when it lands on the Red Planet in 2021, paving the way for future crewed missions to the Moon and beyond. TRN was also being used during NASA’s recent Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resources Identification, Security, Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) mission Touch-and-Go (TAG) event to collect samples of the asteroid Bennu in order to better understand the characteristics and movement of asteroids.
Since reaching Bennu in 2018, the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft has mapped and studied its surface, including its topography and lighting conditions, in preparation for TAG. Nightingale crater was chosen from four candidate sites based on its great amount of sampleable material and accessibility for the spacecraft.


The future of disaster management, using artificial intelligence, machine learning, and a bit of Waffle House and Starbucks 🙂
Ira Pastor, ideaXme life sciences ambassador interviews Craig Fugate Chief Emergency Management Officer of One Concern and former administrator of the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA).
The international context of this interview: In choosing our leaders it is becoming increasingly important to select people who can both anticipate and address and where possible avoid large scale disasters. Here, Craig Fugate discusses evaluating past disasters, planning for future events and reacting to the “unexpected” — “think big and move fast”.
Ira Pastor comments:
The U.S. has sustained 279 weather and climate disasters since 1980 where overall damages/costs reached or exceeded $1 billion (including CPI adjustment to 2020). The total cost of these 279 events exceeds $1.825 trillion.
Craig Fugate is the Chief Emergency Management Officer of One Concern, a “Resilience-as-a-Service” solutions company that brings disaster science together with machine learning for better disaster recovery decision making.
Craig is the former Director of the Florida Division of Emergency Management, and former administrator of the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security, whose primary purpose is to coordinate the response to disasters that has occurred in the United States and that overwhelms the resources of local and state authorities.
Mr. Fugate has decades of experience at the local, state, and federal levels in disaster preparedness and management. He has also overseen preparation and response efforts for disasters such as wildfires and hurricanes, health crises, and national security threats.

Human body bio-factories of tommorow for organ and tissue replacement.
Ira Pastor, ideaXme life sciences ambassador interviews Dr Alexander Titus Chief Strategy Officer (CSO) at the Advanced Regenerative Manufacturing Institute (ARMI).
Ira Pastor comments:
The Advanced Regenerative Manufacturing Institute (ARMI) is one of 14 institutes of the Manufacturing USA network, and is a member-driven, non-profit organization, whose mission is to make practical the large-scale manufacturing of engineered tissues and tissue-related technologies.
BioFabUSA, created by ARMI, was established to lead the charge in large-scale manufacturing of engineered tissues and regenerative medicine research, turning foundational breakthroughs in the manufacture of engineered tissues and tissue-related technologies into life-changing possibilities for everyone.
Dr. Alexander Titus is the Chief Strategy Officer (CSO) at the Advanced Regenerative Manufacturing Institute (ARMI) where he is part of the leadership team working to advance the U.S. regenerative manufacturing industry, as well as develop technologies for disaster preparedness. Dr. Titus’s career is focused on the intersection of technology and public benefit, with experience spanning the private and public sectors, as well as non-profits and academia.
Prior to his role ARMI, Dr Titus was the inaugural Assistant Director for Biotechnology, within the Office of the CTO at the Department of Defense (DoD), where he was the Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense-level senior executive in charge of the DoD’s enterprise strategy for biotechnology, where he led the team developing the biotechnology modernization roadmap for the DoD.
Dr. Titus joined the DoD from McKinsey & Company, where he was a management consultant and a member of the inaugural cohort of Defense & Security Specialists working with the national security community on high-priority issues related to organization effectiveness, leadership, and analytics.

We stored the light by putting it in a suitcase so to speak, only that in our case the suitcase was made of a cloud of cold atoms,” says physicist Patrick Windpassinger from Mainz University in Germany. “We moved this suitcase over a short distance and then took the light out again.
The storage and transfer of information is a fundamental part of any computing system, and quantum computing systems are no different – if we’re going to benefit from the speed and security of quantum computers and a quantum internet, then we need to figure out how to shift quantum data around.
One of the ways scientists are approaching this is through optical quantum memory, or using light to store data as maps of particle states, and a new study reports on what researchers are calling a milestone in the field: the successful storage and transfer of light using quantum memory.
The researchers weren’t able to transfer the light very far – just 1.2 millimetres or 0.05 inches – but the process outlined here could form the foundation of the quantum-powered computers and communication systems of the future.

Attention readers, if you are using Google Chrome browser on your Windows, Mac, or Linux computers, you need to update your web browsing software immediately to the latest version Google released earlier today.
Google released Chrome version 86.0.4240.111 today to patch several security high-severity issues, including a zero-day vulnerability that has been exploited in the wild by attackers to hijack targeted computers.
Tracked as CVE-2020–15999, the actively exploited vulnerability is a type of memory-corruption flaw called heap buffer overflow in Freetype, a popular open source software development library for rendering fonts that comes packaged with Chrome.
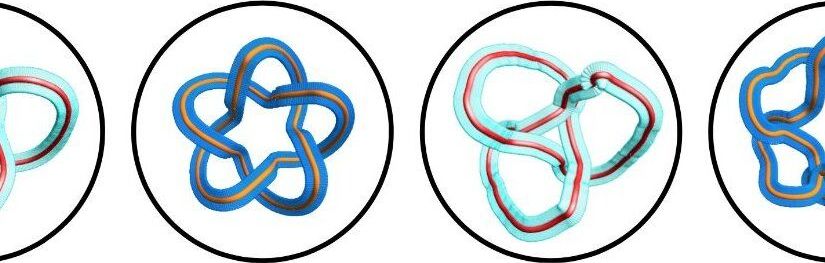
In a world first, researchers from the University of Ottawa in collaboration with Israeli scientists have been able to create optical framed knots in the laboratory that could potentially be applied in modern technologies. Their work opens the door to new methods of distributing secret cryptographic keys—used to encrypt and decrypt data, ensure secure communication and protect private information. The group recently published their findings in Nature Communications.
“This is fundamentally important, in particular from a topology-focused perspective, since framed knots provide a platform for topological quantum computations,” explained senior author, Professor Ebrahim Karimi, Canada Research Chair in Structured Light at the University of Ottawa.
“In addition, we used these non-trivial optical structures as information carriers and developed a security protocol for classical communication where information is encoded within these framed knots.”