Contact successful!
Diwata-2 was successfully launched to space on October 29, 2018 at 12:08 GMT+08 from the Tanegashima Space Center in Japan via H-IIA F40 rocket. It is one of the small satellites piggybacked with the main payloads IBUKI-2, also known as GOSAT-2 (JAXA’s Second Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite), and KhalifaSat, a remote sensing Earth observation satellite developed by the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) in the United Arab Emirates. The other small satellites are the Japanese-made Tenkou, PROITERES-2, Stars-AO, and AUTcube-2. Diwata-2 was inserted into the Sun-Synchronous Orbit at an altitude of 621 km, 43 minutes and 20 seconds after rocket lift-off.
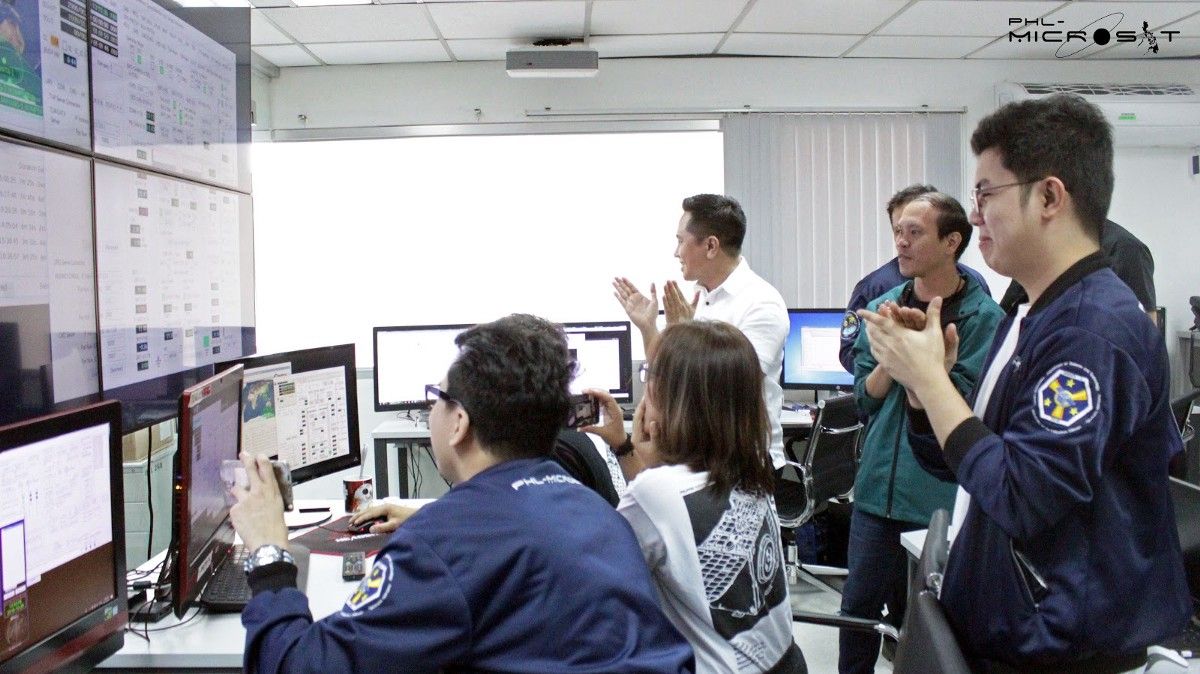
On Oct 29, 2018 at 13:52 GMT+08, initial contact was established between Diwata-2 and the Ground Receiving Station (GRS) located at the Department of Science and Technology Advanced Science and Technology Institute (DOST-ASTI). Short telemetry data was received from the satellite on that day. Diwata-2 was initially tracked using pre-launch orbital parameters. As of 12:40 PM yesterday, October 31, 2018, the GRS can now read the satellite’s status, including vital signs such as fully charged batteries, normal power consumption, and good communication link. Commands were successfully sent and initial check procedures will continue throughout the first week from launch. Initial image captures from the cameras can be expected in the coming days.
Another milestone for Philippine space initiatives
The team, program collaborators and stakeholders celebrated in two major simultaneous events: one at the Tanegashima Space Center together with the Japanese partners, and one at the GT Toyota Auditorium in Quezon City with the public. Pocket viewing sessions were also held at the DOST Region VI office in Iloilo, Bicol State University, Cebu Technological University, and Caraga State University. Simultaneously, Japanese professors Dr. Tetsuro Ishida (from Hokkaido University) and Dr. Yuji Sakamoto (from Tohoku University) and Filipino scholars Gerwin Guba, Leur Labrador, Julie Banatao, Leonard Paet, and Paolo Violan who were part of the team who built the Diwata-2 in Tohoku University, were also tuned in.
Read more