Glad to see others sharing this perspective.
Quantum effects could be the key to unlocking the mystery of machine learning, and maybe even consciousness.

Glad to see others sharing this perspective.
Quantum effects could be the key to unlocking the mystery of machine learning, and maybe even consciousness.
Nice.
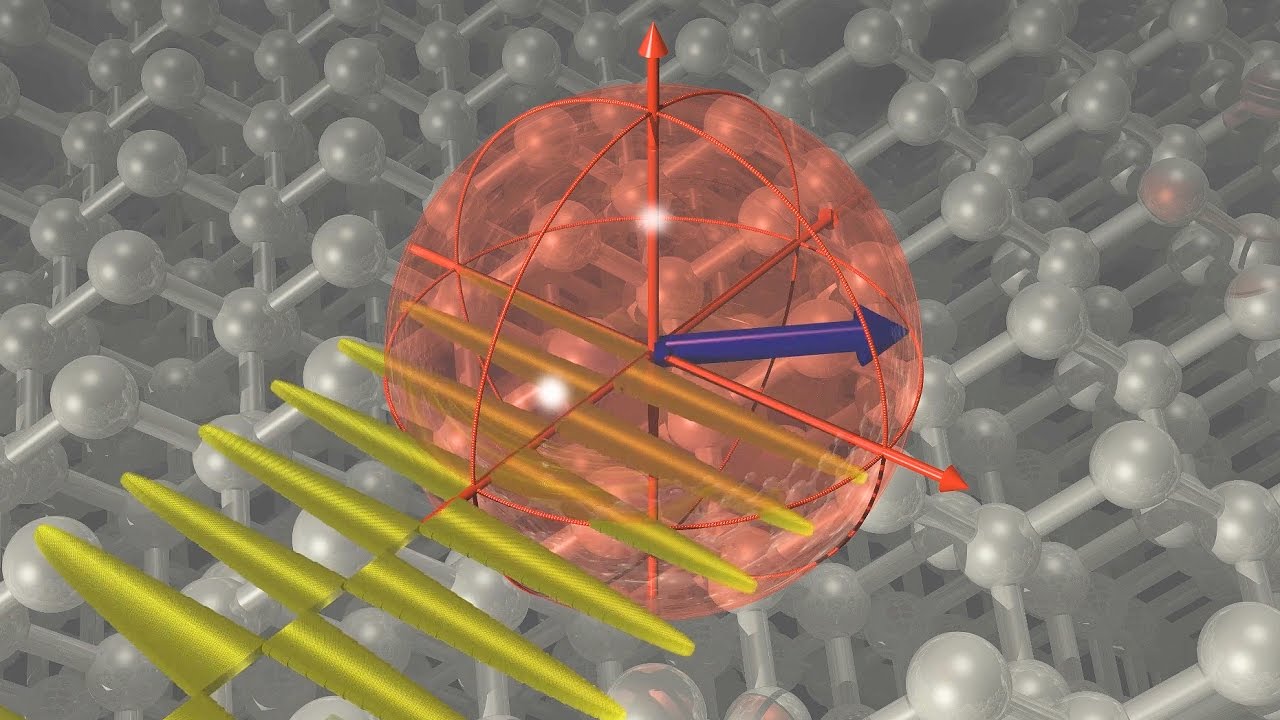
Scientists in Australia have developed a quantum bit that’s 10 times more stable than existing technologies, and the new record could vastly expand the kinds of calculations quantum computers can perform.
Whereas conventional computers process information recorded in binary bits that either take a 0 or 1 value, quantum computers use quantum bits – also called qubits – that can occupy 0, 1, or a superposition that can be both at the same time.
The new qubit developed by researchers from the University of New South Wales (UNSW) is called a “dressed” quantum bit, because the team combined the single atom at its heart with an electromagnetic field.

Now, from the wild side.
Quantum Theory Proves Consciousness Moves To Another Universe After Death. There is an interesting new theory emerging from a scientist long familiar with physics, quantum mechanics and astrophysics. Biocentrism teaches that life and consciousness are fundamental to the universe. It is consciousness that creates the material universe, not the other way around. At least, the new thinking that has given birth to the new theory of biocentrism, which the professor, Dr. Robert Lanza, freely espouses. Lana has been voted the 3rd most important scientist alive by the NY Times. Lanza is an expert in regenerative medicine and scientific director of Advanced Cell Technology Company. Before he has been known for his extensive research which dealt with stem cells, he was also famous for several successful experiments on cloning endangered animal species. Biocentrism—is a concept proposed in 2007 by American doctor of medicine Robert Lanza, a scientist in the fields of regenerative medicine and biology, which sees biology as the central driving science in the universe, and an understanding of the other sciences as reliant on a deeper understanding of biology. Biocentrism states that life and biology are central to being, reality, and the cosmos—consciousness creates the universe rather than the other way around. It asserts that current theories of the physical world do not work, and can never be made to work, until they fully account for life and consciousness. While physics is considered fundamental to the study of the universe, and chemistry fundamental to the study of life, biocentrism claims that scientists will need to place biology before the other sciences to produce a theory of everything.

I never get tired of articles highlighting the potential around leveraging Quantum teleporting as a method to replace networks and communications. Now the real question is how soon and how much of the existing infrastructure will need to be replaced to begin taking advantage of this technology earlier than others? As with most things, governments are often early adopters as well as Financial Services and ISPs are a close 2nd in the adoption of such technologies.
An experiment conducted about quantum teleportation could improve and transform the modern phone and Internet communication by having highly secure and encrypted messaging.
A recent study has suggested that comet outbursts are caused by avalanches and not geysers.
Will the testing of the new electric aircraft start a revolution in the aviation industry? Read what NASA has to say.

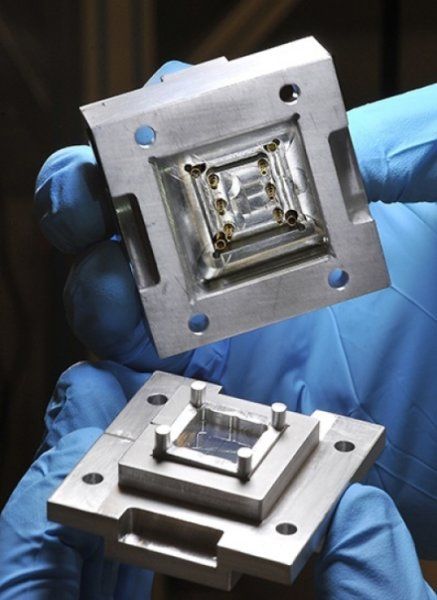
Great advancement around how to make QC available on small scale devices.
Researchers from the Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC) at the University of Waterloo led the development of a new extensible wiring technique capable of controlling superconducting quantum bits, representing a significant step towards to the realization of a scalable quantum computer.
“The quantum socket is a wiring method that uses three-dimensional wires based on spring-loaded pins to address individual qubits,” said Jeremy Béjanin, a PhD candidate with IQC and the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Waterloo. He and Thomas McConkey, PhD candidate from IQC and the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Waterloo, are lead authors on the study that appears in the journal Physical Review Applied as an Editors’ Suggestion and is featured in Physics. “The technique connects classical electronics with quantum circuits, and is extendable far beyond current limits, from one to possibly a few thousand qubits.”
One promising implementation of a scalable quantum computing architecture uses a superconducting qubit, which is similar to the electronic circuits currently found in a classical computer, and is characterized by two states, 0 and 1. Quantum mechanics makes it possible to prepare the qubit in superposition states, meaning that the qubit can be in states 0 and 1 at the same time. To initialize the qubit in the 0 state, superconducting qubits are brought down to temperatures close to −273 degrees Celsius inside a cryostat, or dilution refrigerator.
In Brief:
This new development in photoelectronics makes the technology more cost (and quantum) efficient. This opens ways for graphene to be further integrated in the field of photoelectronics.
EICREA professors Frank Koppens and Gerasimos Konstantatos led researchers in the ICFO in developing a hybrid photodetector that is better-performing in terms of speed, accuracy and range, and operates in the visible spectrum, near infrared (NIR) and short-wave infrared (SWIR), with wavelengths ranging from 400 to 3000 nm.
(Phys.org)—Over the past few decades, quantum effects have greatly improved many areas of information science, including computing, cryptography, and secure communication. More recently, research has suggested that quantum effects could offer similar advantages for the emerging field of quantum machine learning (a subfield of artificial intelligence), leading to more intelligent machines that learn quickly and efficiently by interacting with their environments.
In a new study published in Physical Review Letters, Vedran Dunjko and coauthors have added to this research, showing that quantum effects can likely offer significant benefits to machine learning.
“The progress in machine learning critically relies on processing power,” Dunjko, a physicist at the University of Innsbruck in Austria, told Phys.org. “Moreover, the type of underlying information processing that many aspects of machine learning rely upon is particularly amenable to quantum enhancements. As quantum technologies emerge, quantum machine learning will play an instrumental role in our society—including deepening our understanding of climate change, assisting in the development of new medicine and therapies, and also in settings relying on learning through interaction, which is vital in automated cars and smart factories.”

New method for information storage via QC uncovered.
Abstract: Researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have made a discovery that could lay the foundation for quantum superconducting devices. Their breakthrough solves one the main challenges to quantum computing: how to transmit spin information through superconducting materials.
Every electronic device — from a supercomputer to a dishwasher — works by controlling the flow of charged electrons. But electrons can carry so much more information than just charge; electrons also spin, like a gyroscope on axis.
Harnessing electron spin is really exciting for quantum information processing because not only can an electron spin up or down — one or zero — but it can also spin any direction between the two poles. Because it follows the rules of quantum mechanics, an electron can occupy all of those positions at once. Imagine the power of a computer that could calculate all of those positions simultaneously.