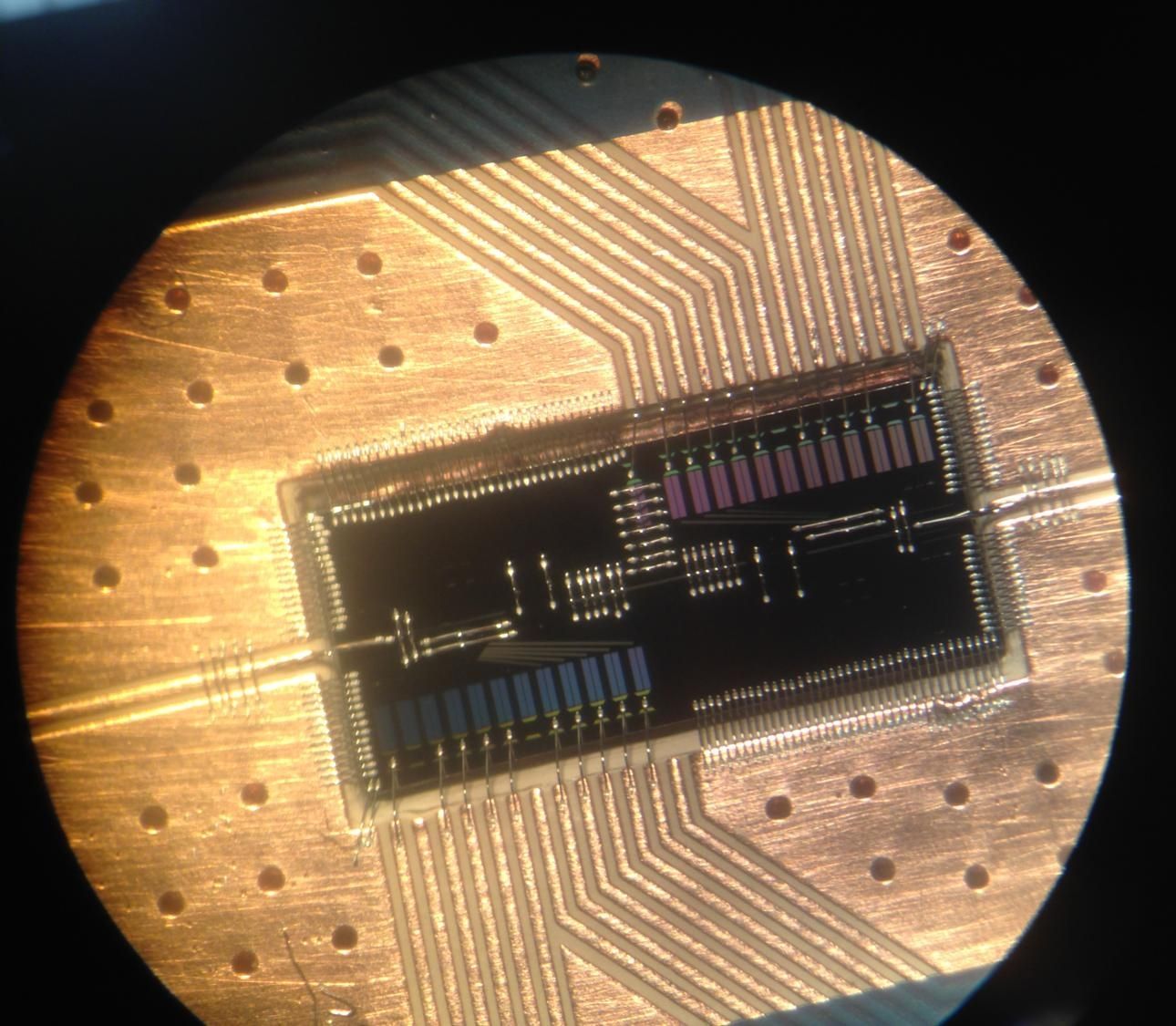
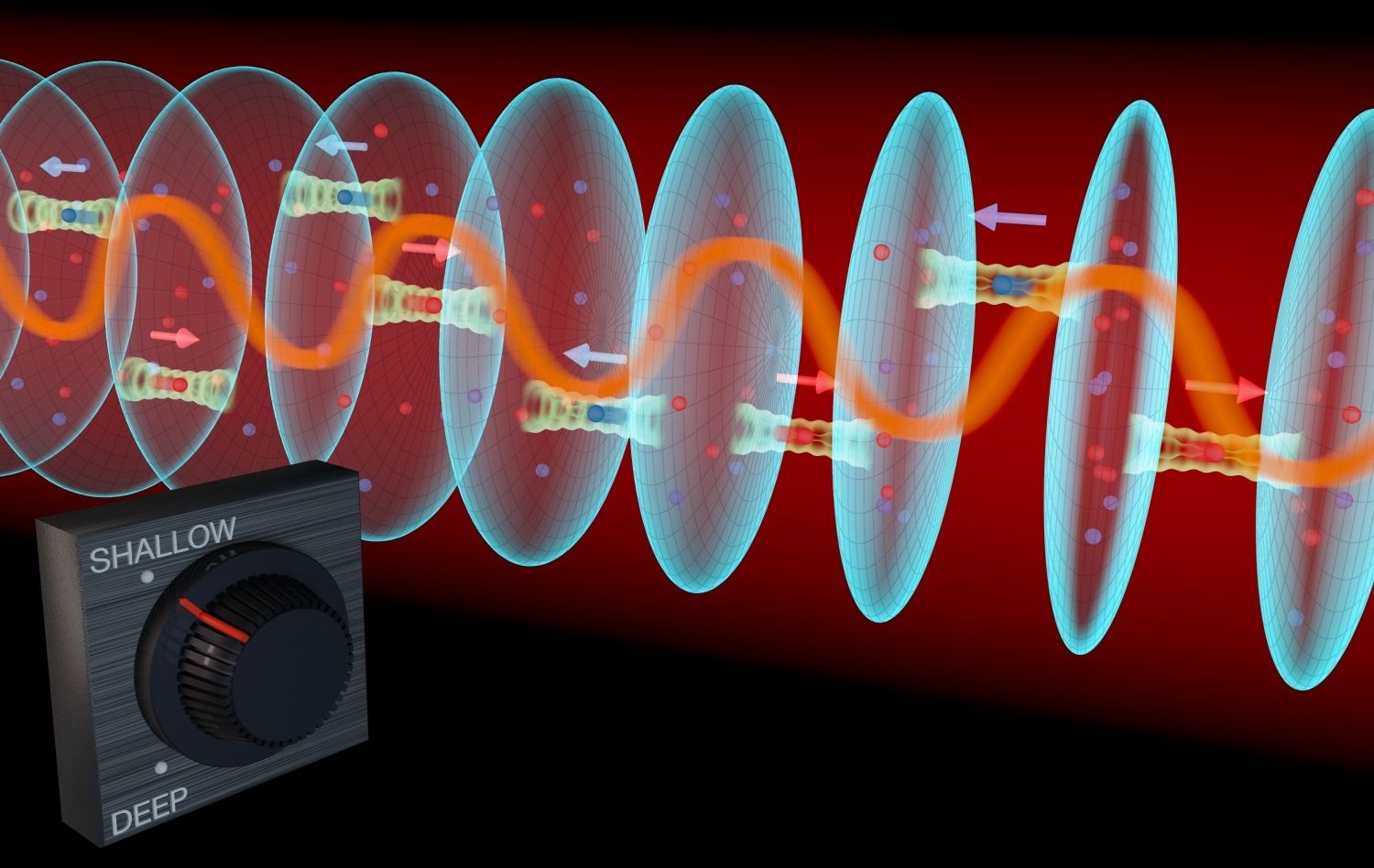
In a step that brings silicon-based quantum computers closer to reality, researchers at Princeton University have built a device in which a single electron can pass its quantum information to a particle of light. The particle of light, or photon, can then act as a messenger to carry the information to other electrons, creating connections that form the circuits of a quantum computer.
The research, published in the journal Science and conducted at Princeton and HRL Laboratories in Malibu, California, represents a more than five-year effort to build a robust capability for an electron to talk to a photon, said Jason Petta, a Princeton professor of physics.
“Just like in human interactions, to have good communication a number of things need to work out—it helps to speak the same language and so forth,” Petta said. “We are able to bring the energy of the electronic state into resonance with the light particle, so that the two can talk to each other.”