Very nice.
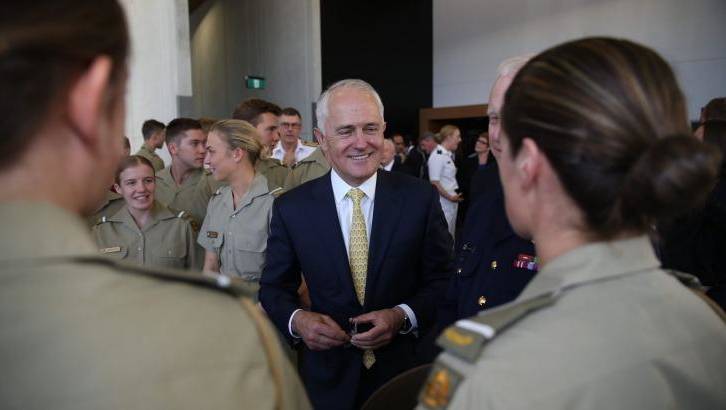
Quantum physicist Mario Krenn and his colleagues in the group of Anton Zeilinger from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Vienna and the Austrian Academy of Sciences have developed an algorithm which designs new useful quantum experiments. As the computer does not rely on human intuition, it finds novel unfamiliar solutions. The research has just been published in the journal Physical Review Letters. The idea was developed when the physicists wanted to create new quantum states in the laboratory, but were unable to conceive of methods to do so. “After many unsuccessful attempts to come up with an experimental implementation, we came to the conclusion that our intuition about these phenomena seems to be wrong. We realized that in the end we were just trying random arrangements of quantum building blocks. And that is what a computer can do as well — but thousands of times faster”, explains Mario Krenn, PhD student in Anton Zeilinger’s group and first author research.
After a few hours of calculation, their algorithm — which they call Melvin — found the recipe to the question they were unable to solve, and its structure surprised them. Zeilinger says: “Suppose I want build an experiment realizing a specific quantum state I am interested in. Then humans intuitively consider setups reflecting the symmetries of the state. Yet Melvin found out that the most simple realization can be asymmetric and therefore counterintuitive. A human would probably never come up with that solution.”
The physicists applied the idea to several other questions and got dozens of new and surprising answers. “The solutions are difficult to understand, but we were able to extract some new experimental tricks we have not thought of before. Some of these computer-designed experiments are being built at the moment in our laboratories”, says Krenn.